Germany
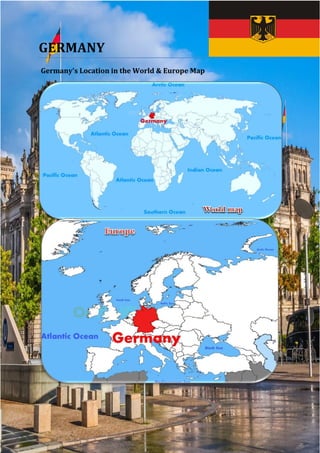
- 1. GERMANY Germany's Location in the World & Europe Map
- 2. Population: 82.5 million, including 18.6 million with migration back round Surface area: 357,340 km² Form of government: parliamentary democracy Founded: 1949, followed by German reunification with accession of the German Democratic Republic (GDR) on 3 October 1990 Head of state: Frank-Walter Stein Meier (as of January 2017) Capital: The five largest cities: Berlin Berlin (3.5m inhabitants), Hamburg (1.7m inhabitants), Munich (1.4m inhabitants), Cologne (1m inhabitants), Frankfurt am Main (732,688 inhabitants) Official language: German National holiday: 3 October (Day of German Unity) Membership: European Union, G8, G20, NATO, OECD, OSCE, UN Religions: Roman Catholic (28.5%), Evangelical Church in Germany (26.5%), Muslim (almost 5%), other (almost 4%), without confession (36.2%) Climate: moderately cool Western lies climate, between the oceanic climate of the Atlantic and the continental climate of eastern Europe Telephone country code: Currency: +49 euro (€1 = 100 cents)
- 3. INTRODUCTION Germany is one of Europe's largest nations, with one of the largest populations. Although it has played a major part in European and world history, it has been a single, unified nation for less than 100 years. The area that now makes up Germany originally was a cluster of partially independent cities and states. In 1871 the Prussian chancellor Otto von Bismarck created a unified Germany. In this century, Germany fought in two world wars (World War I, 1914–1918, and World War II, 1939–1945), and lost both. Following the defeat of Nazi Germany in World War II, the nation was divided by the countries that had defeated it: the United States, France, Great Britain, and the Soviet Union. The American, French, and British zones were combined in 1949 to create the Federal Republic of Germany (West Germany). That same year, the Soviet zone became the German Democratic Republic (East Germany). Germany was separated for four decades. Both Germanys recovered from the damage of the war with impressive speed. However, progress was faster and more dramatic in the West than in the East. Because of this, nearly three million East Germans eventually fled to West Germany, seeking better lives. Finally, in 1961, the East Germans put up the Berlin Wall and sealed off the nation's borders. In the late 1980s, however, Germany became caught up in the changes sweeping communist Eastern Europe. The destruction of the Berlin Wall in November 1989 became one of the most important symbols of the communist system's collapse. In March 1990, the East Germans held their first free elections. The two German nations were reunited on October 3, 1990. Location Germany is located in Europe and has an area of 137, 828 square miles. It measures about 520 miles north to south and is between the latitudes of 47 and 55 degrees north. The middle of the country measures from east to west about 385 miles and its longitude extends from 6 to 15 degrees west. Germany borders Denmark on the extreme north of the Jutland Peninsula, while the Baltic Sea sits on the east side and the North Sea on the west side of the peninsula. Netherlands, Belgium, and Luxembourg border Germany to the west along with France to the Southwest. Switzerland and Austria share the entire southern border. To the southeast is the Czech Republic, while Poland shares the eastern border by way of the Neisse River. Geography In the south, Germany is part of the outermost ranges of the Alps. It then stretches across the plane of the northern edge of the Alps. The centre of the country is the Central German Uplands, which extend from the Massif Central of France in the west into Czechoslovakia and Poland in the east. Germany is a landscape covered with variety. It boasts a mixture of forested black mountains, intermediate plateaus with scarped edges, and lowland basins. The North German Plain forms part of the greater North European Plain in the Lowlands. Marshes, mud flats, and the islands of the North and Baltic seas surround it. Germany has altitudes ranging from a maximum elevation of 9,718 feet in the Zugspitze of the Bavarian Alps to a minimum of sea level in the north.
- 4. Climate Germany’s weather is moderate, neither too hot nor too cold. Berlin has an average July temperature of between 59-75 degrees Fahrenheit with above average rainfall. However, rainfall does vary according to region. The North German Plain has the lowest average rainfall of 20-29 inches annually while rainfall in the Central German Uplands is 28-59 inches. The Alpine regions often experience rainfall up to and exceeding 78 inches. Berlin is also famous for its bracing air called the Berliner Luft. This mountain wind that can show up during any season causes an immediate change in temperature along with very warm conditions and a cloudless sky. Summers are usually hot and dry while snowfall begins around November and January temperatures often drop below freezing. Flora & Fauna The flora and fauna of Germany It is found in forests, which occupy just over 30% of the country. After the Second World War, the primitive forests were destroyed to be used as fuel. Those that are currently planted by man and most are used for forestry. 60% of these forests are made up of pines and other conifers. The remaining 40% consists of beech, oak, birch and walnut trees. One of the plants most exploited in Germany is the vine, whose crops occupy the slopes of rivers. The fauna of Germany is scarce and little varied. This is partly due to the climate, and also to the aforementioned war, in which many species were decimated Flora 1- Cornflower: It is native to the valleys of this country. The cornflower is the national flower of Germany, where it also takes the name of golden button. 2- Blue Brunonia: It is also called corn flower. It does not enjoy good reputation because it was the flower chosen as a symbol by the Nazi army. It is a perennial plant that grows in open forests and sandy soils. It has beautiful blue flowers. 3- Tulip: It is a plant from Anatolia. In Germany it is highly valued by flower growers. In the 17th century the rarest tulip bulbs cost the price of an entire farm. 4- Lily of the valley: It is native to the Röhn Valley, in Bavaria. The flowers are small, bell- shaped, and perfumed. In Germany they are called May bell. 5- German chamomile: It is a plant that grows wild throughout the country. The petals of the flower are very precious for the preparation of herbal tea. Fauna 1- European boar: The distribution of this species went from France to Russia. The armed conflicts wreaked havoc with this boar. The European wild boars served as food for the population. Today it is in a state of recovery in some forests. 2- Brown bear: This large mammal was almost extinct from the German forests. It is being reintroduced from Poland. 3- European fox: The common fox is the one that most abounds in the German coniferous forests. It is also called red fox. He is a skillful nocturnal hunter and during the day he remains hidden in the burrow.
- 5. 4- Royal Eagle: It is currently located in the mountainous area of Bavaria. The golden eagle was taken as a symbol of power by several empires. One of these was the French Empire of Napoleon. He was also chosen for the Nazi flag as an imperial eagle. In addition, it is the symbol on the flag of Mexico. 5- Herring: Since time immemorial the herring has been the national fish of Germany. So much so that, in gastronomy, the dish with herring always has a German name. Population Germany is the most populous country in the European Union with an estimated 2018 population of 82.29 million, which ranks 17th in the world. Despite a drop in the country's growth rate, its 2018 population is now estimated at 82.29 million, which makes Germany the 17th most populous country in the world. In Germany a decades-long tendency to population decline has been offset by waves of immigration. The 2011 national census recorded a population of 80.2 million people. At the end of 2012 it had risen to 82.0 million according to federal estimates. This represents about 14% increase over 1950. Germany has the 34th-highest annual population growth rate (-0.16%) among all European countries. The top 10 European countries by population growth rate are: Luxembourg, Cyprus, Ireland, Iceland, Kazakhstan, Norway, Azerbaijan, Turkey, Spain, Liechtenstein. Religion About 30% of Germans belong to the official Protestant church. An estimated 28% of the population is Catholic. The Protestants live mainly in the north, and the Catholics, in the south. Other Christian denominations include Methodists, Baptists, Mennonites, and the Society of Friends (Quakers). Before the 1930s, Germany had a Jewish population of about 530,000. However, the great majority fled or were killed by the government during World War II (1939–45). Today, only about 40,000 Jews live in Germany. Most of these are recent refugees from Russia. Muslims (followers of Islam) now account for nearly 3% of the population. They are mostly guest workers from Turkey. Language Standard (or High) German is the nation's official language, but many other dialects are spoken throughout the country. Low German is spoken along the North Sea and Baltic Sea coasts and on Germany's offshore islands. It has some features in common with Dutch and even English (examples: Standard German Wasser, Low German Water; Standard German Apfel, Low German Appel). Sorbian is a Slavic language spoken by approximately 60,000 people in eastern Germany. A number of different languages, including Turkish, are spoken by Germany's immigrant populations.
- 6. Currency The official currency of Germany is the Deutschmark (DM). DM1 is equal to 100 pfennig while coins are 1, 2, 5, 10, and 50 pfennigs and 1, 2, and 5 DM. Bills are in the amounts of 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 200, 500, and 1000 DM. 1 U. S. dollar is currently equal to DM 2.08 while DM 1 is equal to 56 cents. Additionally, DM 1 is equivalent to 0.32 British pounds, 0.51 Euros, and 3.35 French francs. TOURISM HISTORY IN GERMANY The history of tourism in Germany goes back to cities and landscapes being visited for education and recreation. From the late 18th century onwards, cities like Dresden, Munich, Weimar and Berlin were major stops on a European Grand tour. Spas and Seaside resorts on the North and Baltic Sea ( Rugia and Usedom islands, Heiligendamm, Norderney and Sylt islands) particularly developed during the 19th and early 20th century, when major train routes were built to connect the seaside spas to urban centres. An extends bathing and recreation industry materialized in Germany around 1900. At rivers and close to natural landscapes (along the Middle Rhine valley and in Saxon Switzerland for example) many health spas, hotels and recreational facilities were established since the 19th century. Since the end of World War II tourism has expanded greatly, as many tourists visit Germany to experience a sense of European history and the diverse German landscape. The country features 14 national parks, including the Jasmund National Park, the Vorpommern Lagoon Area National Park, the Müritz National Park, the Wadden Sea National Parks, the Harz National Park, the Hainich National Park, the Saxon Switzerland National Park, the Bavarian Forest National Park and the Berchtesgaden National Park. In addition, there are 14 Biosphere Reserves, as well as 98 nature parks. Tourism & Culture in Germany Germany is the seventh most visited country in the world, with a total of 407.26 million overnights during 2012. This number includes 68.83 million nights by foreign visitors, the majority of foreign tourists in 2009 coming from the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, and Switzerland (see table). Additionally, more than 30% of Germans spend their holiday in their own country. According to Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Reports, Germanys rated as one of the safest travel destinations worldwide. Not only is Germany indisputably the most popular destination for international conferences in Europe, it is also continually gaining in importance as a holiday destination. Culture and nature are the two central elements at the core of the Destination Germany brand – and this is reflected in the tourism-related demand. Explore Europe’s most popular cultural destination! You can look forward to 40 UNESCO World Heritage sites, 6,000-plus museums, acclaimed theatres and orchestras, high-calibre events and a buzzing creative scene. Almost one third of all European visitors to Germany opt for a city break – and the numbers are rising. Outstanding architecture, cultural and historical treasures and the highest standards of heritage preservation can be found in the capital Berlin, urban areas such as the Rhine-Main region – home to Frankfurt, Wiesbaden, Mainz and Darmstadt – the Rhine-Ruhr region with Cologne, Düsseldorf and Essen, and also other major cities such as Hamburg, Munich and Dresden. There are numerous festivals, celebrating everything from music to wine or beer, along with arts and
- 7. cultural events and, of course, the country’s many Christmas markets, which are as popular as they are enchanting. The huge diversity of events always makes it worthwhile extending your stay a little longer. Germany is also ideal as a destination for health and relaxation – whether travelling with the whole family, unwinding after a business trip or engaging in active pursuits. With around 200,000 kilometres of walking trails and 70,000 kilometres of cycle paths you can explore the country at its most unspoilt, getting close to nature while being kind to the environment. Along the way you’ll discover amazing and diverse natural landscapes. More than one third of the country’s land area is under some form of protection. With a total of 16 national parks, 15 UNESCO biosphere reserves and over 100 nature parks, there are more than 130 preserved national landscapes just waiting to be explored. Germany offers a wide range of options for sustainable travel. Its leafy towns and cities boast excellent public transport networks and a good cycling infrastructure. Hotels and restaurants support the use of regional produce within a very lively culinary scene that will delight anyone who enjoys good food. Many attractions and amenities also cater for disabled guests through the ‘Tourism for all’ project. FOLKLORE The most famous German folktale is the Nibelungenlied dating back to AD 1200. Its characters, including Siegfried, Brunhilde, and Hagen, have become famous around the world through the operas of Richard Wagner (1813–83). Another important set of tales was collected by Jacob and Wilhelm Grimm in the nineteenth century. Tales of the Brothers Grimm is the second most frequently translated book after the Bible. EDUCATION Education is free and required between the ages of six and eighteen. After four years of primary school (Grundschule), there are different roads students may take. They may spend two years in "orientation grades" and then six years in a Realschule in preparation for technical training. Or they may spend five years in a Hauptschule, followed by a three-year apprenticeship, a system in which a student learns a trade by working alongside a skilled worker. The other option is a nine-year gymnasium program that prepares students for a university education. This system was also used in the former East Germany. University attendance is free of charge Major Holidays Germany's legal holidays include New Year's Day (January 1), Good Friday (late March or early April), Easter (late March or early April), Pentecost (in May), Labour Day (May 1), and Christmas (December 25). Many different local and regional festivals are celebrated as well. Even the observance of some religious holidays varies from one region to another. Catholic areas celebrate the Feast of Corpus Christi (eleven days after Pentecost) and All Saints' Day (November 1). Lutheran regions observe Reformation Day (October 31) and Repentance and Prayer Day (the third Wednesday in November). In December, there are special Christmas markets (Weihnachtsmarkte) in many towns. They sell candles, Christmas trees, and other seasonal goods.
- 8. Rites of Passenger Germans live in a modern, industrialized Christian country. Many of the rites of passage that young people undergo are religious rituals, such as baptism, first communion, confirmation, and marriage. In addition, many familes mark a student's progress through the education system with graduation parties. German young men between the ages of eighteen and twenty-five are subject to being drafted into the armed forces. As of the late 1990s, the length of service was one year. Duty is usually near a young man's home town. The German armed forces are an important part of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) defense alliance. Conscientious objectors (people whose religious beliefs do not allow them to participate in warfare) can engage in substitute service in hospitals, nursing homes, and similar institutions. As of the late 1990s, conscientious objectors' service obligation was fifteen months. Relationships Germans are usually thought of as hardworking, efficient, and without a sense of humour. Regional differences make it hard to pin down a national character or set of traits. The division between north and south is older and deeper than that between the formerly divided East Germany and West Germany. The Rhine-landers of the north are said to be easy going and good-natured, while the Bavarians of the south are thought of as lively and excitable. On the whole, however, Germans tend to be more serious and aloof than Americans. In Germany, it is customary to shake hands when you greet another person. The most common greetings (with regional differences) areGuten Morgen(good morning),Guten Tag(hello),Guten Abend(good evening), andGute Nacht(good night).Auf Wiedersehenmeans "goodbye." Livings Conditions Germans take great pride in their homes; most spend about 10% of their income on home furnishings and decoration. Families live in small houses or apartments with a kitchen, a bathroom, a living room, and one or two bedrooms. Young children often share a bedroom. Germans receive high-quality medical care, and the life expectancy (the average age a person can expect to live to) is seventy-two years for men and seventy-nine years for women. The German love of beer has taken its toll on the nation's health: alcoholism follows smoking as one of the nation's leading causes of death. Culture Heritage In music, Germany is famous for its great composers, including Johann Sebastian Bach (1685–1750), Ludwig van Beethoven (1770–1827), Felix Mendelssohn (1809– 47), Robert Schumann (1886–1963), Johannes Brahms (1833–97), and Richard Wagner (1813–83). Well- known twentieth-century composers include Paul Hindemith (1895–1963), Kurt Weill (1900–50), Karlheinz Stockhausen (1928–), Carl Orff (1895–1982), and Hans Werner Henze (1926–). In literature, Germany's greatest names include Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (1749–1832), Friedrich von Schiller (1759–1805), Heinrich Heine (1797–1856), and Rainer Maria Rilke (1875–1926). Modern German writers include Bertolt Brecht (1898–1956), Nobel Prize winner Thomas Mann (1875–1955), Günter Grass (1927–), and Nobel Prize winner Heinrich Böll (1917–85).
- 9. A great early name in German visual arts is that of Albrecht Durer, whose masterpieces include both paintings and woodcuts. In the twentieth century, German artists worked in the Expressionist movement. In 1919, German architect Walter Gropius founded the famous Bauhaus school of art and design. This school had a great influence on architecture around the world. Food The traditional German diet is high in starch (noodles and dumplings in the south, potatoes in the north).Würste(sausages)—in hundreds of varieties—are a staple throughout the country. Bread is usually eaten at every meal. In addition, the Germans are famous for their love of beer. Various regions have their own special foods. They includeWeisswurst(light-colored sausage) and Black Forest cherry cake in the south.Labskaus(stew), seafood dishes, and bean soup with bacon (Bohnensuppe mit Speck) are favorites in the north. Spaetzle, tiny dumplings, are enjoyed by all Germans. A recipe for spaetzle follows. Recipe Spaetzle Ingredients 4 cups flour 1 teaspoon salt ¼ teaspoon pepper 2 cups chicken broth (canned is fine) 4 eggs ¼ cup milk 2 Tablespoons butter ½ cup bread crumbs Directions 1. Combine flour, salt, and pepper in a large bowl. 2. In a smaller bowl, blend broth, eggs, and milk. 3. Add liquid to flour mixture, beating vigorously for about 2 minutes. 4. Force dough through a large-holed colander. 5. Bring a large kettle of salted water to a boil. Gently add the dough bits, and simmer gently for about 5 minutes. Spaetzle will float to the surface when done. 6. Drain spaetzle and rinse with cold water. 7. Melt butter in a skillet, and add boiled spaetzle. Cook, shaking the pan, until the spaetzle are lightly browned. Sprinkle finished spaetzle with bread crumbs and serve. While it may be tasty, the traditional German diet, with its cold meats, starches, sugary desserts, and beer, is high in calories and cholesterol. Many Germans are trying to change their eating habits in order to improve their health. Most Germans eat their main meal at noon and prefer a lighter, often cold, supper. Germans keep the knife and fork in their hands while eating and consider it bad manners to place a hand under the table, on one's lap.
- 10. Employments The total labour force of Germany numbers over 37 million people. Of these, nearly two million are foreign workers, including Turks, citizens of parts of the former Yugoslavia, and Italians. The German workday begins early. Many people employed in factories start work at 7:00AM, and most stores and offices are open by 8:00. Labourers in industry usually work a little more than thirty-five hours a week. Two of Germany's largest employers are auto manufacturers. Daimler Chrysler (producer of the Mercedes-Benz) employs over 320,000 people worldwide. Nearly half of all German workers belong to labour unions. There is an extensive social security net and job security is very important. Wages are high, making the German labour force one of the best paid in the world. The German currency, the Deutsche Mark (German Mark), ranks among the strongest currencies in the world. Sports Football (the game that Americans call soccer) is Germany's most popular sport. Germany has a tradition of world-class gymnasts. Other popular sports include shooting, handball, golf, horseback riding, and tennis. In tennis, Germany has produced two recent world masters: Steffi Graf and Boris Becker. Recreational sports include hiking, bicycling, camping, sailing, and swimming, as well as both downhill skiing and cross-country skiing in the country's alpine regions. Crafts and Hobbies In their homes or in small shops, German craftspeople still produce works of art and souvenirs, including the cuckoo clocks for which they are famous. The wood carvings produced in Bavaria are world-famous. Social Problems The high cost of the unification of East and West Germany, plus a worldwide recession, weakened the German economy in the early 1990s. Other challenges facing Germany include reducing pollution and providing enough housing at prices people can afford. As unemployment has increased, tensions between immigrants and Germans have led to discrimination and even violence. The area that was East Germany still requires much social and economic rebuilding to make up for the lower living standards that took place there under the communist government. Festivals in Germany There are plenty more top German festivals to experience, where you can join your German counterparts in celebrating everything from beer to books. These mainly festivals in Germany:- Berlin International Film Festival Rock am Ring and Rock im Park Oktoberfest Festival-Mediaval Leipzig Book Fair Karneval
- 11. TOURIST DESTINATIONS PLACES IN GERMANY Germany has so much to offer its visitors: sprawling alps, winding rivers, lush valleys, and about 20,000 elegant castles. The country also has an incredibly complicated history, reflected in its many monuments and museums. There are so many attraction places in Germany. 1. HEIDELBERGER SCHLOSS, HEIDELBERG: Though now in ruins, Heidelberger Schloss (Heidelberg Castle) remains an impressive structure that can be seen from nearly anywhere in Heidelberg. Once at the top, take in the views of the city below (including the Neckar River and the Old Bridge), take in the impressive Renaissance architecture, roam the castle’s gardens, and visit the Heidelberg Tun - the World’s Largest Wine Barrel! For these reasons and more, Heidelberg is considered one of the best cities to visit in Germany. Best time to visit: The castle is open year-round, with the heaviest crowds in the summer. Visit in the spring for good weather but less crowds. Entrance fee: EUR 7 for adults, EUR 4 reduced (includes use of the Funicular Railway, Great Tun, German Apothecary Museum) 2. FERNSEHTURM (TELEVISION TOWER), BERLIN: It’s impossible to miss the towering Fernsehturm as you explore Berlin! Standing 368 metres tall, the Television Tower is the tallest structure in Germany and was originally built by the German Democratic Republic as a symbol of communist power. you can also visit its observation deck for incredible panoramic views of the cosmopolitan city of Berlin. Be sure to grab a drink at the bar or, if you’re really feeling fancy, have a bite at the tower’s rotating restaurant. Best time to visit: Visit late at night (21:00 - 23:00) for cheaper tickets and sparkling views of the city Entrance fee: Adults from EUR 13 and children from EUR 8.50.
- 12. 3. ROTHENBURG OB DER TAUBER, ANSBACH OF MITTELFRANKEN: With so much to offer its visitors, we’re considering the entire town of Rothenburg ob der Tauber one of Germany’s top tourist attractions. Prepare to step back in time, as this medieval town has been virtually untouched since the early 1600s. Best time to visit: Rothenburg ob der Tauber can be fairly crowded year-round, and is beautiful in all seasons. Visit in December for some gorgeous Christmas markets. Entrance fee: Free 4. BRANDENBURG GATE, BERLIN: Though Berlin has many famous monuments; the Brandenburg Gate The monument was built in 1791 in honor of King Frederick William II and is modelled after the Acropolis in Athens. Best time to visit: This attraction is best seen at night, when you can enjoy it shining in its surrounding yellow floodlights while eating some street food. Entrance fee: Free 5. KÖLNER DOM (COLOGNE CATHEDRAL), COLOGNE: A gorgeous example of High Gothic architecture, the Cologne Cathedral is the main attraction for this German city. Best time to visit: The Cathedral is usually open from 6:00 – 21:00 and 13:00 – 16:30 on Sundays. Do plan a visit on a Sunday if you wish to attend a church service. Entrance fee: EUR 3 6. NEUSCHWANSTEIN CASTLE, FÜSSEN: Perhaps one of the most photographed tourist attractions in Germany, Neuschwanstein is an impressive fairytale-like castle that inspired Walt Disney to create his most famous park, Magic Kingdom. In fact, it is quite easy to see the resemblance between this 19th- century castle and Cinderella’s castle. Best time to visit: Visit during the winter months for fewer crowds and spectacular views of the castle and surrounding hills covered in snow Entrance fee: EUR 13. Free for children under 18
- 13. 7 OKTOBERFEST, MUNICH : You’ll have to plan wisely if you plan to visit this tourist attraction, as it only happens once a year over the course of 16 to 18 days. Running from the end of September until the first weekend of October, Oktoberfest attracts an incredible 6 million visitors every year. Best time to visit: Runs only from the end of September until the beginning of October. Be sure to research specific dates in advance. Entrance fee: Free (varies by location) 8. BERLIN WALL, BERLIN: No visit to Berlin is complete without seeing one of the world’s most famous walls. The Berlin Wall (Berliner Mauer) separated East Germany (including East Berlin) from West Berlin from 1961 until 1990, when it was eventually demolished. Sections of the wall, often graffitied with political messages and symbols of peace, can also be found throughout the city — and around the world! Best time to visit: Anytime. The memorial site is open from Monday to Sunday 8:00 – 22:00 Entrance fee: Free 9. DACHAU CONCENTRATION CAMP, UPPER BAVARIA: Though far more sombre than many of the tourist attractions on this list, a visit to Dachau is an incredibly humbling experience that every visitor to Germany should take in. Dachau was one of the first concentration camps, opened by the Nazis in 1933. Now, it is a memorial site opened to public visits. Best time to visit: Anytime of the year. However, it is best to visit during warmer months as there is a lot to see outside. Entrance fee: Free (EUR 3* for an audio guide) 10. MINIATUR WUNDERLAND, HAMBURG: You don’t have to be a train or transportation aficionado to appreciate this miniature wonder. Located in the centre of Speicherstadt, the city’s historical district, this model railway (the world’s largest) will transport you from the Austrian Alps to Las Vegas and back again, all using more than 15,000 meters of track, 1,300 trains, and about 400,000 human figurines! You’ll want a couple of hours at least to appreciate the sheer scale and amount of fine detail at Miniatur Wunderland. Best time to visit: Visit on a weekday as soon as it opens (08:00) to avoid heavy crowds Entrance fee: EUR 13 for adults and EUR 6.50 for children under 16.
- 14. 11. SANSSOUCI PARK AND PALACE, POTSDAM: With a steep staircase leading up to this summer palace’s once copper dome and long yellow walls, you’d be forgiven for mistaking the Sanssouci summer palace for France’s Versailles. In fact, the two are often compared. The word 'sanssouci' means 'without worry'. The Palace was built for rest and relaxation for Frederick the Great between 1745 and 1747. After visiting the Palace, be sure to stroll through the beautiful garden that contains more than 3,000 fruit trees. Best time to visit: Between May and October (to avoid any closures or limited operating hours) Entrance fee: EUR 12 12. INSEL MAINAU, LAKE CONSTANCE: Floating in Lake Constance, near the city of Konstanz, you will find a small garden island named Mainau, another famous tourist attraction in Germany. Covering about 110 acres of land, the island is nicknamed ‘Flower Island’ as it is covered in parks and gardens teeming with vibrant, colorful flowers and about 500 species of trees, along with beautiful sculptures and fountainsBesides the lovely garden, Mainau is also home to a tropical climate greenhouse and thousands of fluttering butterflies. Best time to visit: Visit in the spring to enjoy the trees and flowers in full bloom Entrance fee: In summer, EUR 21 for adults, EUR 12 for students and free for children under 12. Half price entry after 5pm. In winter, EUR 10 for adults, EUR 6 for students and free for children under 12. Germany is a country full of interesting sites, rich culture, vibrant cities, stunning historical architecture, and lovely European landscapes. There is so much to see and do for the avid traveller. We suggest you take the time and explore all of these 12 sights, guaranteed you won't regret it! *Please note: prices listed in the article are as of December, 2017
- 15. Tourism Development in Germany Demand: A positive trendofdemand: 13 % increasein touristarrivalsand11 % increasein overnightstayswithinjust 5 years Demand: Germany maintains It stop position of overnight stays in Europe …
- 16. Foreign and Domestic Market German visitors present around80 % of tourism arrivals and overnight stays… Foreign Demand: Foreign tourist’s origin especially from the Netherlands, Switzerland, the USA and Great Britain…
- 17. Foreign Destinations: German tourists spent their holidays abroad mainly in Spain and Italy… Success Factors of German Tourism Success Factor: Structure: Example: Implementation of the national theme year of UNESCO World Heritage … Success Factor: Target Group Orientation: The main groups of guests:
- 18. Success Factor: Target Group Orientation: Central markets with growth potential… Success Factor: Quality Development: Success factor: Preserving quality along the entire service chain…
- 19. Conclusions Germany's central and southern regions have forested hills and mountains cut through by the Danube, Main, and Rhine river valleys. In the north, the landscape flattens out to a wide plain that stretches to the North Sea. Germany is located at the heart of Europe and has shaped its history both for good and bad. It has been bordered with nine neighbouring country, which is more than any other European country. Most part of Germany is covered with the wood, and it’s the most famous area of Germany, it is in the southern west part of the country near Swiss Border. This is the Black Forest, a mountainous region full of pines and fir trees. This forest contains the source of the Danube, one of the longest rivers of Europe. Today, life in Germany is subject to a great diversity of cultural influences. It can generally be described as modern and cosmopolitan. The people of Germany love nothing more than gathering together and celebrating, the carnival seasons in their traditional way at wine, Oktoberfest and other beer festivals. The German government works hard to protect the country's wildlife. There are 97 nature reserves in Germany, the biggest of which is the Black Forest. Hence, it can be concluded that Geography is fundamental to the study of tourism, because tourism is geographical in nature. Tourism occurs in places, it involves movement and activities between places and it is an activity in which both place characteristics and personal self-identities are formed, through relationships that are created among places, landscapes and people. Physical geography provides the essential background, against which tourism places are created and environmental impacts and major issues that must be considered in managing the development of tourism places. These are some characteristics are related tourism system in geography. Rural tourism : Focused on countryside Urban tourism : Focused on town & cities Spa tourism : Travel for health & wellness Sport tourism: Focused on spectators travelling to sports events. Eco tourism : Based on nature Heritage tourism: Focused on heritage cities and Heritage buildings. Germany is a country of incredible variety, and the main reason is geography.
