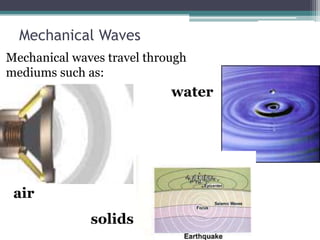
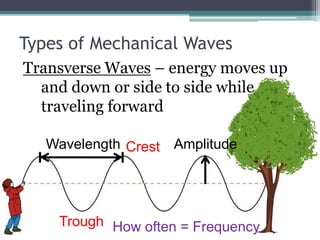
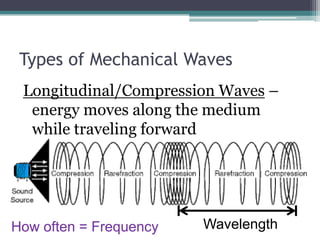
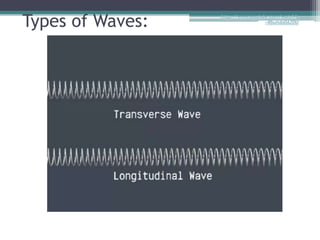
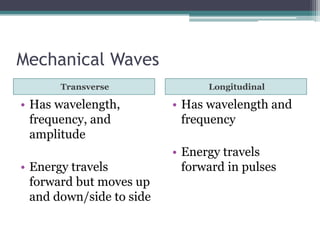
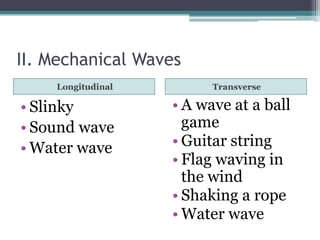
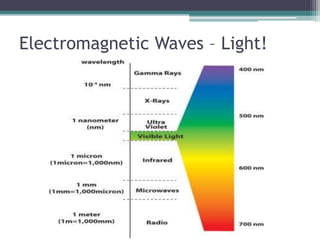
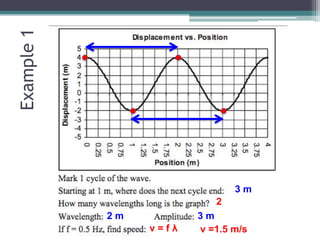
This document provides an organizer for a daily lesson on waves. It includes questions of the day about identifying transverse and longitudinal waves. The agenda lists homework assignments and topics to be covered, including worksheets on waves. Jobs are listed for students. Information is provided about the two types of waves - mechanical and electromagnetic. Mechanical waves can travel through matter and include transverse waves, which move energy up/down or side-to-side, and longitudinal waves, which move energy forward in pulses. Examples of different types of mechanical waves are given. Electromagnetic waves can travel through empty space and include light.