Webinar recording available: https://youtu.be/ELOO4RU6ss4
The EU General Data Protection Regulation is set to be enforced on May 25, 2018. Chances are you've heard about it. Maybe you've even attended other webinars to help sort out what it all means. It is an extremely complex and multi-layered regulation that can result in hefty penalties if you're not prepared.
In this webinar we'll examine what the GDPR means for your Domino environment and the data stored and processed within it, whether your servers are on-premises, hybrid, or in the cloud. After a quick summary of the GDPR's scope and its most important directives, we'll discuss
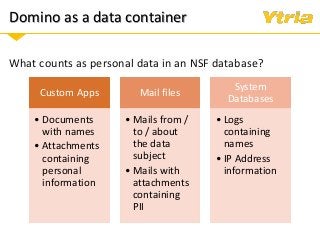
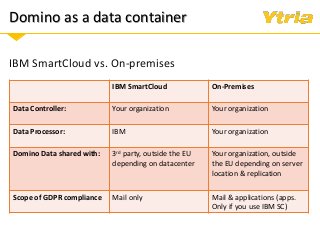
+ Data classification: what is considered personal and sensitive data according to the GDPR, and where it is stored in Domino
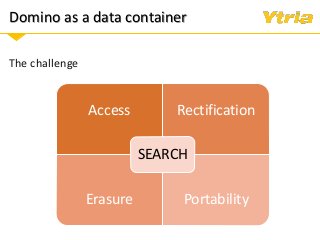
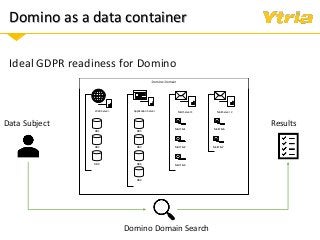
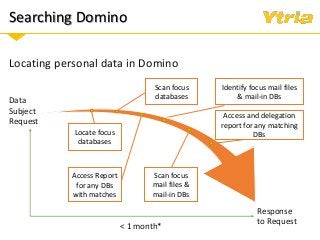
+ Responding to Right of Access requests (where the data processor needs to provide an overview of categories of data being processed pertaining to the individual, as well as copy of the data with whom it's been shared with)
+ Right to erasure in an IBM Domino environment.
Data protection by Design and by Default—and what it means for your Domino mail and apps.
+ Employer obligations and guidelines for storing employee data in Domino.
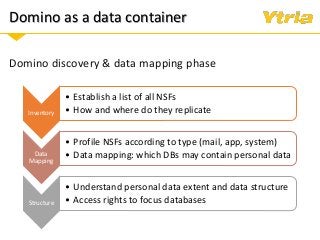
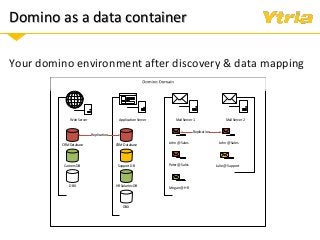
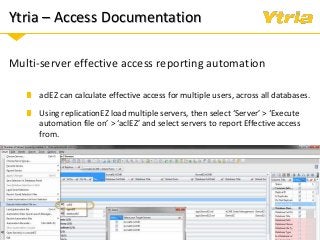
+ Properly understanding and documenting access to personal and sensitive data
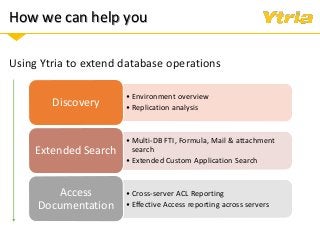
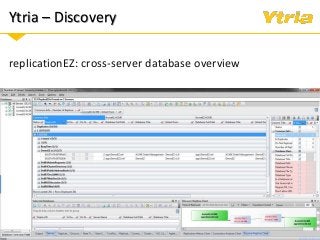
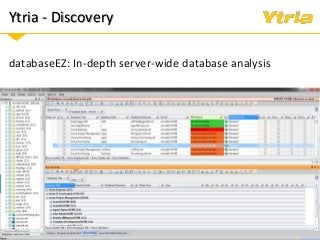
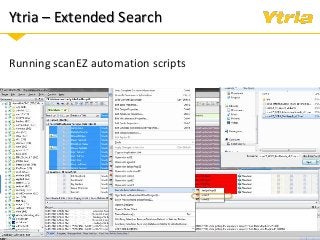
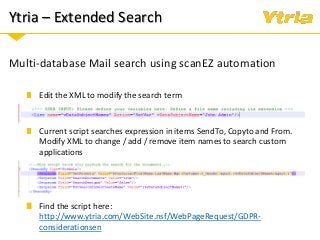
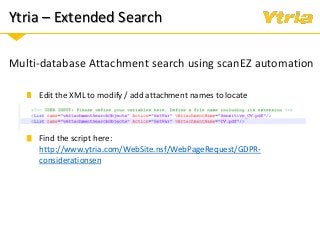
+ How Ytria's EZ Suite tools can help you become compliant.