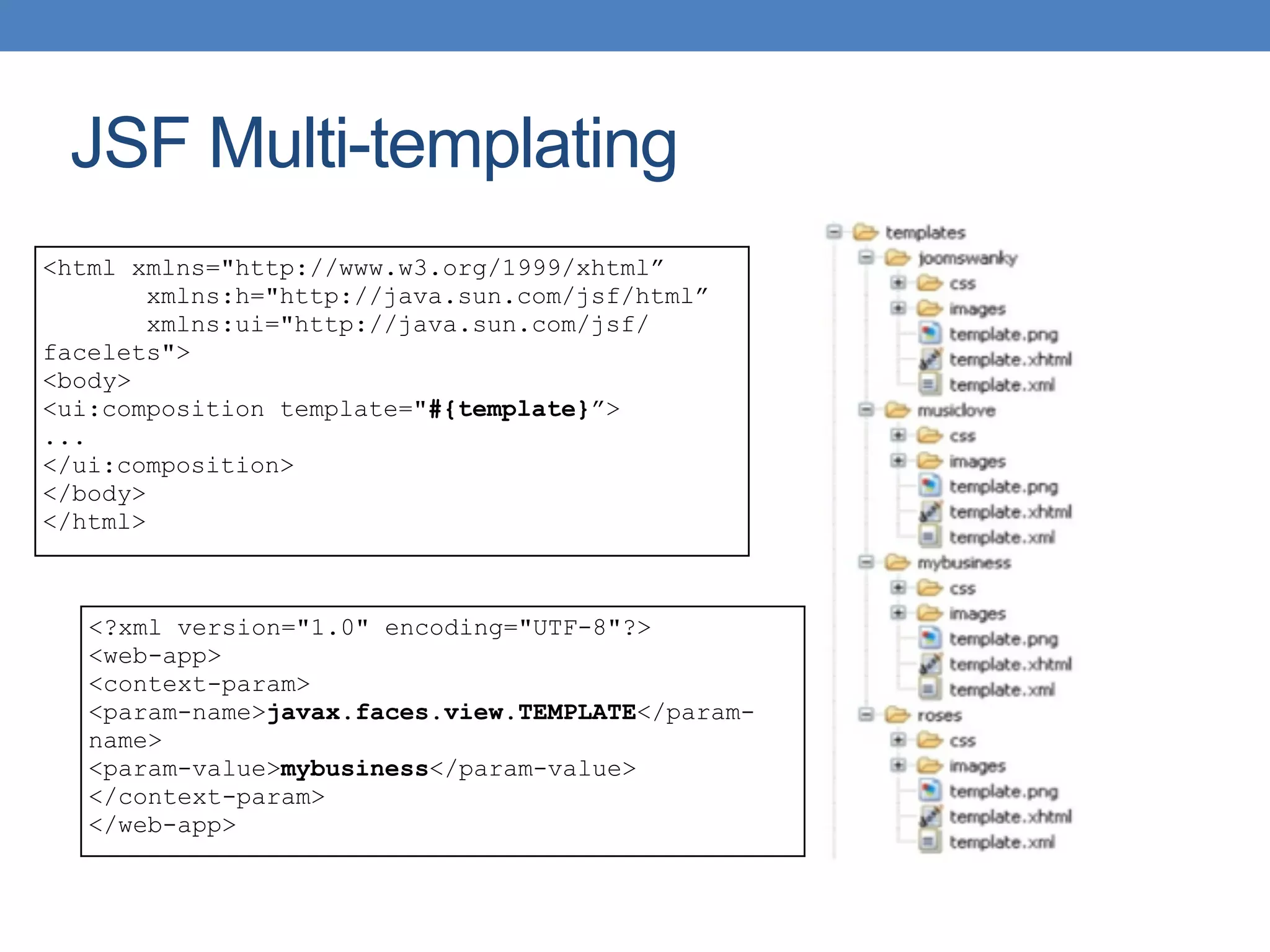
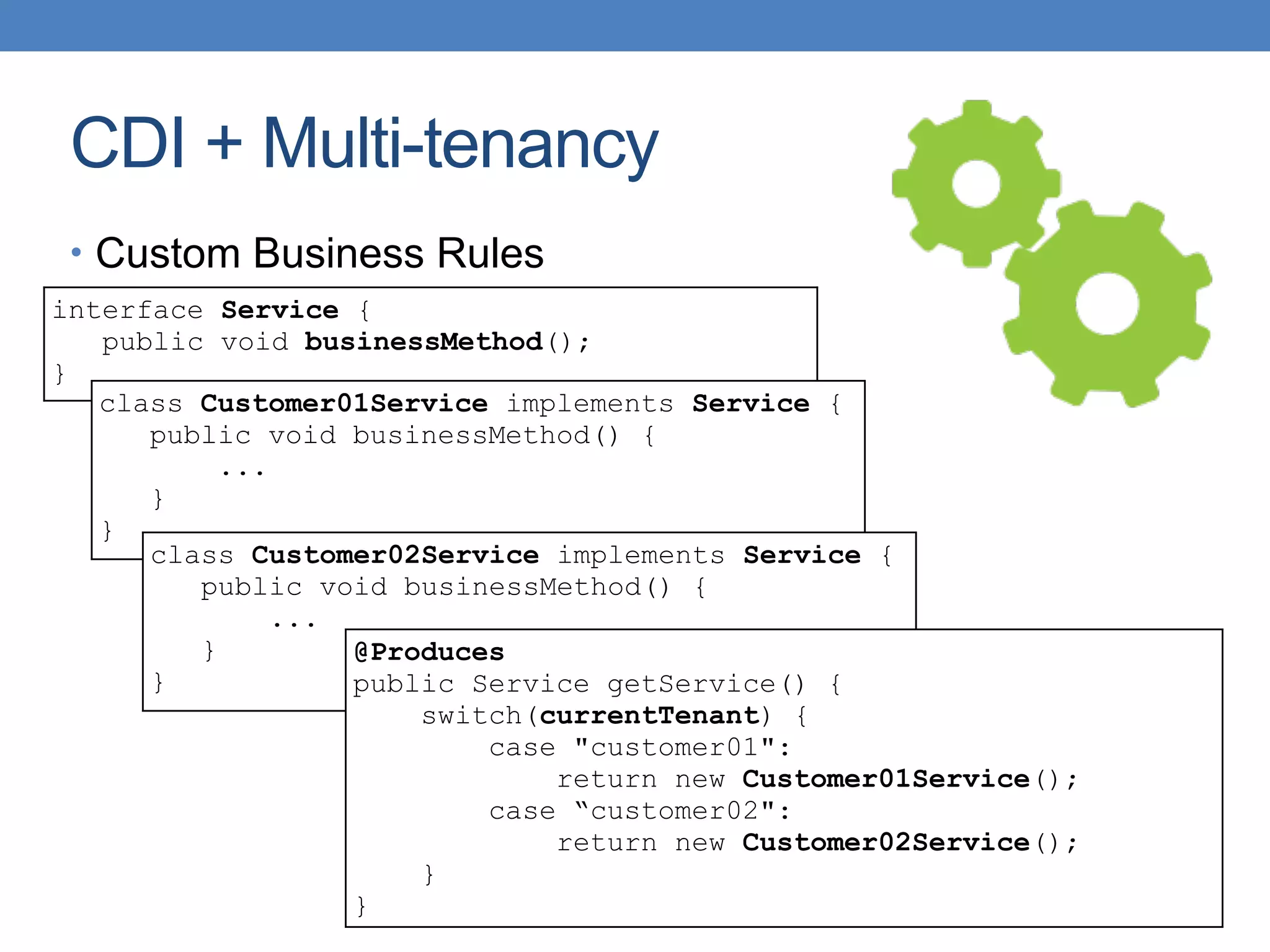
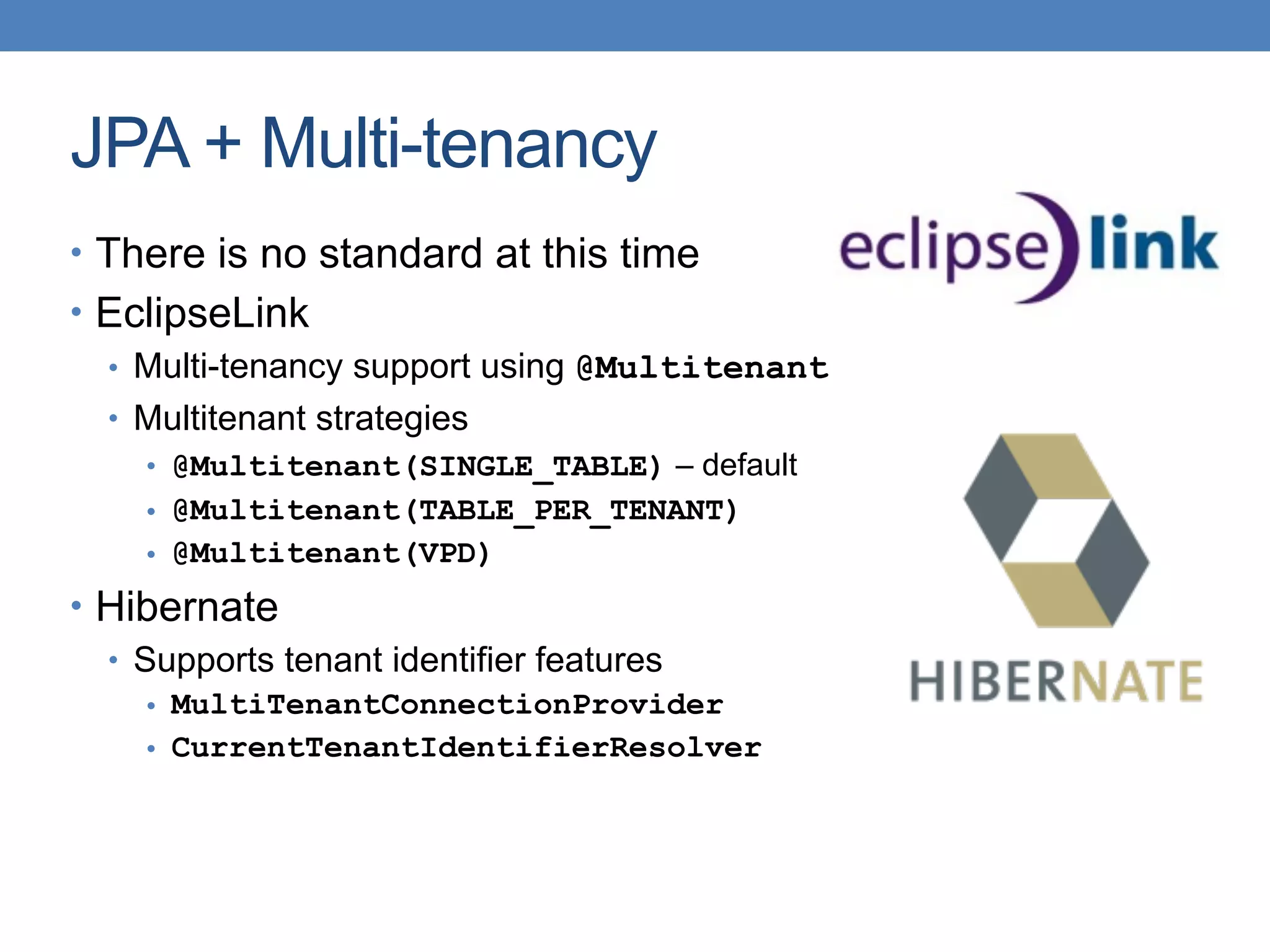
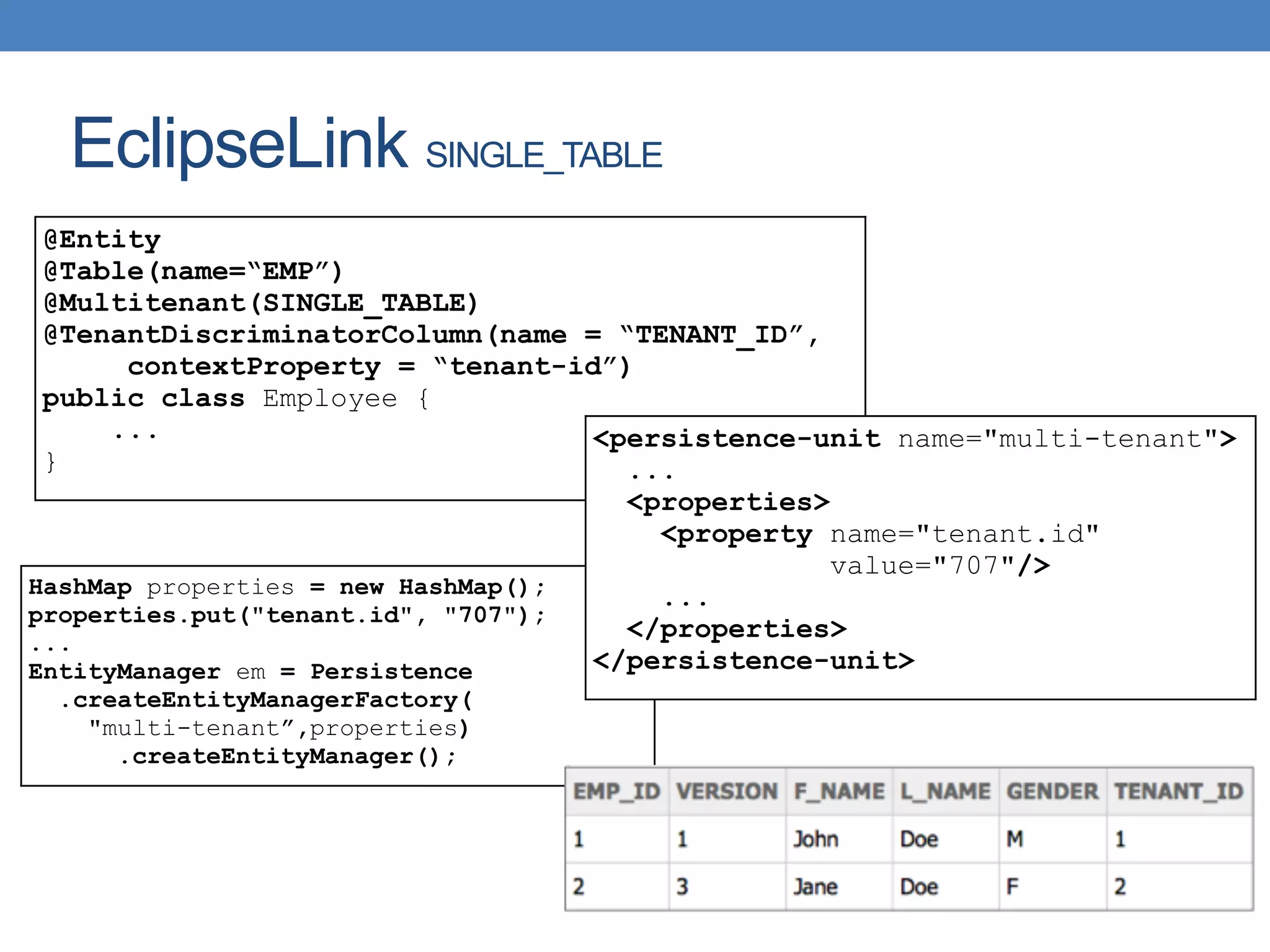
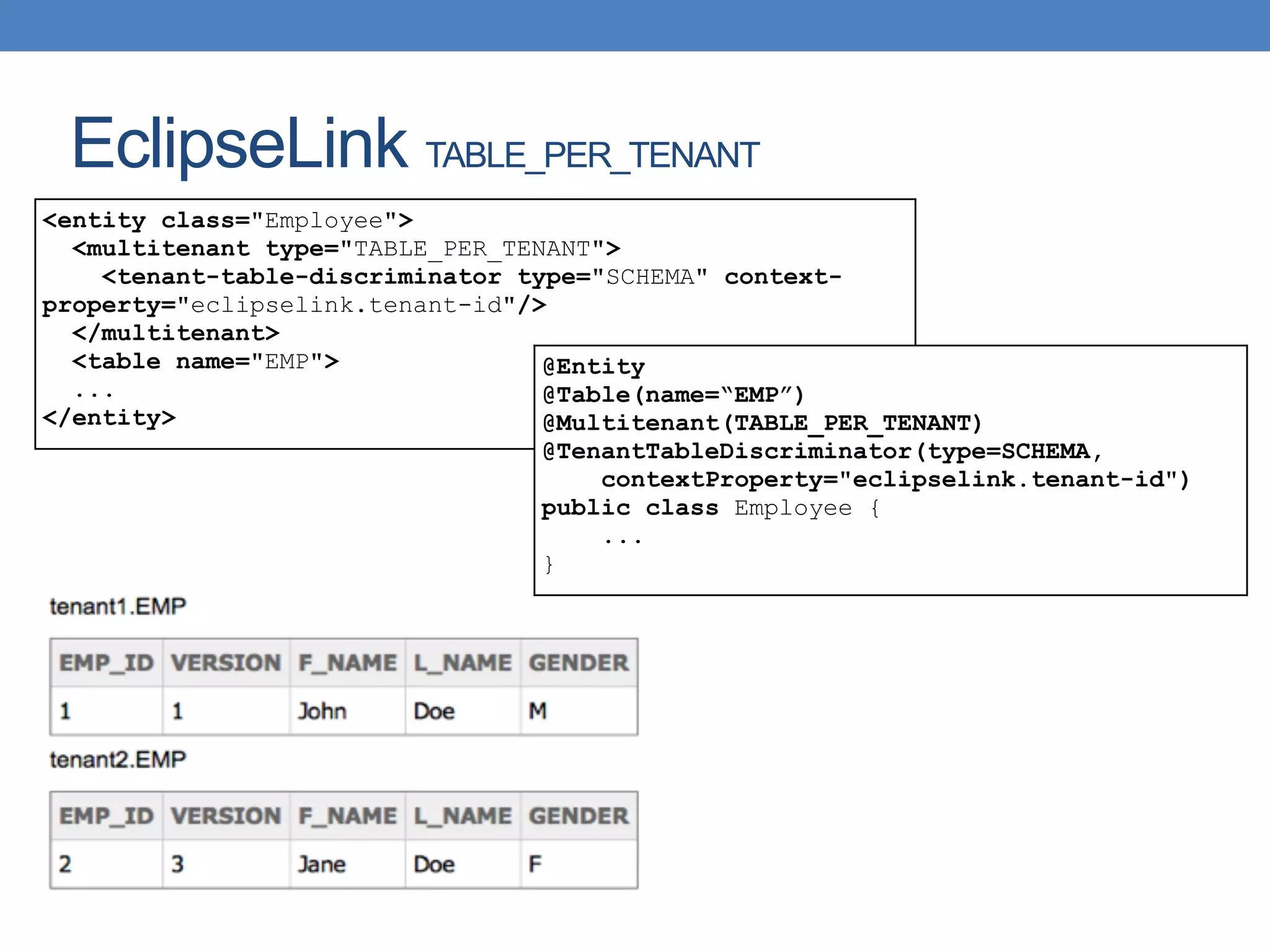
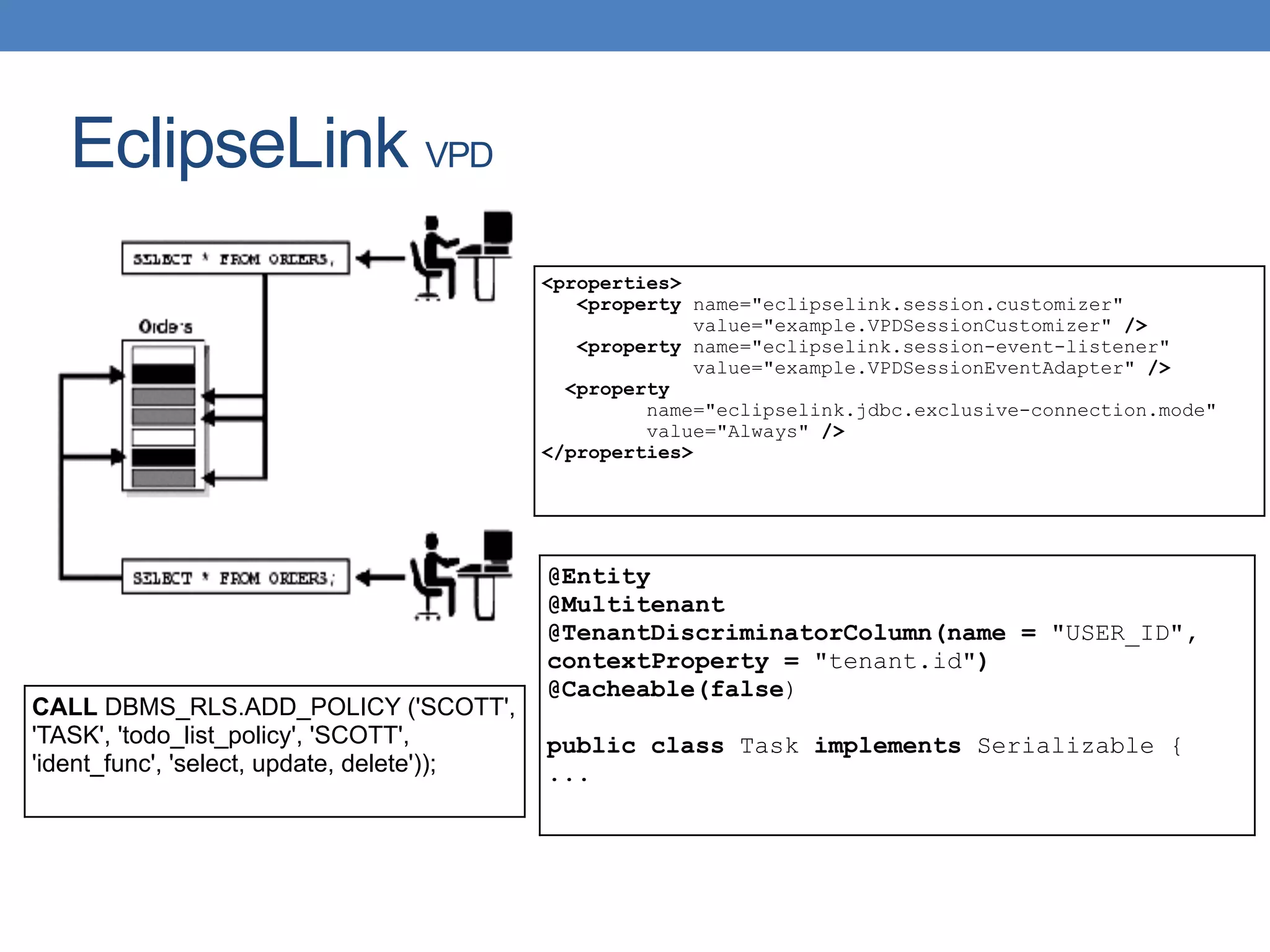
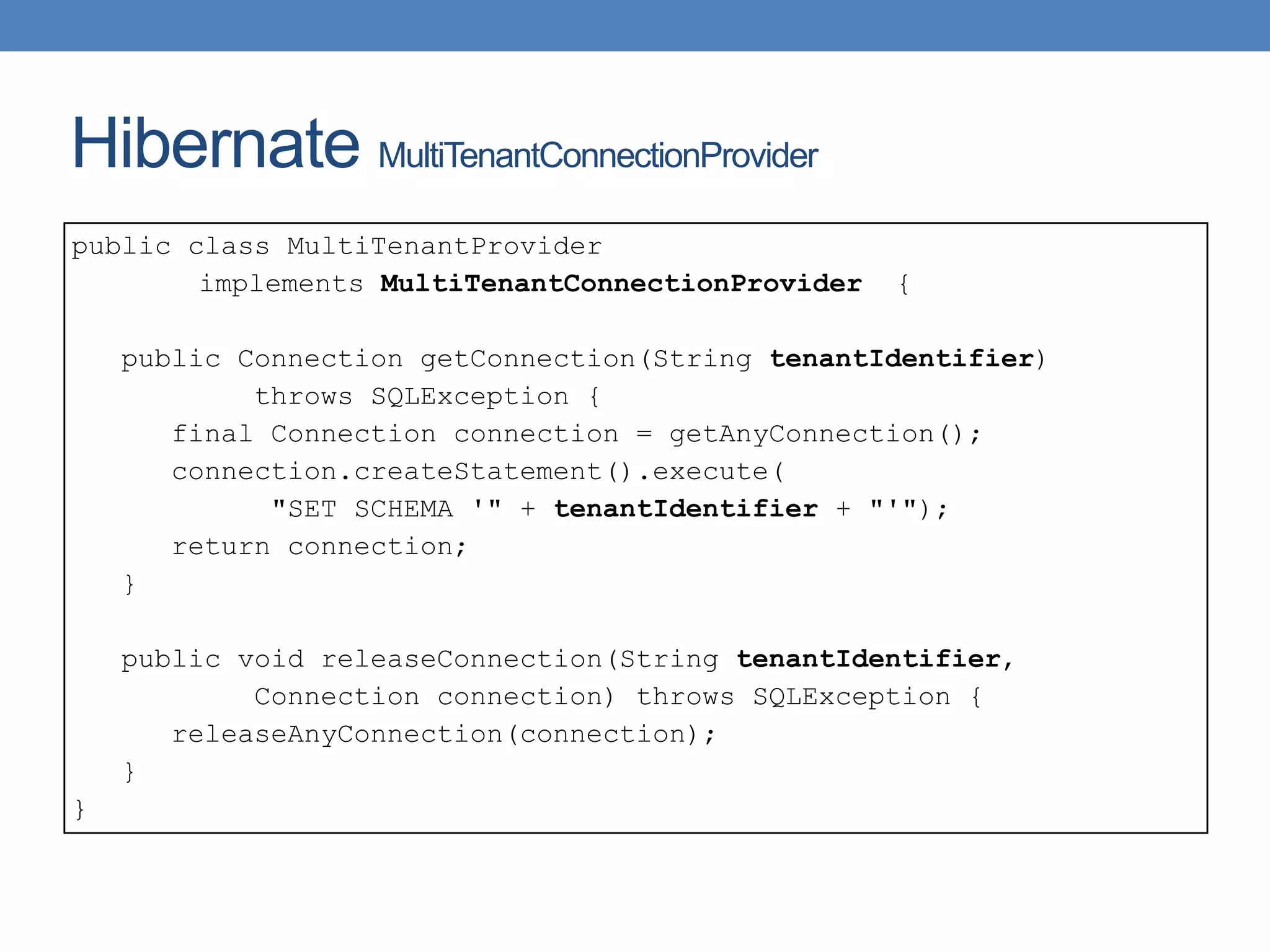
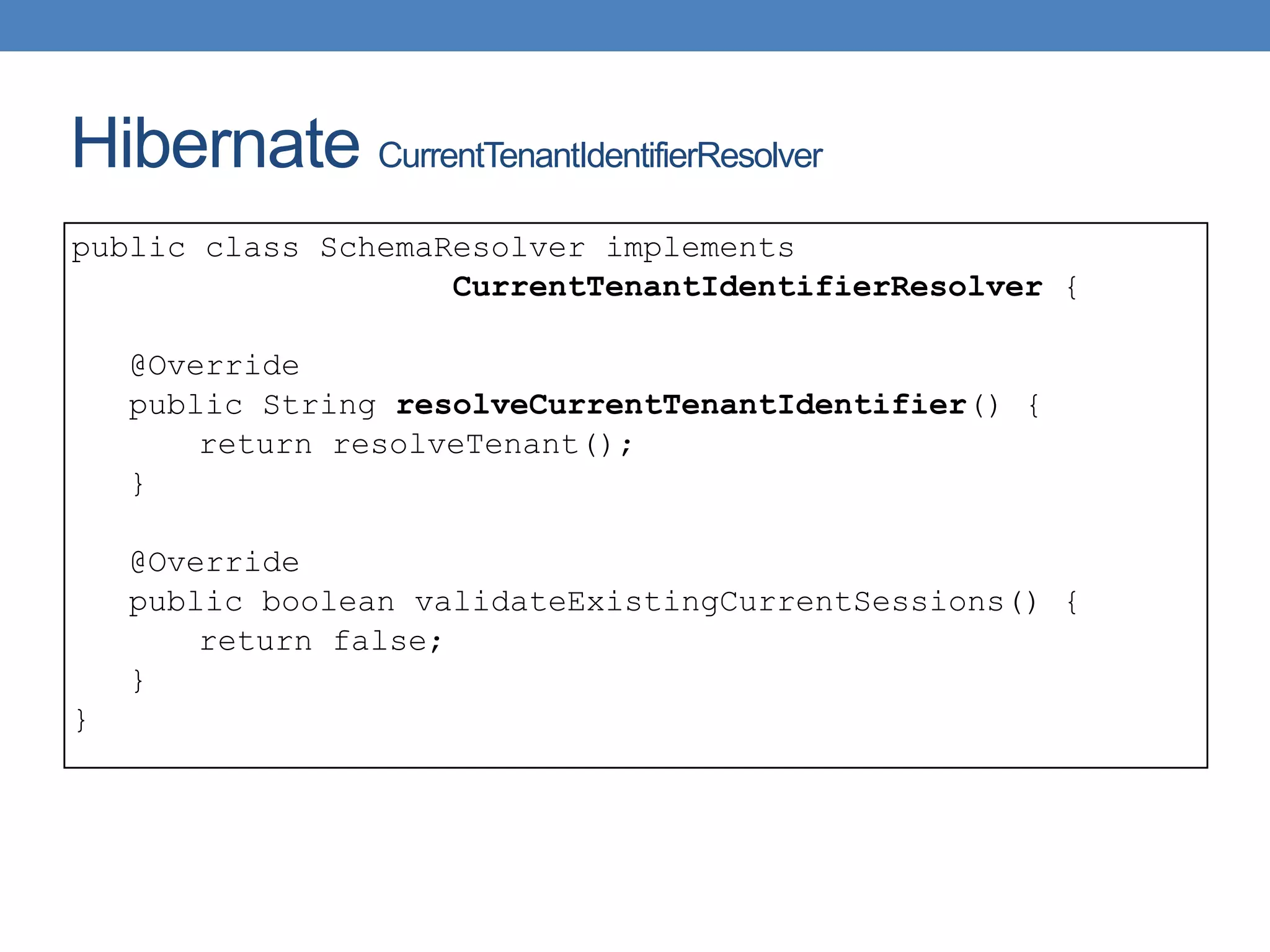
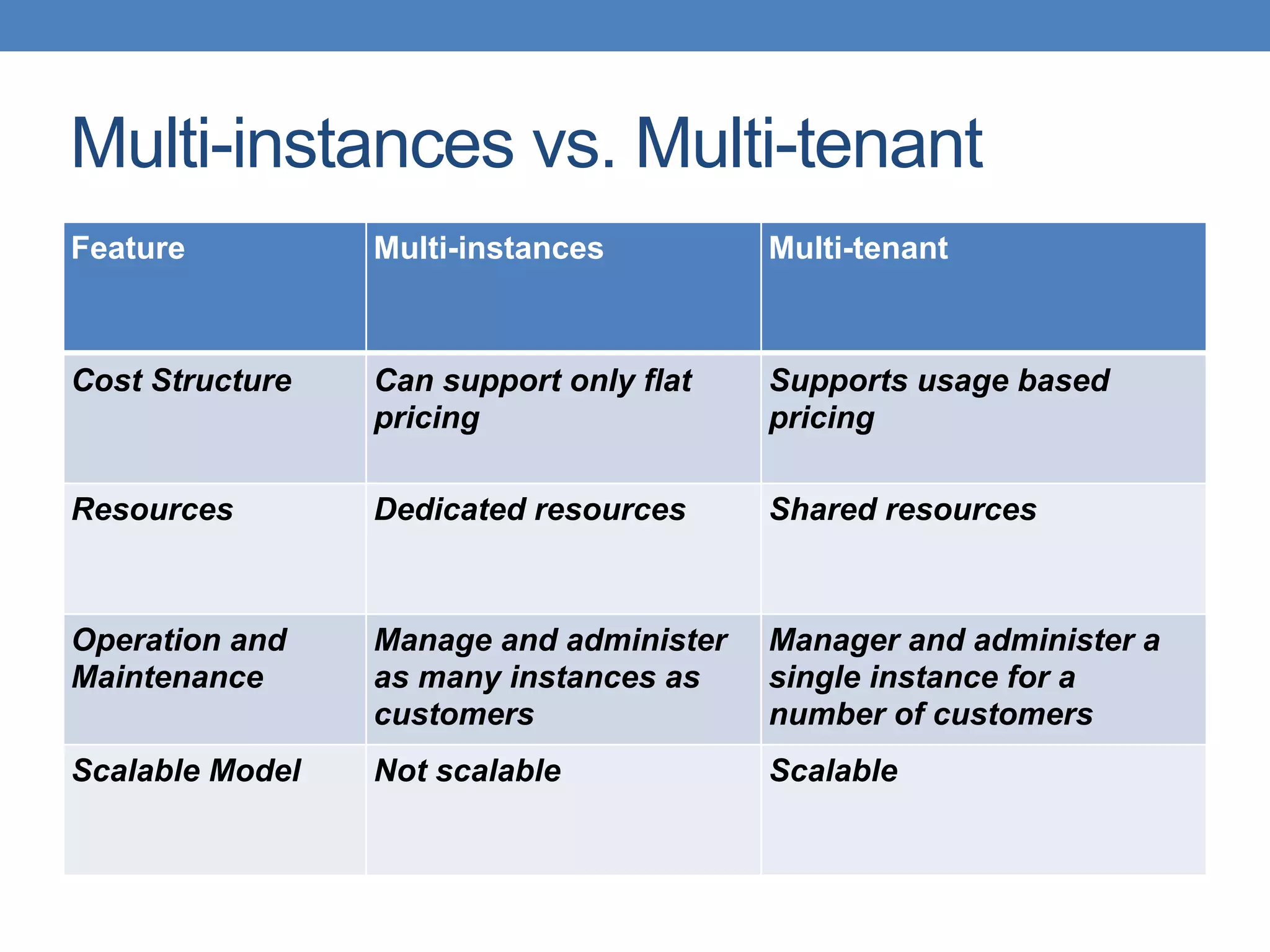
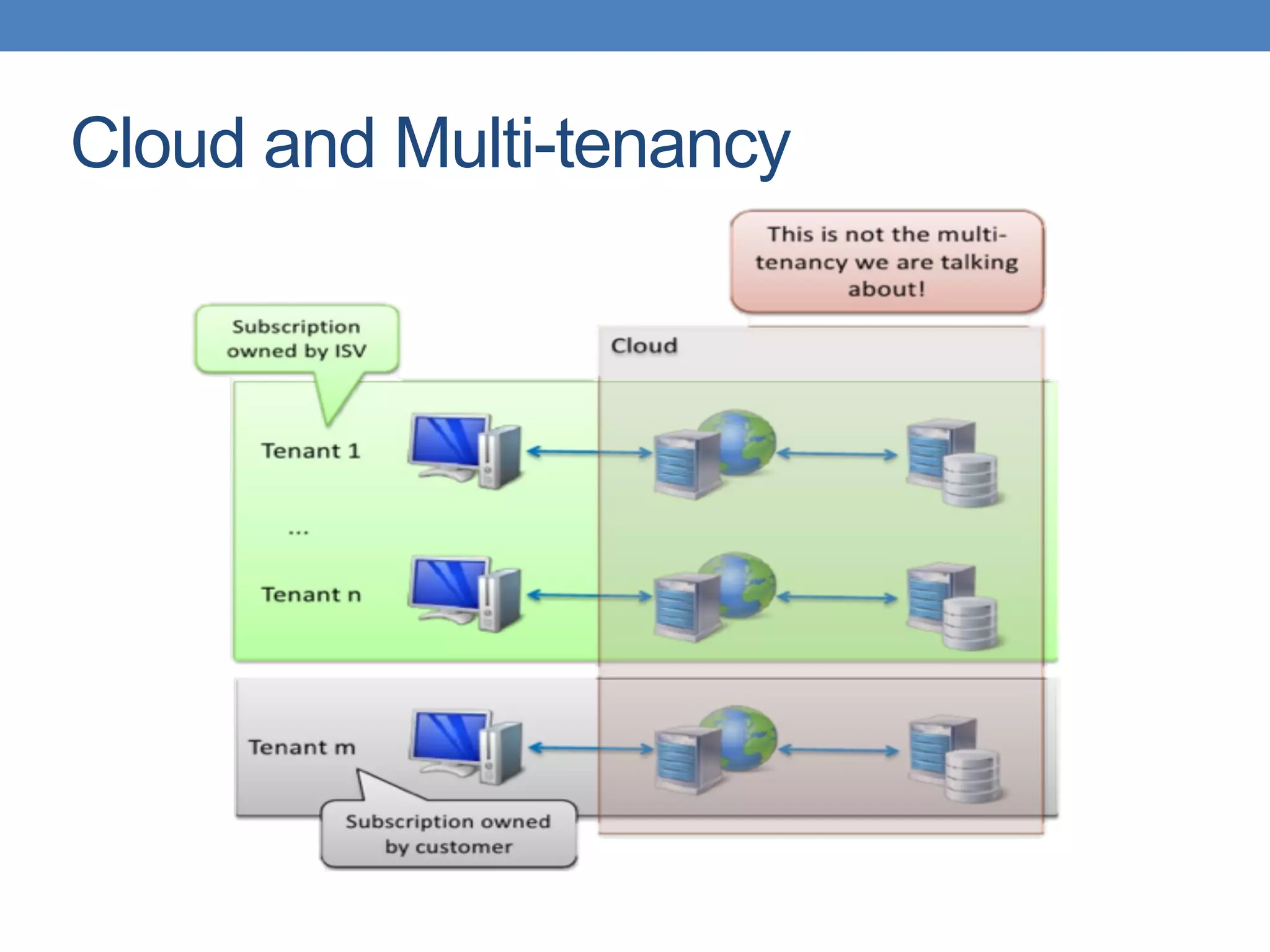
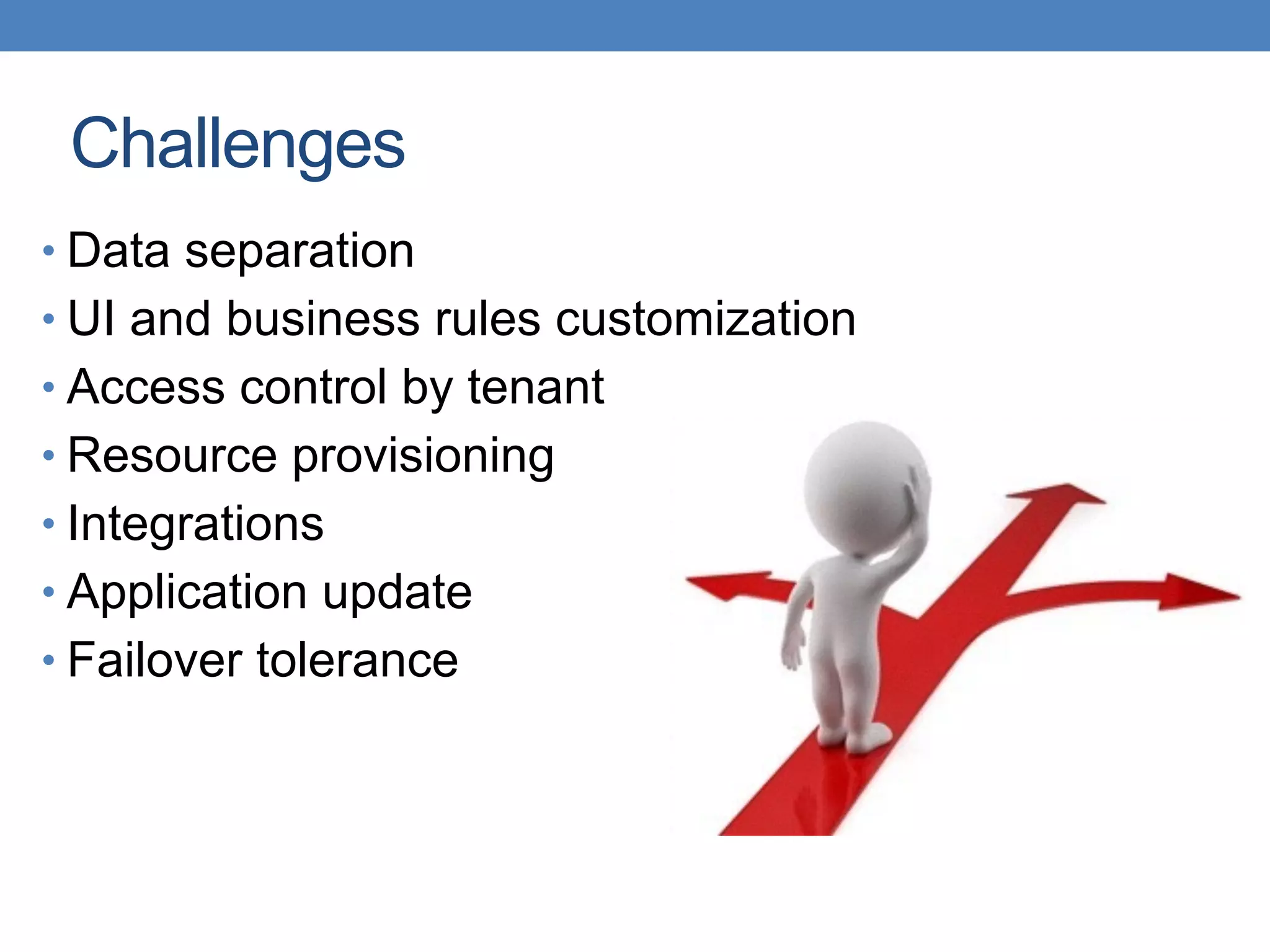
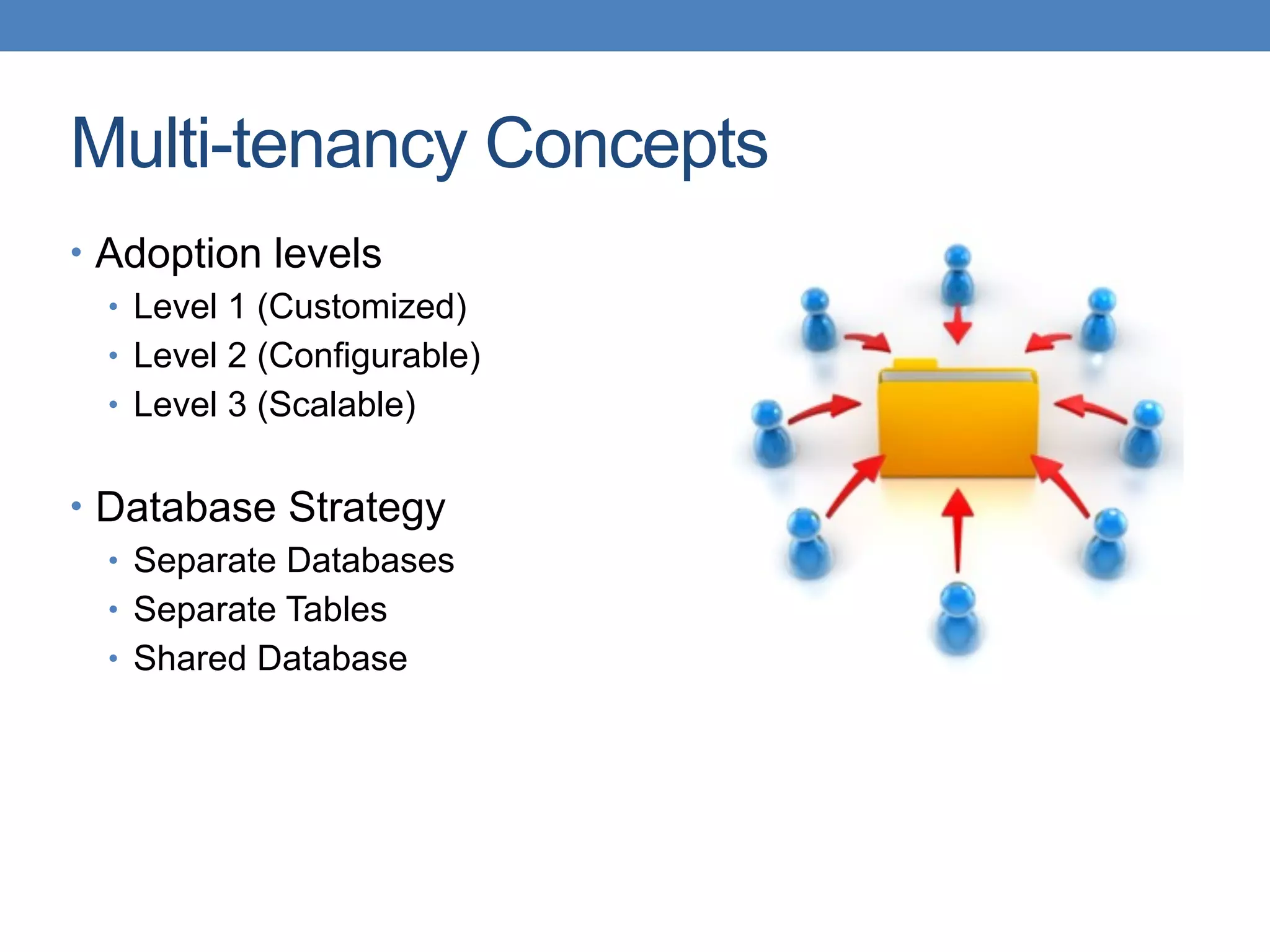
The document discusses the architecture and implementation of multi-tenancy applications using Java EE, outlining various challenges, strategies, and best practices. It covers tenant identification, UI customization, and database support, along with comparisons of multi-instance vs. multi-tenant frameworks. Additionally, it provides code examples for Java servlets, JSF, CDI, and JPA, illustrating approaches to effectively manage multi-tenant environments.




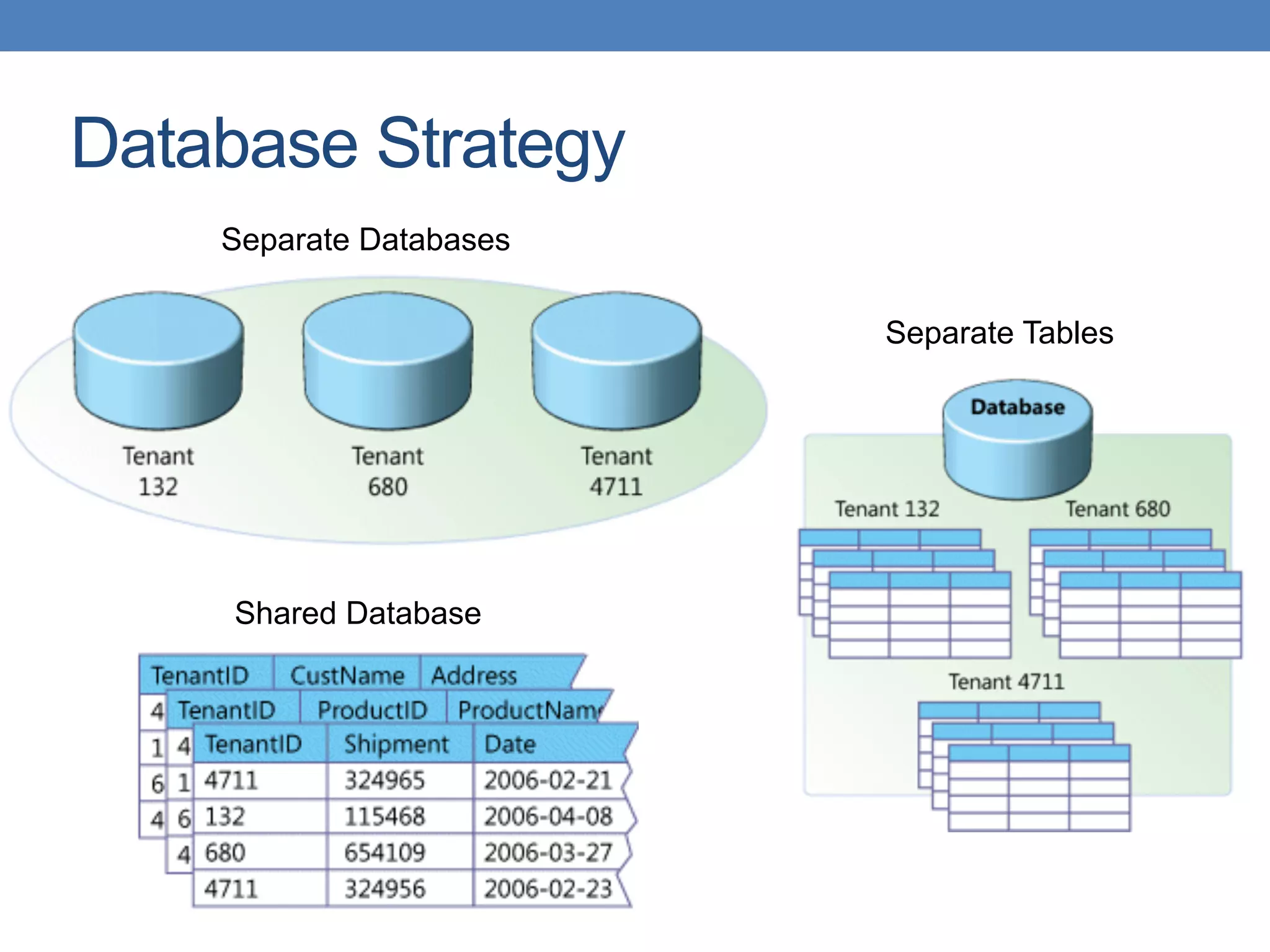
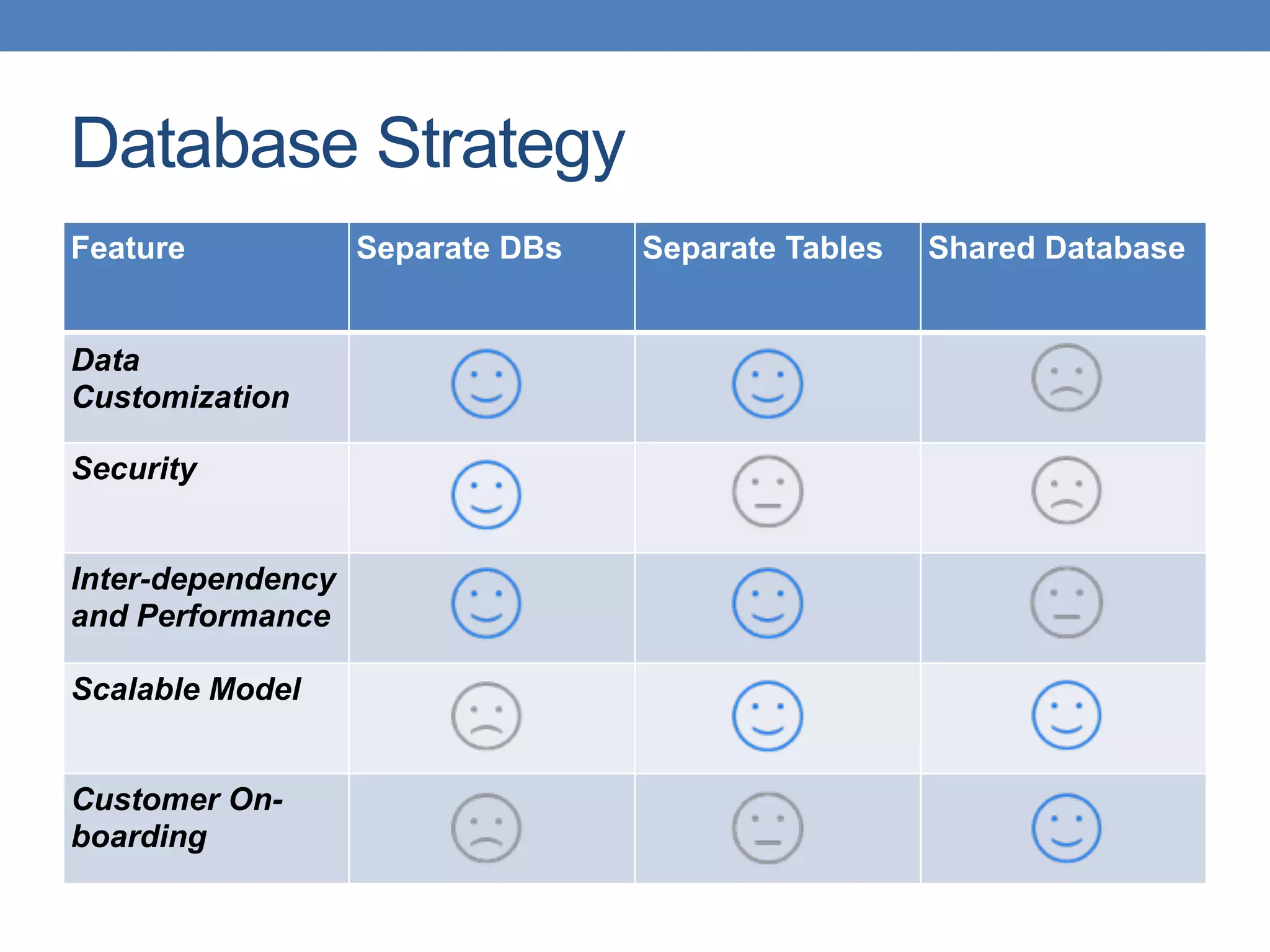
![Level 1 - Customized
• [N] applications and [N] databases](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/confoo2015-supportingmulti-tenancyapplicationswithjavaee-150220140227-conversion-gate02/75/ConFoo-2015-Supporting-Multi-tenancy-Applications-with-Java-EE-13-2048.jpg)
![Level 2 - Configurable
• [1] application and [N] databases](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/confoo2015-supportingmulti-tenancyapplicationswithjavaee-150220140227-conversion-gate02/75/ConFoo-2015-Supporting-Multi-tenancy-Applications-with-Java-EE-14-2048.jpg)
![Level 3 - Scalable
• [1] application and [1] database](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/confoo2015-supportingmulti-tenancyapplicationswithjavaee-150220140227-conversion-gate02/75/ConFoo-2015-Supporting-Multi-tenancy-Applications-with-Java-EE-15-2048.jpg)