IACR 2016 poster
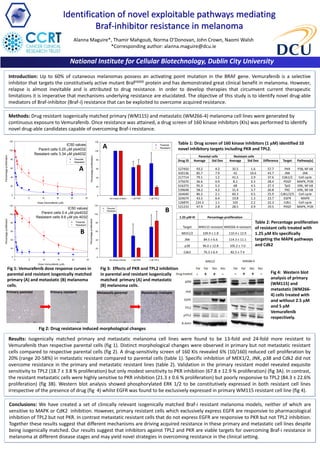
- 1. Fig 1: Vemurafenib dose response curves in parental and resistant isogenically matched primary (A) and metastatic (B) melanoma cells. National Institute for Cellular Biotechnology, Dublin City University Identification of novel exploitable pathways mediating Braf-inhibitor resistance in melanoma Alanna Maguire*, Thamir Mahgoub, Norma O’Donovan, John Crown, Naomi Walsh *Corresponding author: alanna.maguire@dcu.ie Introduction: Up to 60% of cutaneous melanomas possess an activating point mutation in the BRAF gene. Vemurafenib is a selective inhibitor that targets the constitutively active mutant BrafV600E protein and has demonstrated great clinical benefit in melanoma. However, relapse is almost inevitable and is attributed to drug resistance. In order to develop therapies that circumvent current therapeutic limitations it is imperative that mechanisms underlying resistance are elucidated. The objective of this study is to identify novel drug-able mediators of Braf-inhibitor (Braf-i) resistance that can be exploited to overcome acquired resistance. Conclusions: We have created a set of clinically relevant isogenically matched Braf-i resistant melanoma models, neither of which are sensitive to MAPK or CdK2 inhibition. However, primary resistant cells which exclusively express EGFR are responsive to pharmacological inhibition of TPL2 but not PKR. In contrast metastatic resistant cells that do not express EGFR are responsive to PKR but not TPL2 inhibition. Together these results suggest that different mechanisms are driving acquired resistance in these primary and metastatic cell lines despite being isogenically matched. Our results suggest that inhibitors against TPL2 and PKR are viable targets for overcoming Braf-i resistance in melanoma at different disease stages and may yield novel strategies in overcoming resistance in the clinical setting. Results: Isogenically matched primary and metastatic melanoma cell lines were found to be 13-fold and 24-fold more resistant to Vemurafenib than respective parental cells (fig 1). Distinct morphological changes were observed in primary but not metastatic resistant cells compared to respective parental cells (fig 2). A drug-sensitivity screen of 160 KIs revealed 6% (10/160) reduced cell proliferation by 20% (range 20-58%) in metastatic resistant compared to parental cells (table 1). Specific inhibition of MEK1/2, JNK, p38 and Cdk2 did not overcome resistance in the primary and metastatic resistant lines (table 2). Validation in the primary resistant model revealed exquisite sensitivity to TPL2 (18.7 ± 3.8 % proliferation) but only modest sensitivity to PKR inhibition (67.8 ± 12.9 % proliferation) (fig 3A). In contrast, the resistant metastatic cells were highly sensitive to PKR inhibition (21.3 ± 0.6 % proliferation) but poorly responsive to TPL2 (84.3 ± 22.6% proliferation) (fig 3B). Western blot analysis showed phosphorylated ERK 1/2 to be constitutively expressed in both resistant cell lines irrespective of the presence of drug (fig 4) whilst EGFR was found to be exclusively expressed in primary WM115 resistant cell line (fig 4). Primary parental Primary resistant Metastatic resistantMetastatic parental Fig 2: Drug resistance induced morphological changes Methods: Drug resistant isogenically matched primary (WM115) and metastatic (WM266-4) melanoma cell lines were generated by continuous exposure to Vemurafenib. Once resistance was attained, a drug screen of 160 kinase inhibitors (KIs) was performed to identify novel drug-able candidates capable of overcoming Braf-i resistance. Dose Vemurafenib (M) 0 5 10 15 20 25 Percentageproliferation 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 IC50 values Parent cells 0.4 M plx4032 Resistant cells 9.6 M plx 4032 Parental Resistant Parental cells Resistant cells Drug ID Average Std Dev Average Std Dev Difference Target Pathway(s) 527450 93.2 4.2 35.5 1.6 57.7 PKR P38, NF-kB 420136 85.7 7.9 42 10.6 43.7 JNK JNK 217714 79.1 1.2 41.5 2.9 37.6 Cdk1/2 Cell cycle 375670 36.6 0.9 8.2 0.3 28.4 PDGF MAPK, PI3K 616373 95.3 5.3 68 4.5 27.3 Tpl2 ERK, NF-kB 539648 58.2 4.2 31.4 3.7 26.8 PKC ERK, NF-kB 164640 86.2 2.1 60.3 0.5 25.9 Cdk1/2/5 Cell cycle 324674 43.5 6.4 19.8 1.3 23.7 EGFR MAPK 126870 124.3 1.1 102 2.2 22.3 Cdk1 Cell cycle 521233 47.9 2.8 28.5 0.9 19.5 PDGF MAPK, PI3K Table 1: Drug screen of 160 kinase inhibitors (1 µM) identified 10 novel inhibitory targets including PKR and TPL2. No kinase inhibitor 1 uM PKR 1 uM TPL2 Percentageproliferation 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 No kinase inhibitor 1 uM PKR 1 uM TPL2 Percentageproliferation 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 B 1.25 µM KI Percentage proliferation Target WM115 resistant WM266-4 resistant MEK1/2 109.9 ± 1.8 110.4 ± 12.9 JNK 84.5 ± 6.6 114.3 ± 11.1 p38 96.0 ± 12.8 105.2 ± 7.0 Cdk2 76.3 ± 6.4 82.5 ± 7.4 Table 2: Percentage proliferation of resistant cells treated with 1.25 µM KIs specifically targeting the MAPK pathways and Cdk2 A Fig 4: Western blot analysis of primary (WM115) and metastatic (WM266- 4) cells treated with and without 2.5 µM and 5 µM Vemurafenib respectively. Parental Resistant B Dose Vemurafenib (M) 0 5 10 15 20 25 Percentageproliferation 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 IC50 values Parent cells 0.25 M plx4032 Resistant cells 3.34 M plx4032 Parental Resistant A Parental Resistant Fig 3: Effects of PKR and TPL2 inhibition in parental and resistant isogenically matched primary (A) and metastatic (B) melanoma cells.