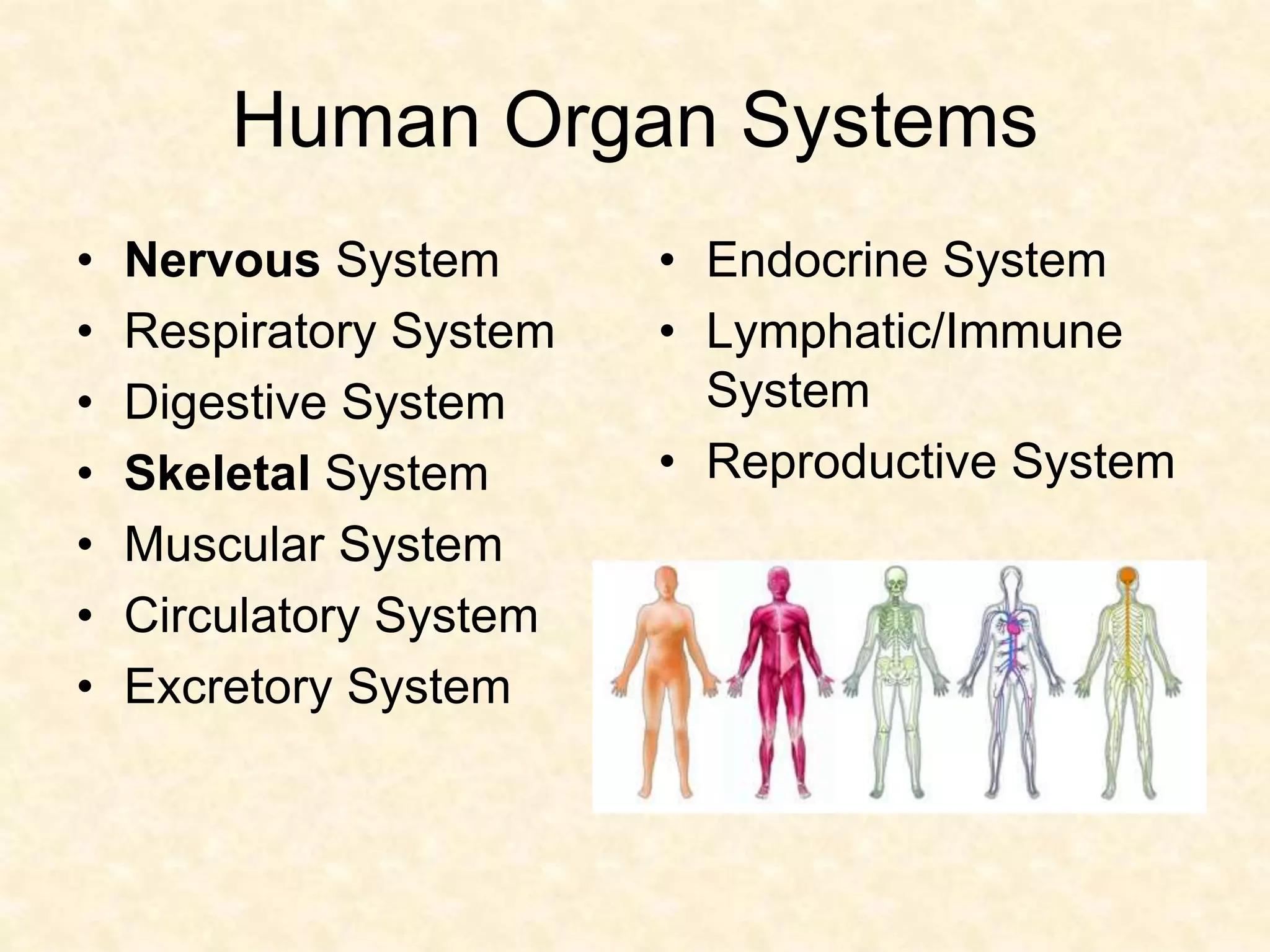
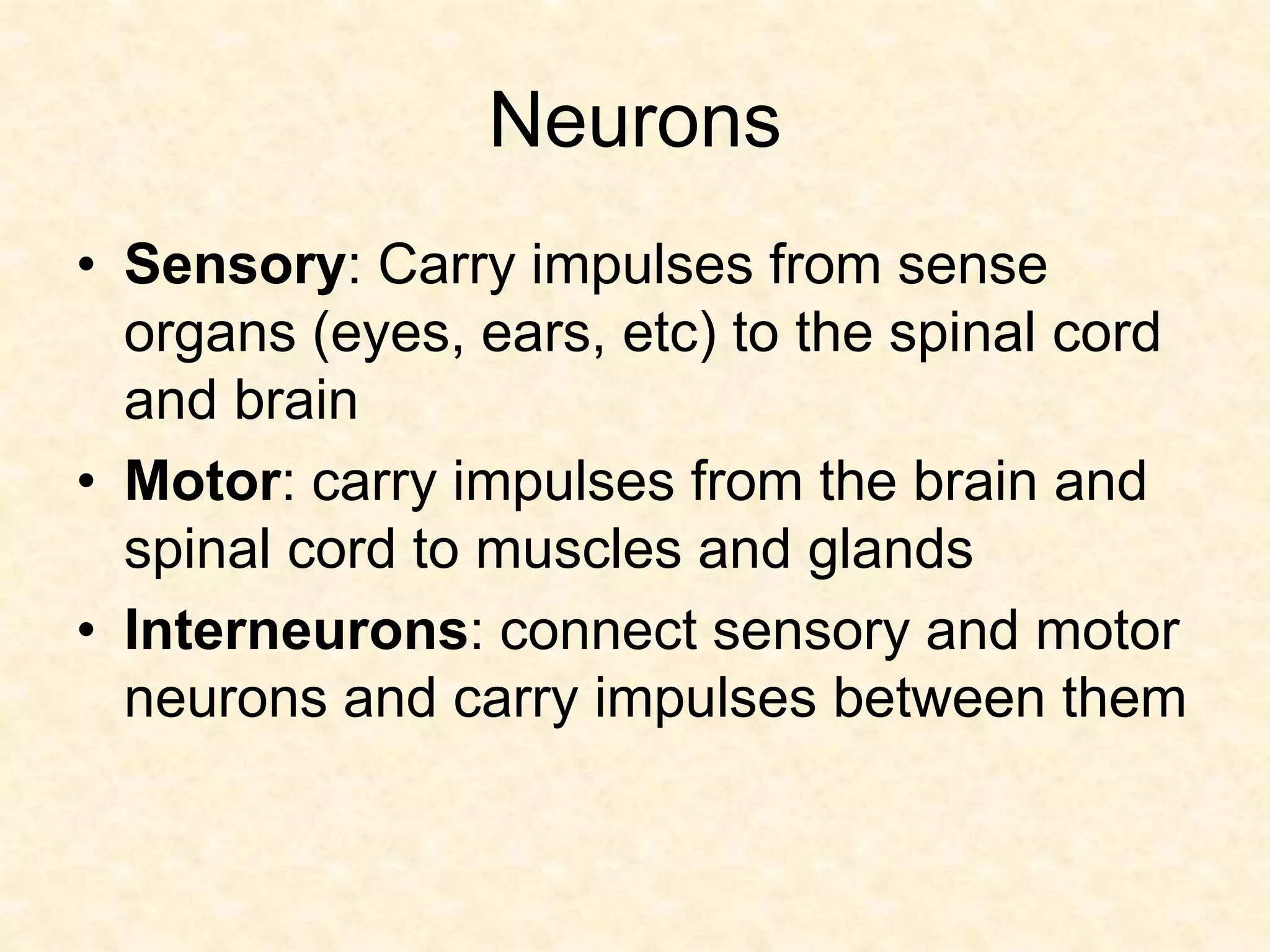
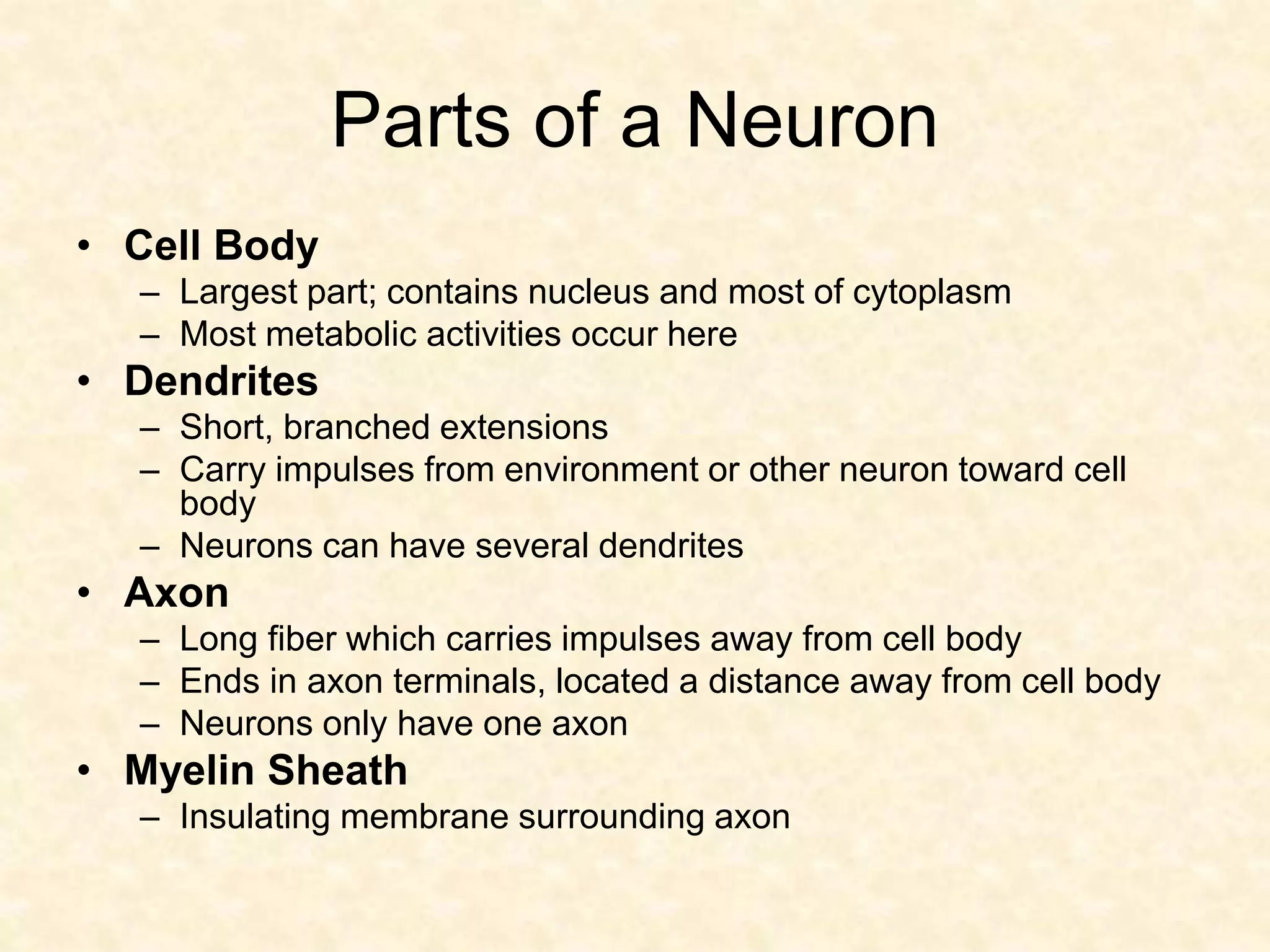
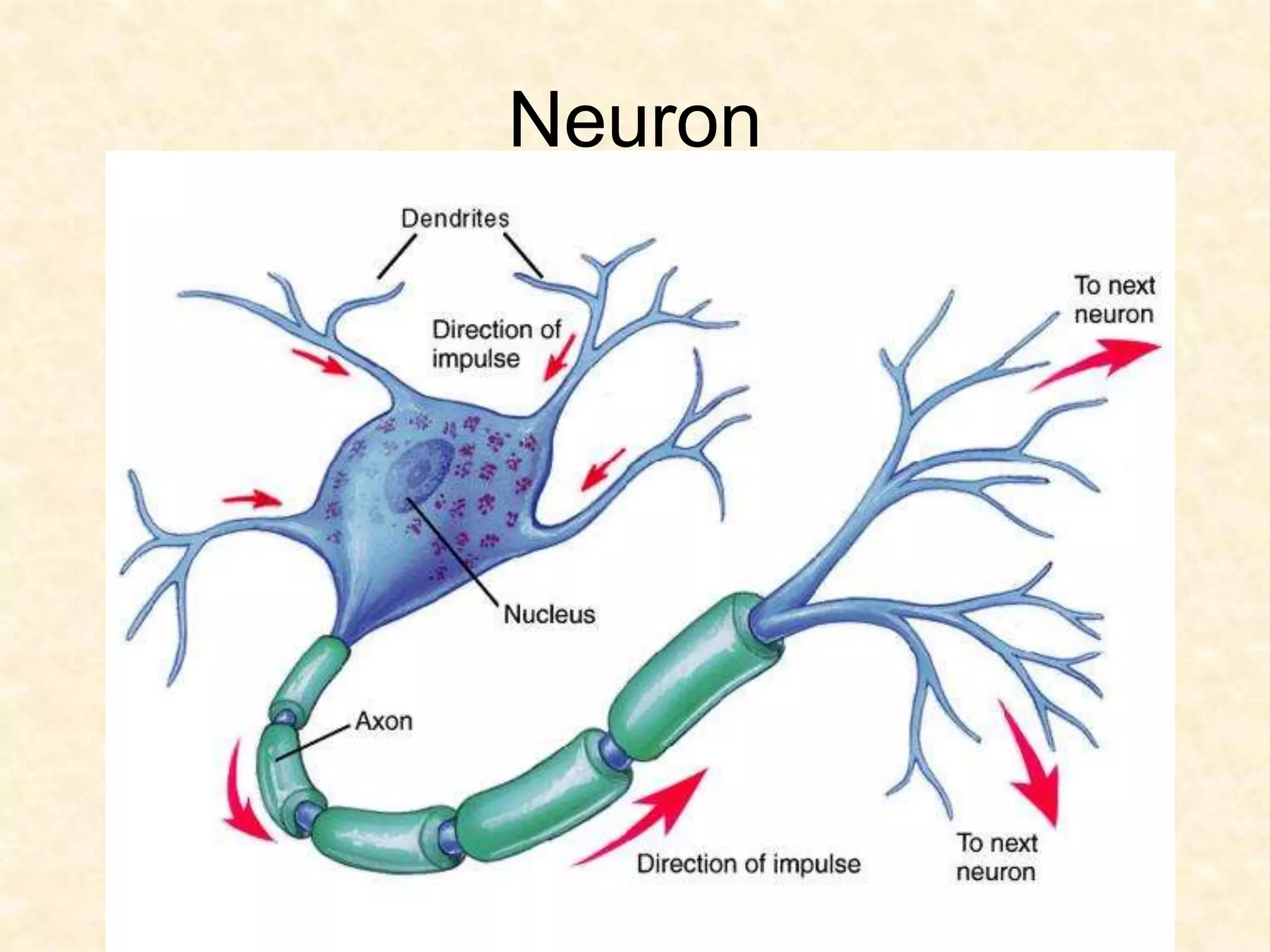
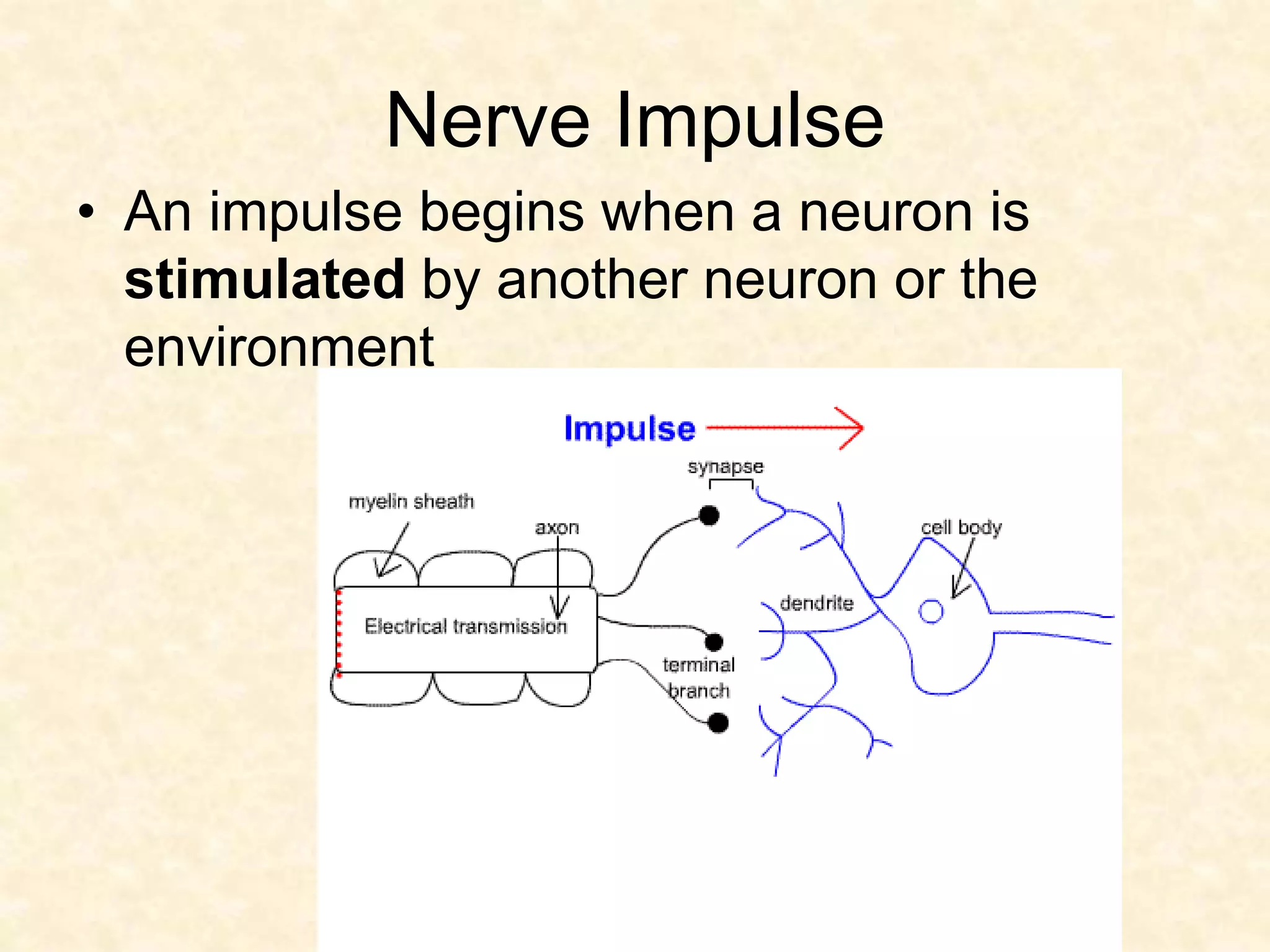
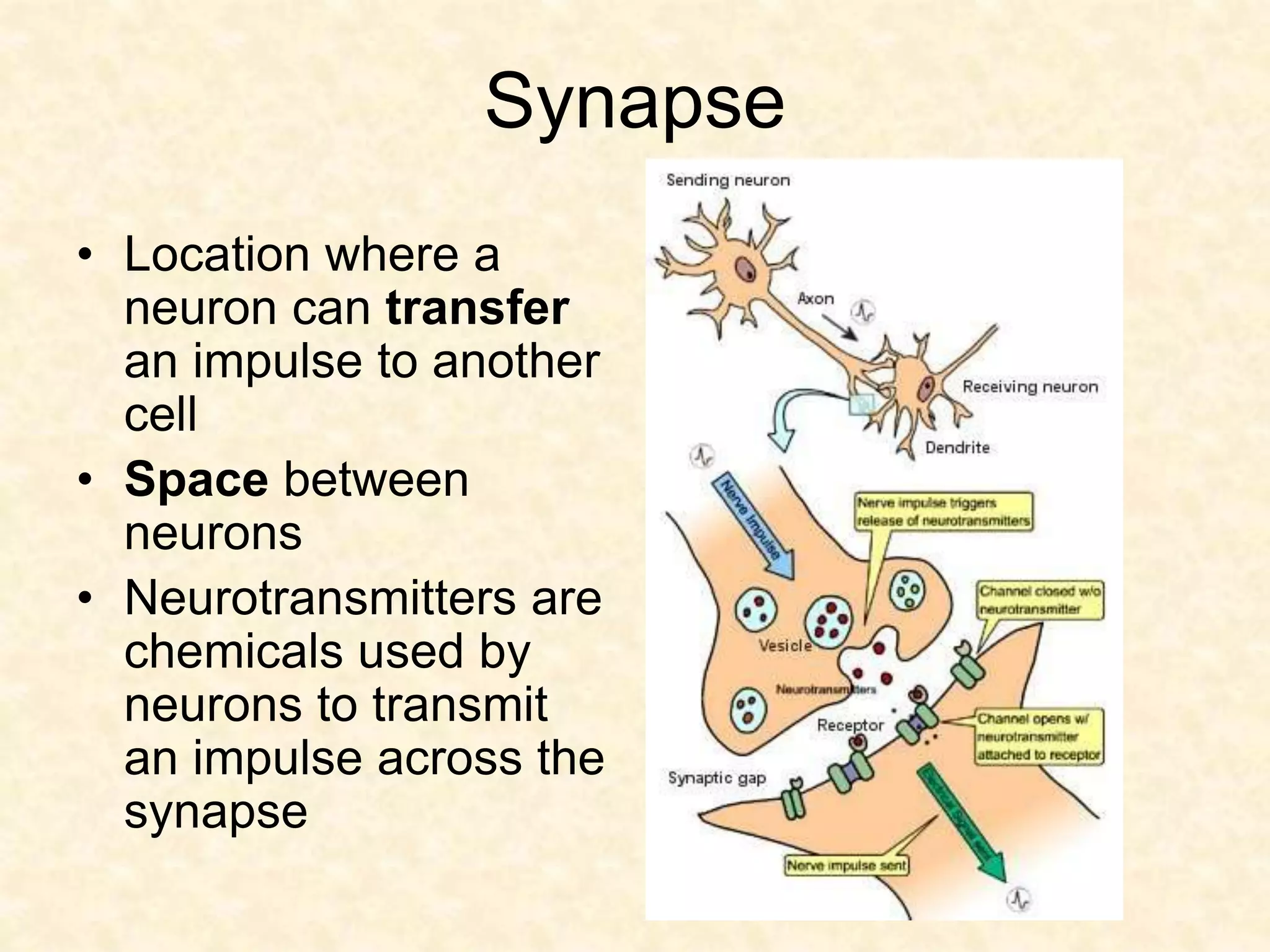
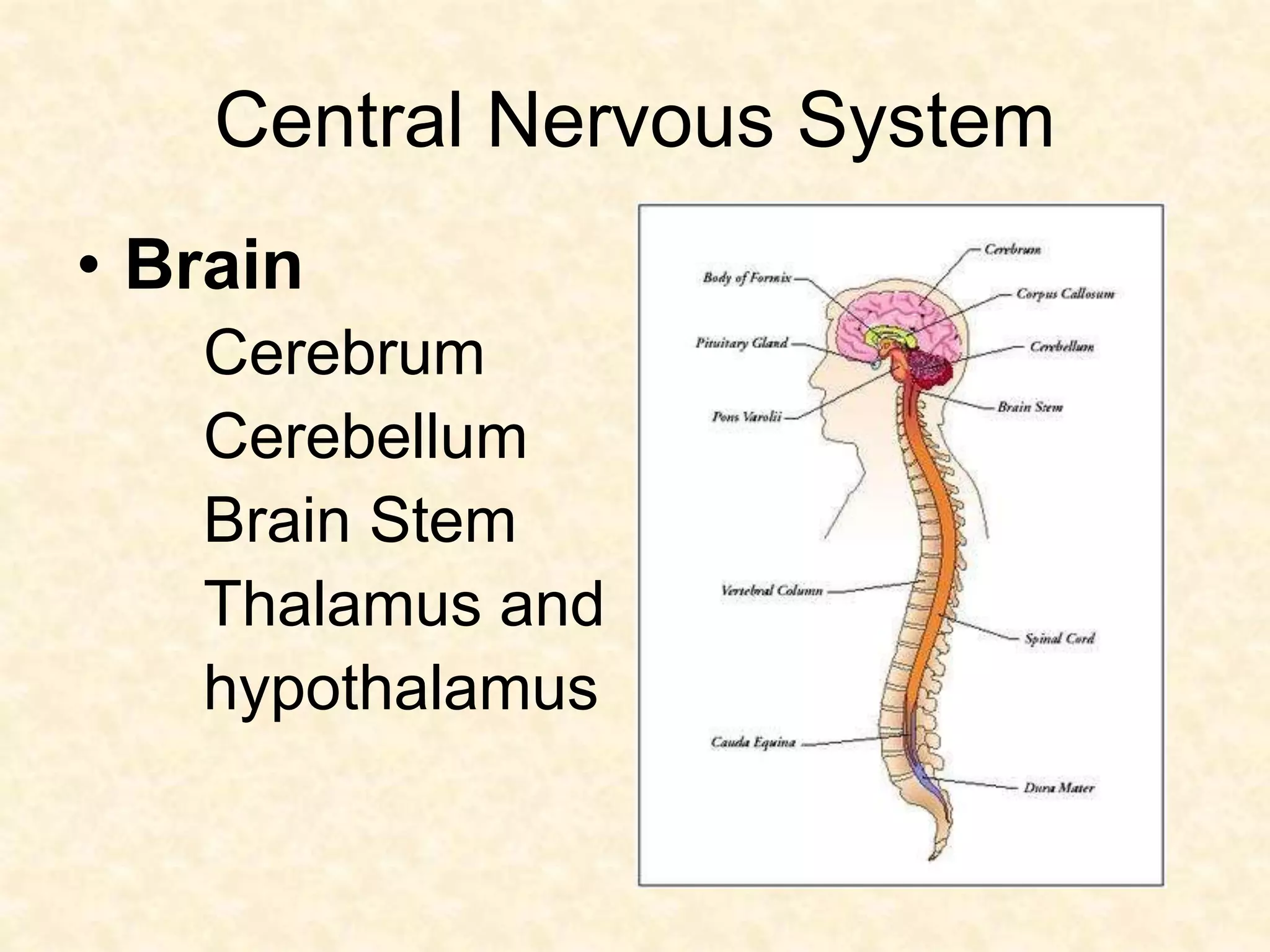
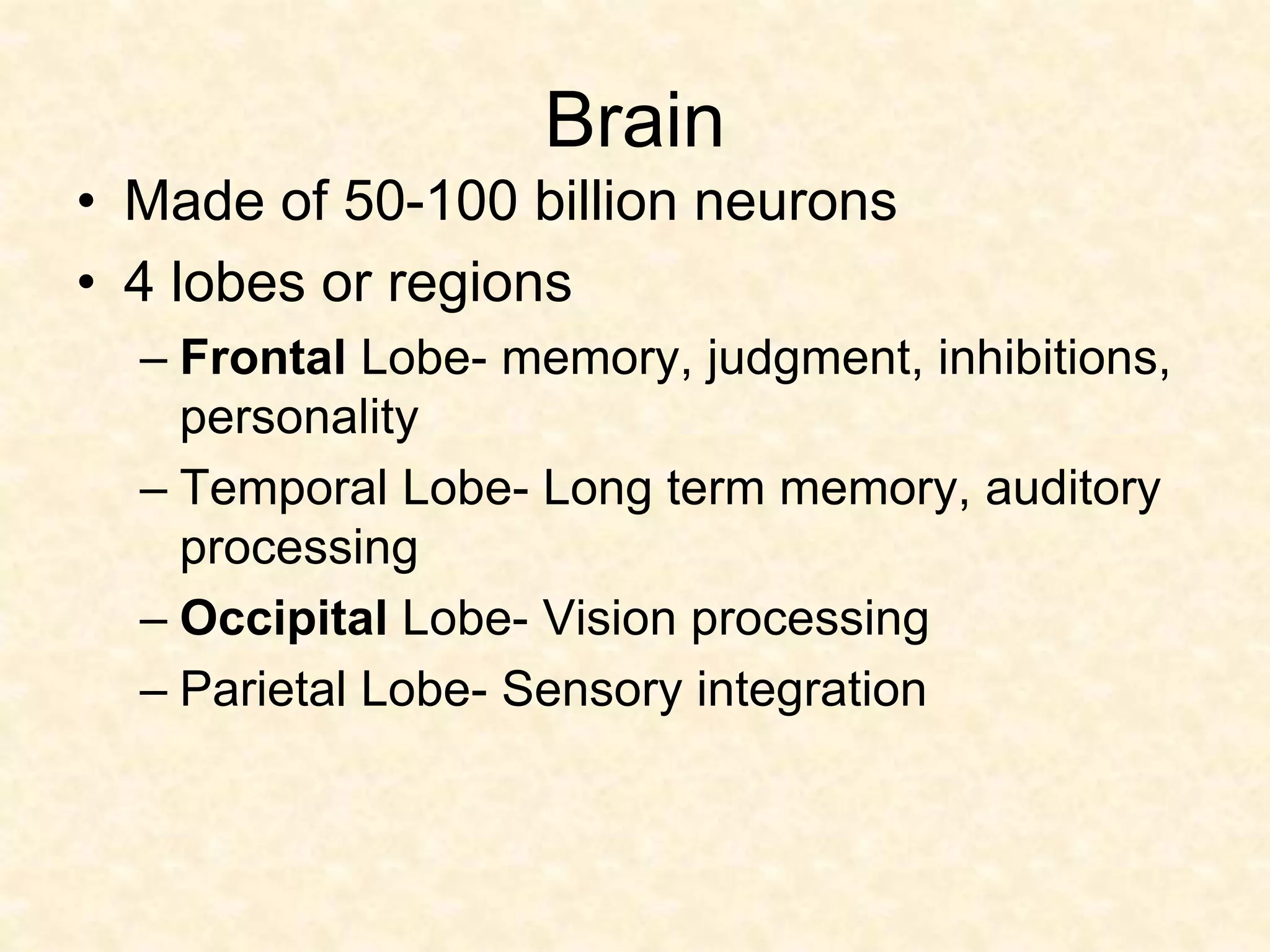
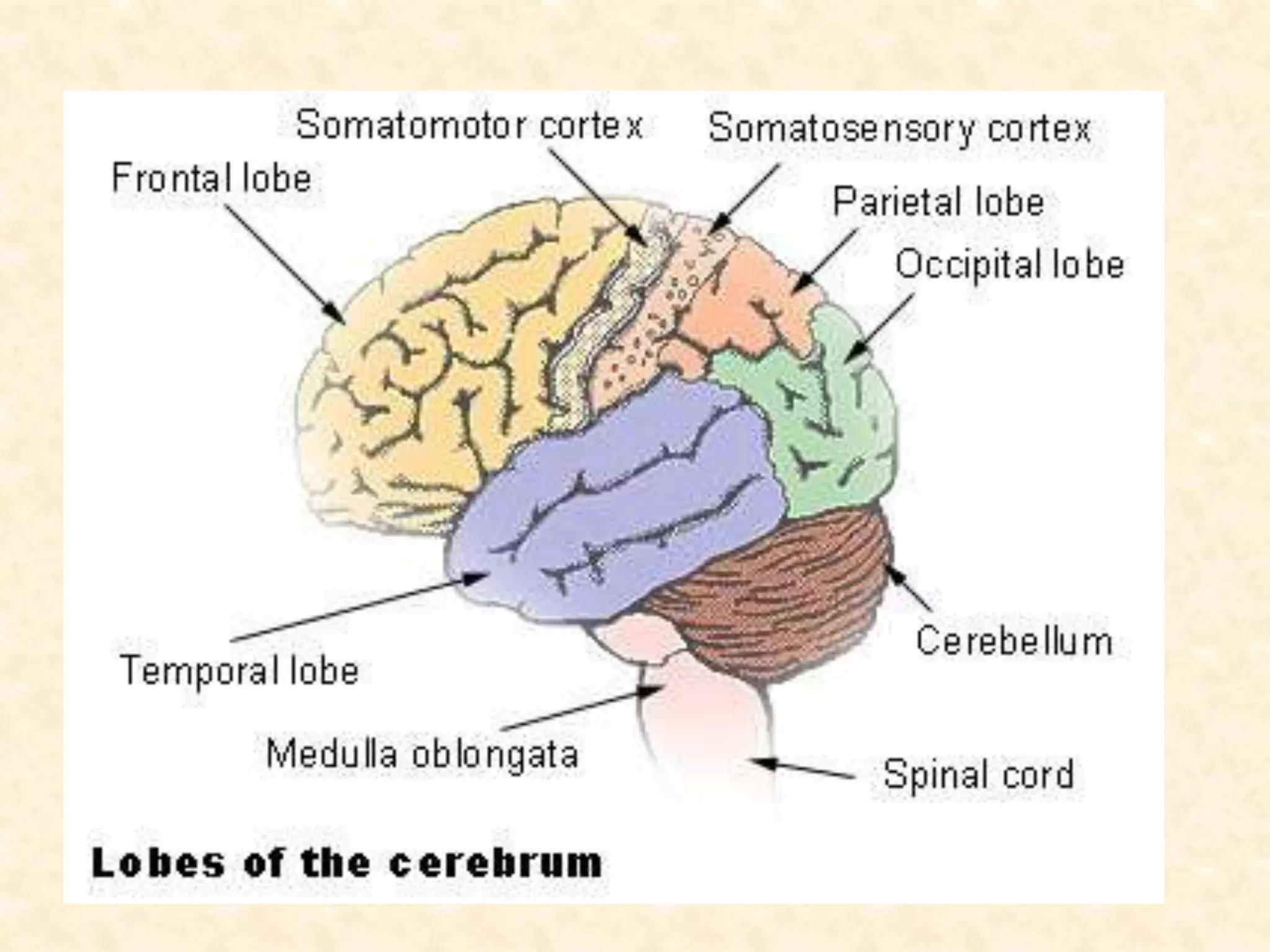
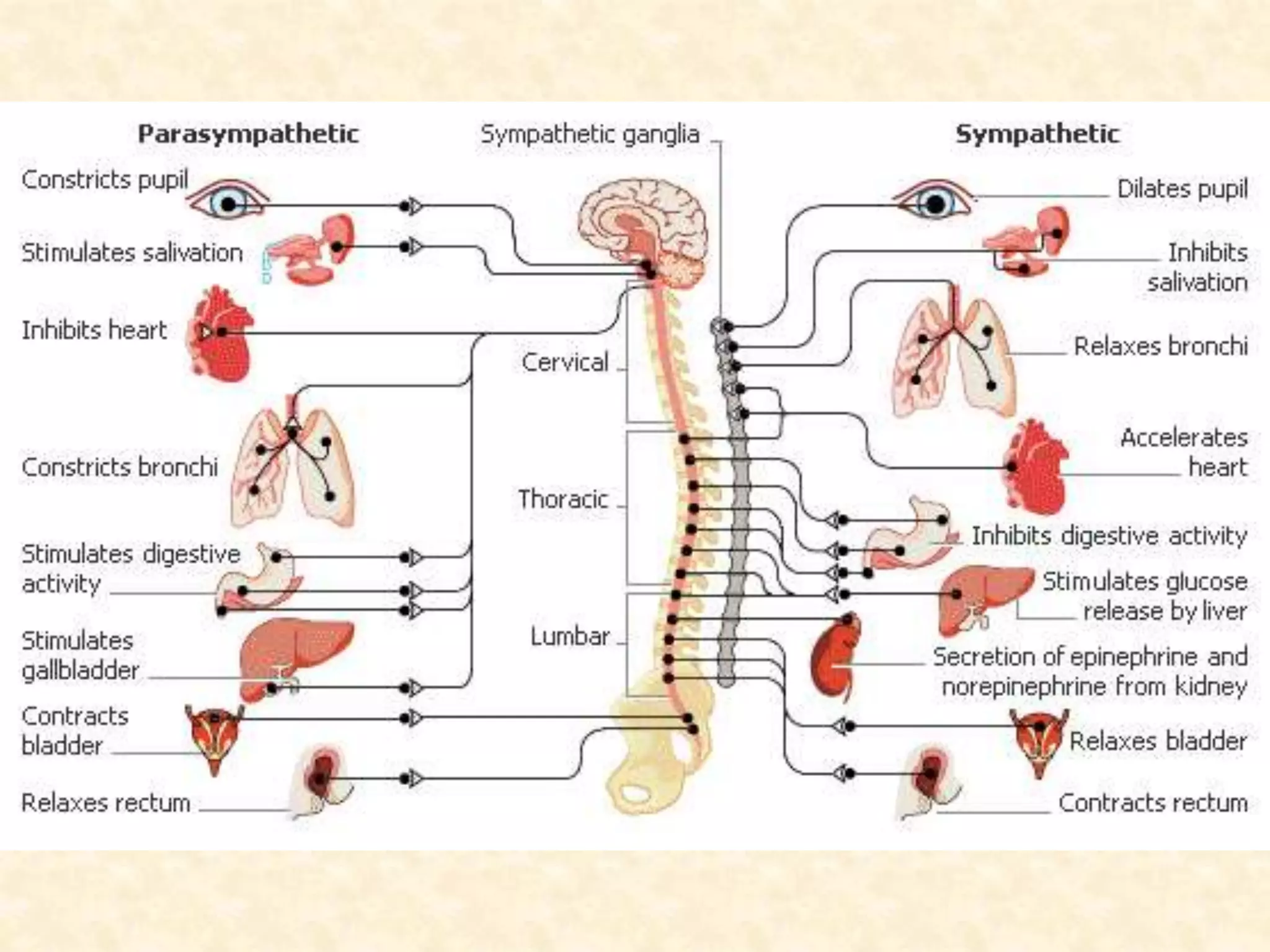
The human nervous system is made up of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system. The nervous system controls and coordinates functions throughout the body using electrical signals called nerve impulses that are carried by specialized cells called neurons. There are three main types of neurons - sensory neurons that carry impulses from sense organs to the CNS, motor neurons that carry impulses from the CNS to muscles and glands, and interneurons that connect sensory and motor neurons. The peripheral nervous system is divided into sensory and motor divisions, and regulates both conscious and involuntary activities.