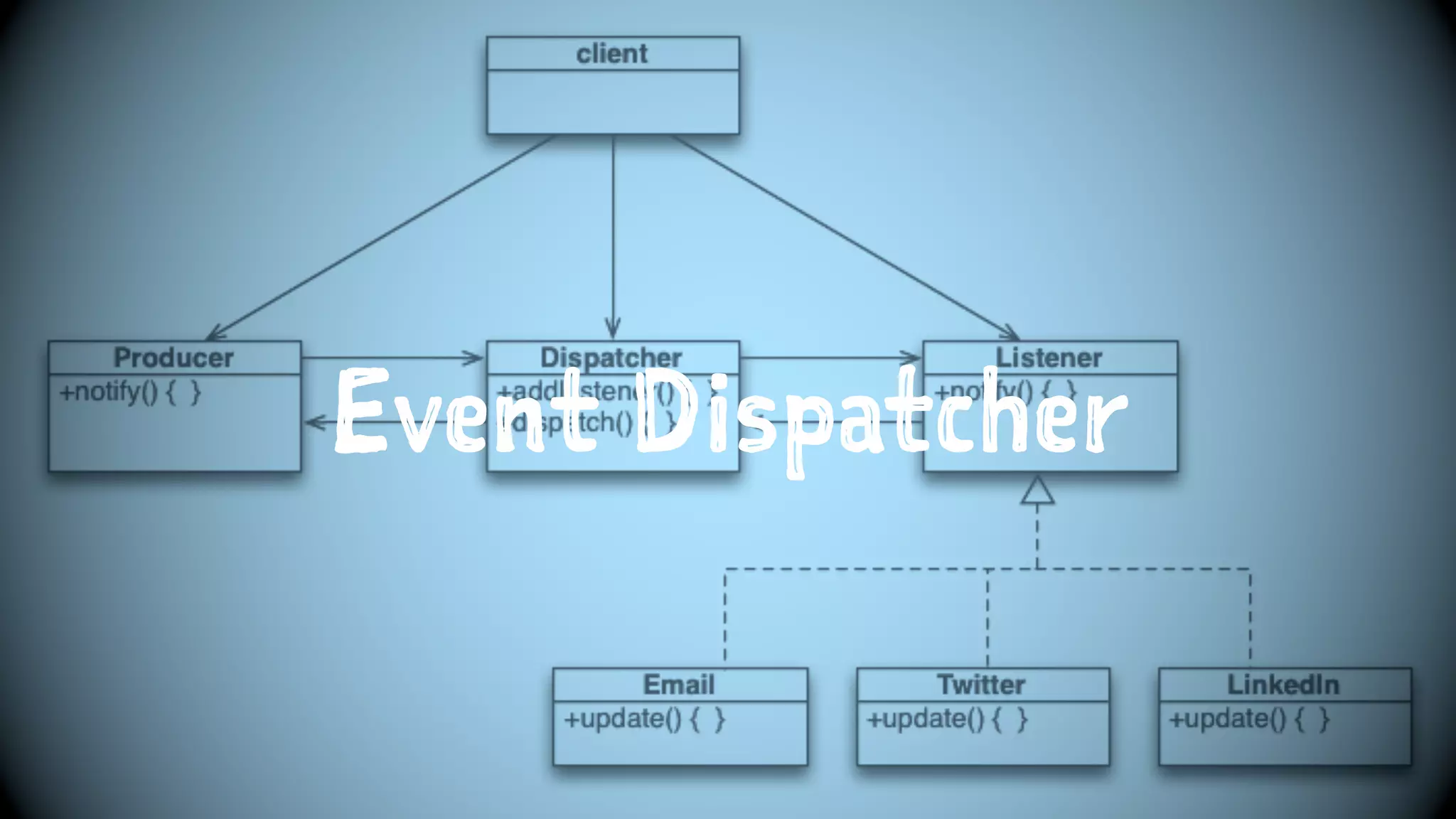
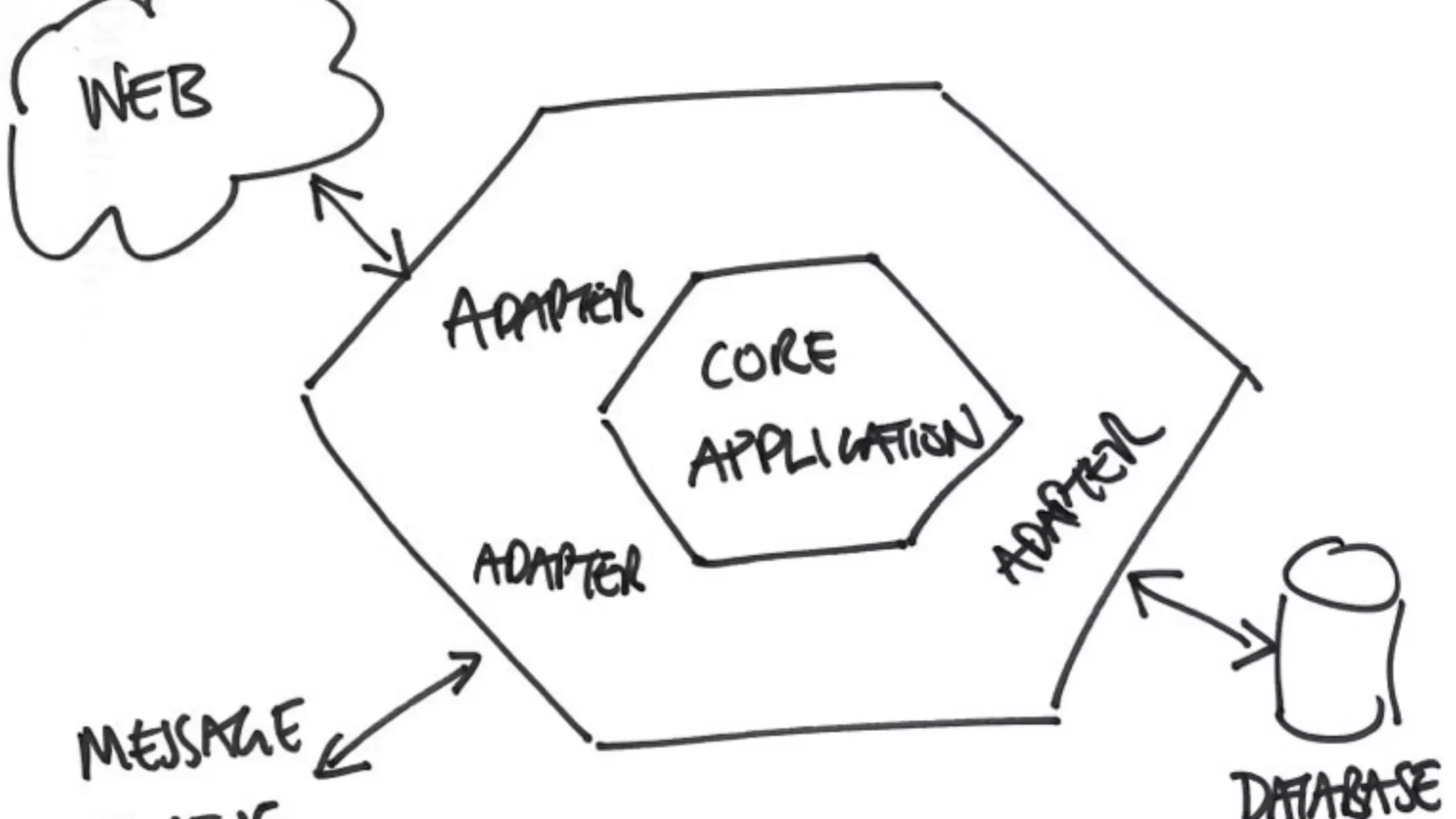
The document details the author's journey in embracing design patterns within software development, emphasizing their importance in creating reusable and maintainable code. It illustrates various refactoring techniques using PHP examples, highlighting how to improve code organization, manage dependencies, and dispatch events effectively. The author concludes by advocating for best practices in coding to enhance flexibility, maintainability, and testability in software projects.



![I probably wrote that
<?php
include 'header.php';
include 'pages/'. $_GET['page'].'.php';
include 'footer.php';](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/how-i-started-to-love-design-patterns-160919163418/75/How-I-started-to-love-design-patterns-4-2048.jpg)
![At some point I used Symfony
class EntityController extends Controller
{
public function myAction($identifier)
{
$entity = $this->getContainer()
->get('doctrine.orm.entity_manager')
->getRepository(Entity::class)
->find($identifier);
return $this->render('my-template.html.twig', [
'entity' => $entity,
]);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/how-i-started-to-love-design-patterns-160919163418/75/How-I-started-to-love-design-patterns-5-2048.jpg)






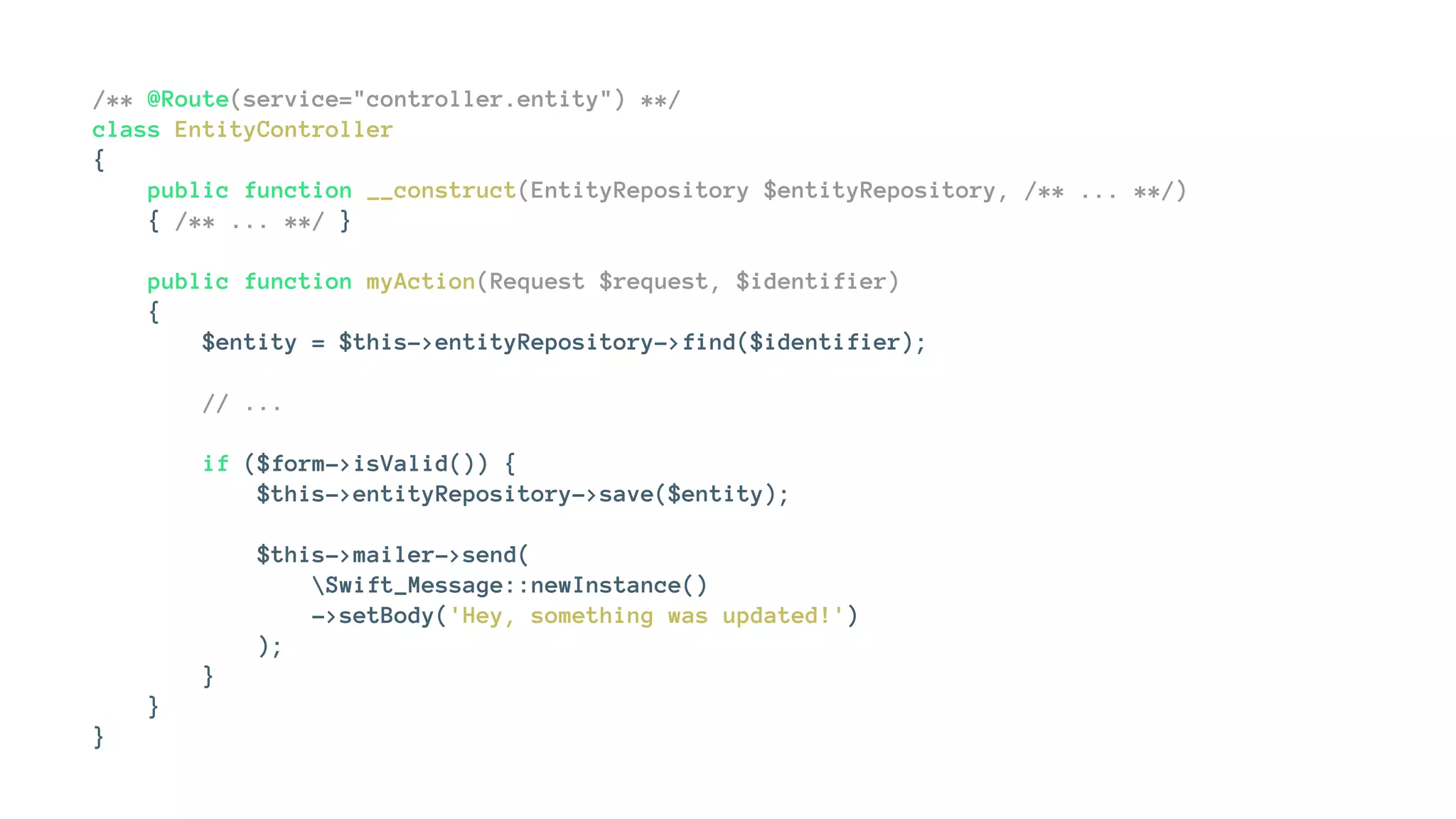
![Let's do some refactoring
class EntityController extends Controller
{
public function myAction(Request $request, $identifier)
{
$entity = $this->getContainer()
->get('doctrine.orm.entity_manager')
->getRepository(Entity::class)
->find($identifier);
$form = $this->createForm(EntityFormType::class, $entity);
$form->handleRequest($request);
if ($form->isValid()) {
$entity = $form->getData();
$doctrine->persist($entity);
$doctrine->flush($entity);
$mailer = $this->getContainer()->get('mailer');
$mailer->send(
Swift_Message::newInstance()
->setBody('Hey, something was updated!')
);
}
return $this->render('my-template.html.twig', [
'entity' => $entity,
]);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/how-i-started-to-love-design-patterns-160919163418/75/How-I-started-to-love-design-patterns-13-2048.jpg)












![Store the entity in-memory?
final class InMemoryRepositoryEntity implements EntityRepository
{
private $entities = [];
public function find($identifier) : Entity
{
if (!array_key_exists($identifier, $this->entities)) {
throw new EntityNotFound();
}
return $this->entities[$identifier];
}
public function save(Entity $entity) : Entity
{
$this->entities[$entity->getIdentifier()] = $entity;
return $entity;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/how-i-started-to-love-design-patterns-160919163418/75/How-I-started-to-love-design-patterns-29-2048.jpg)