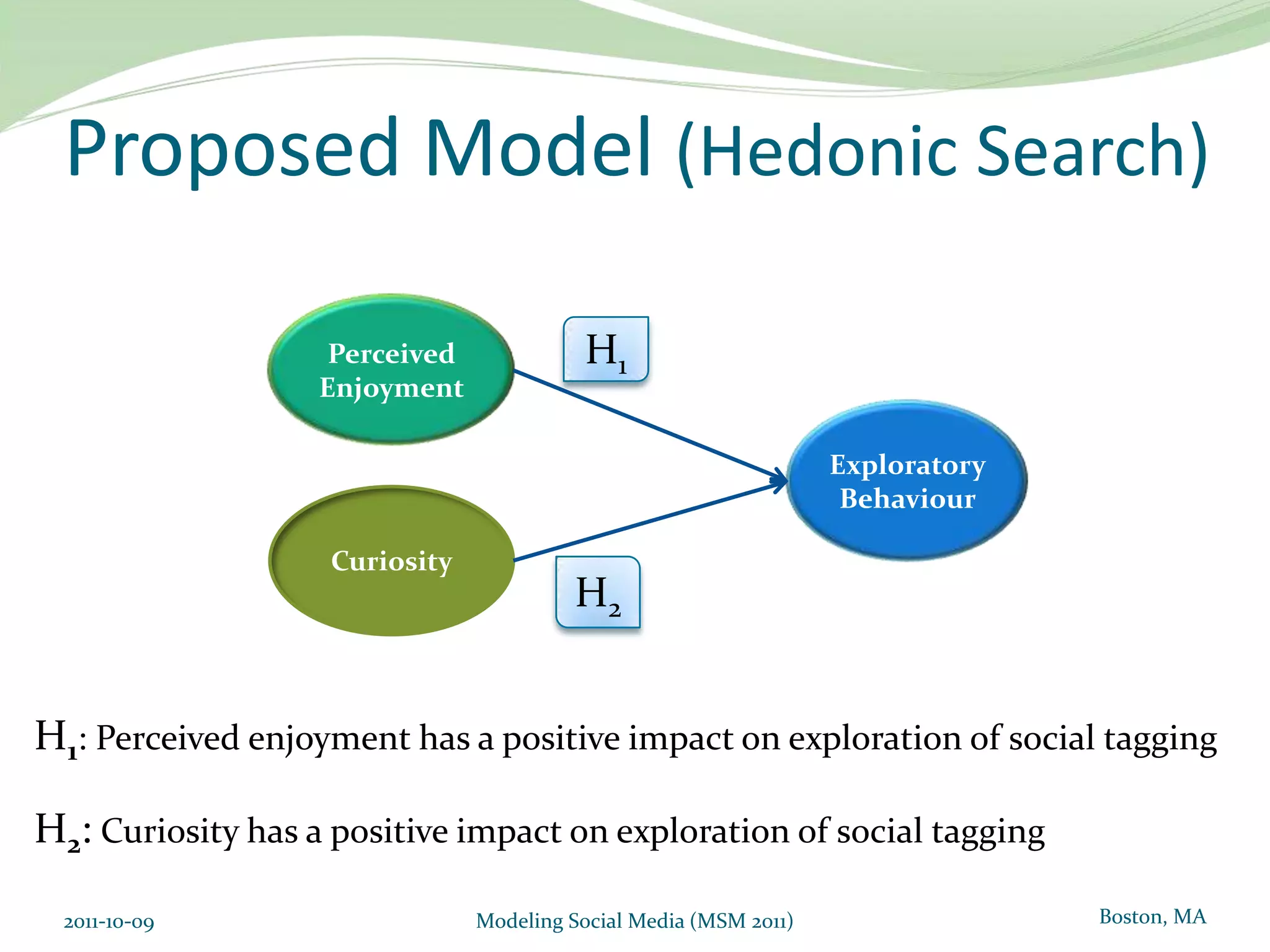
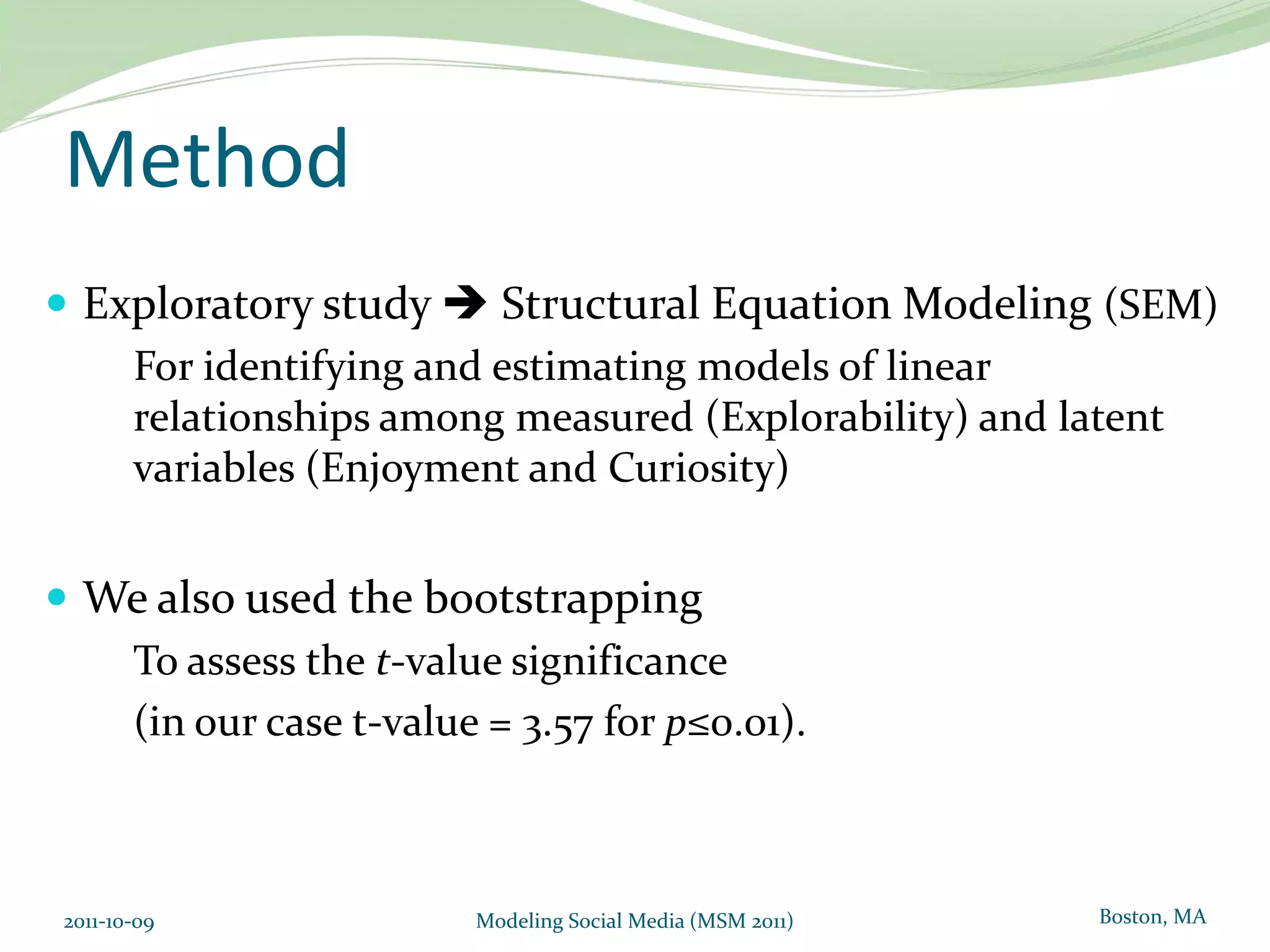
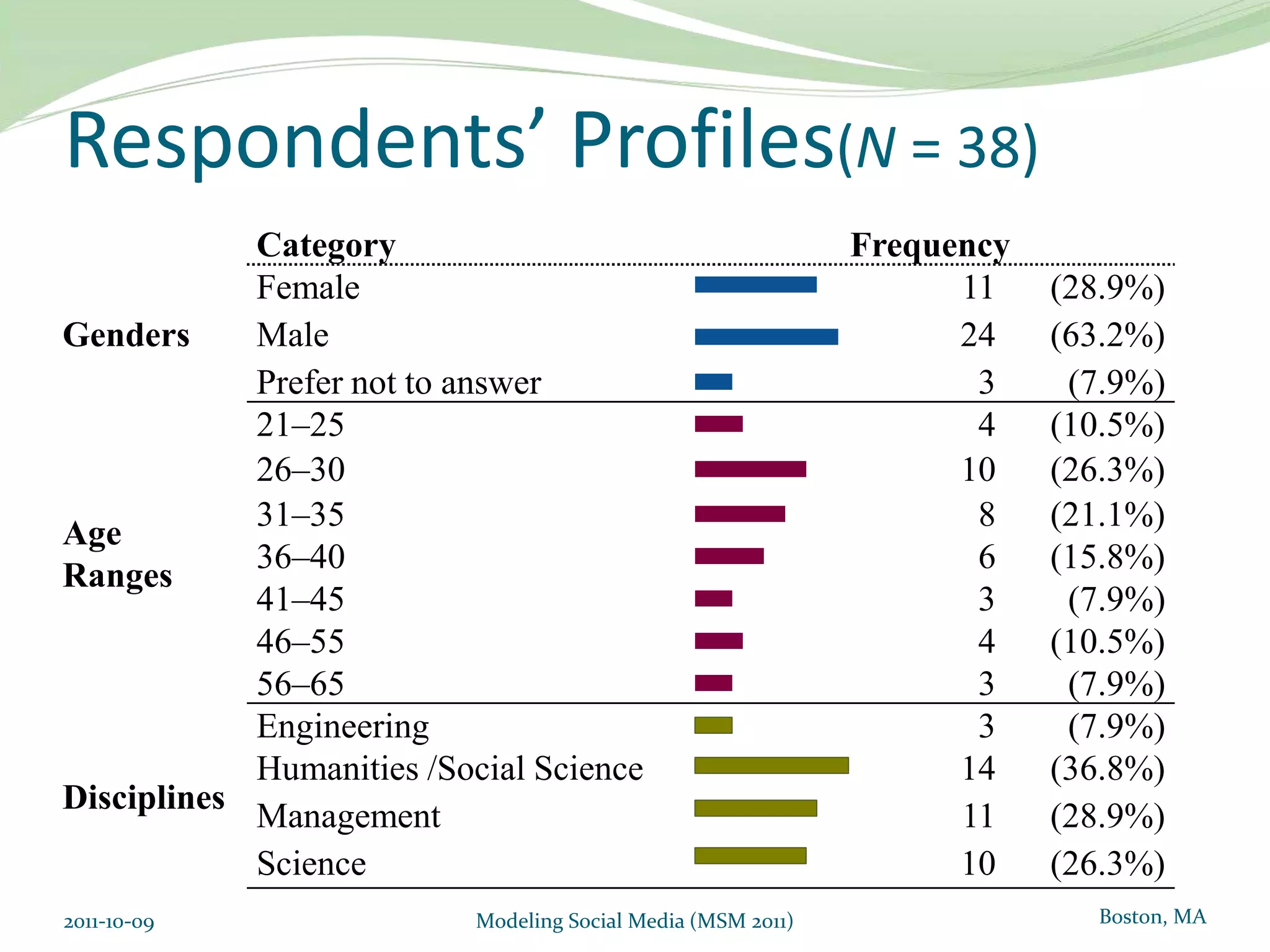
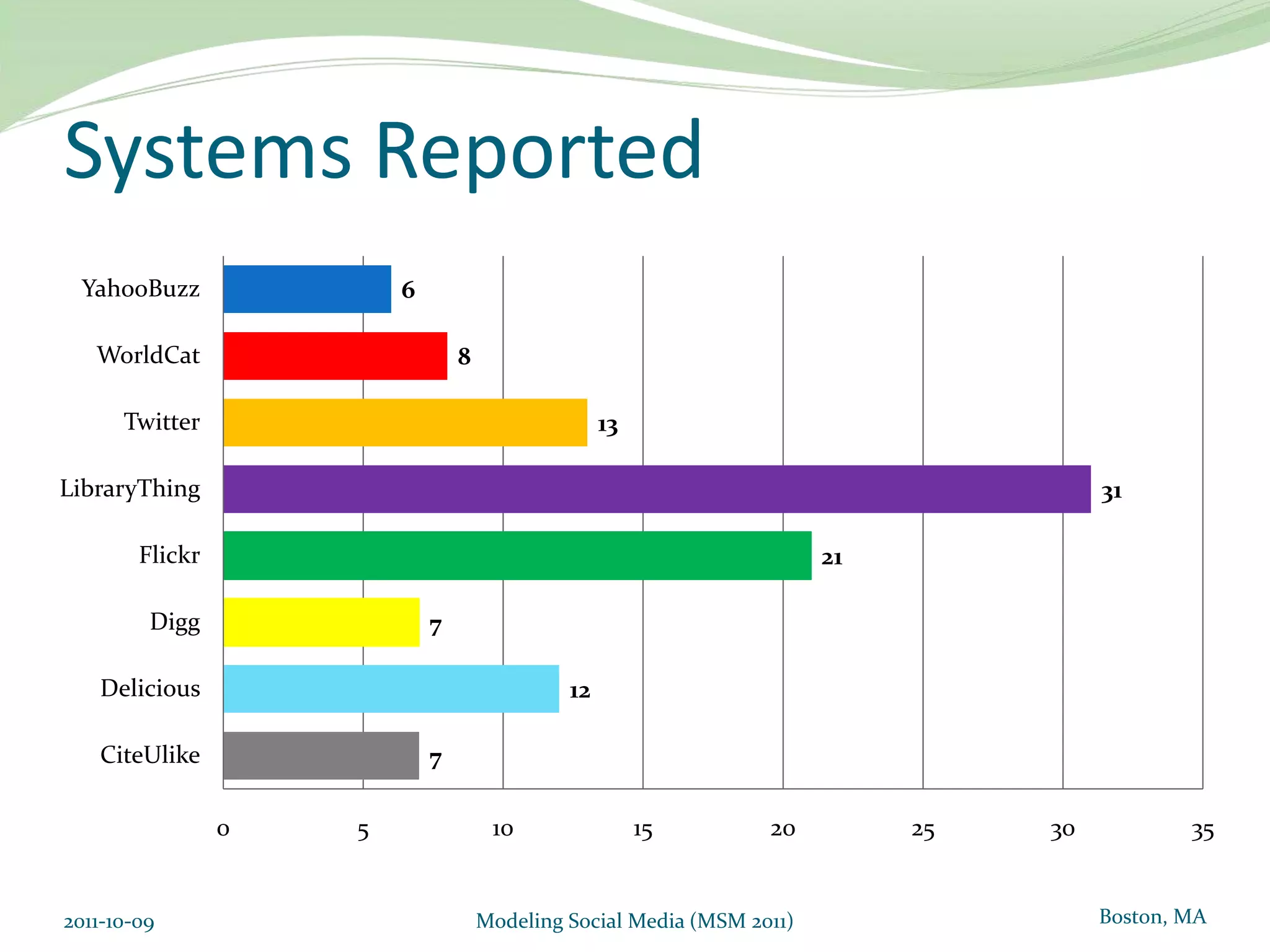
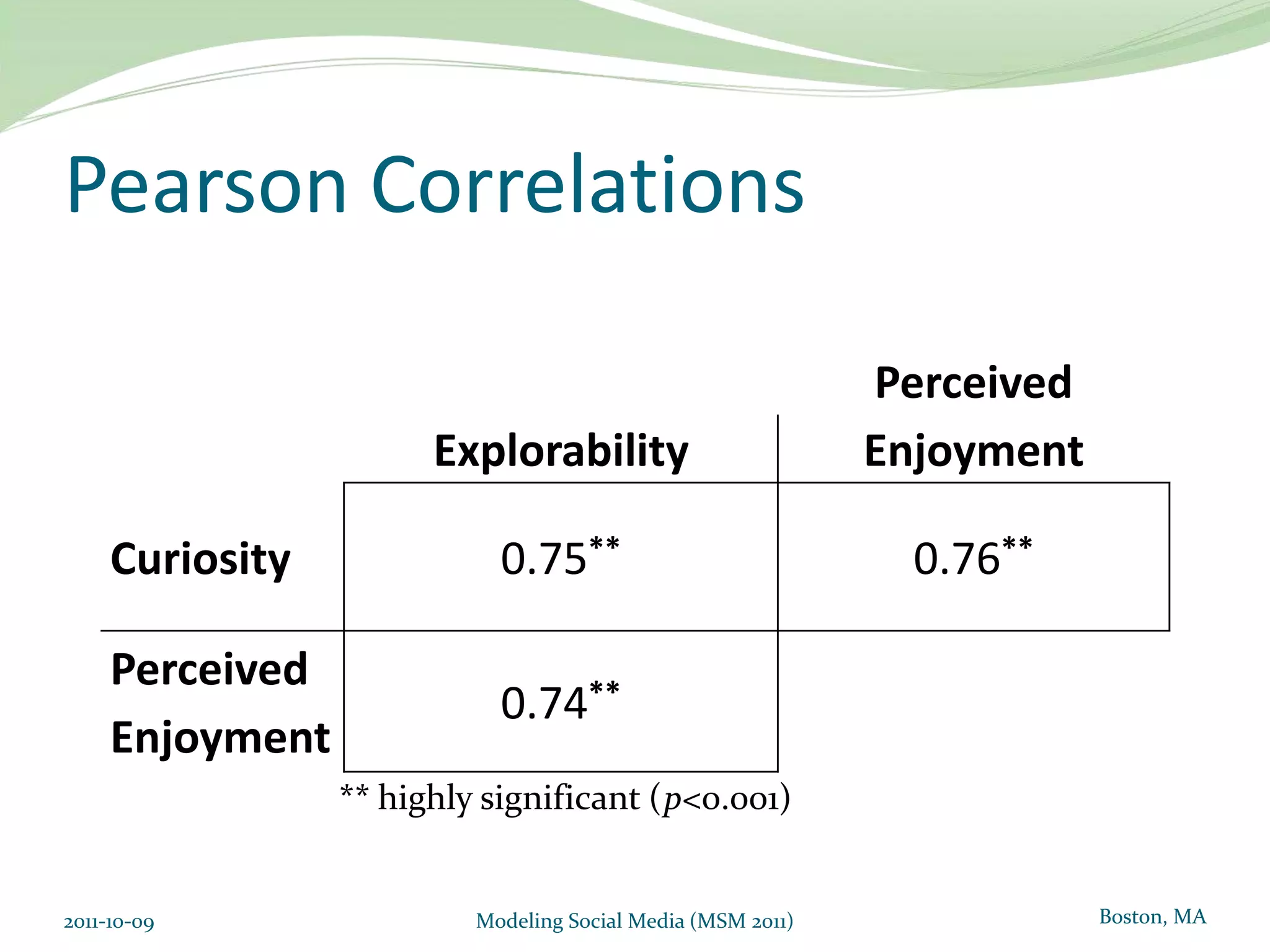
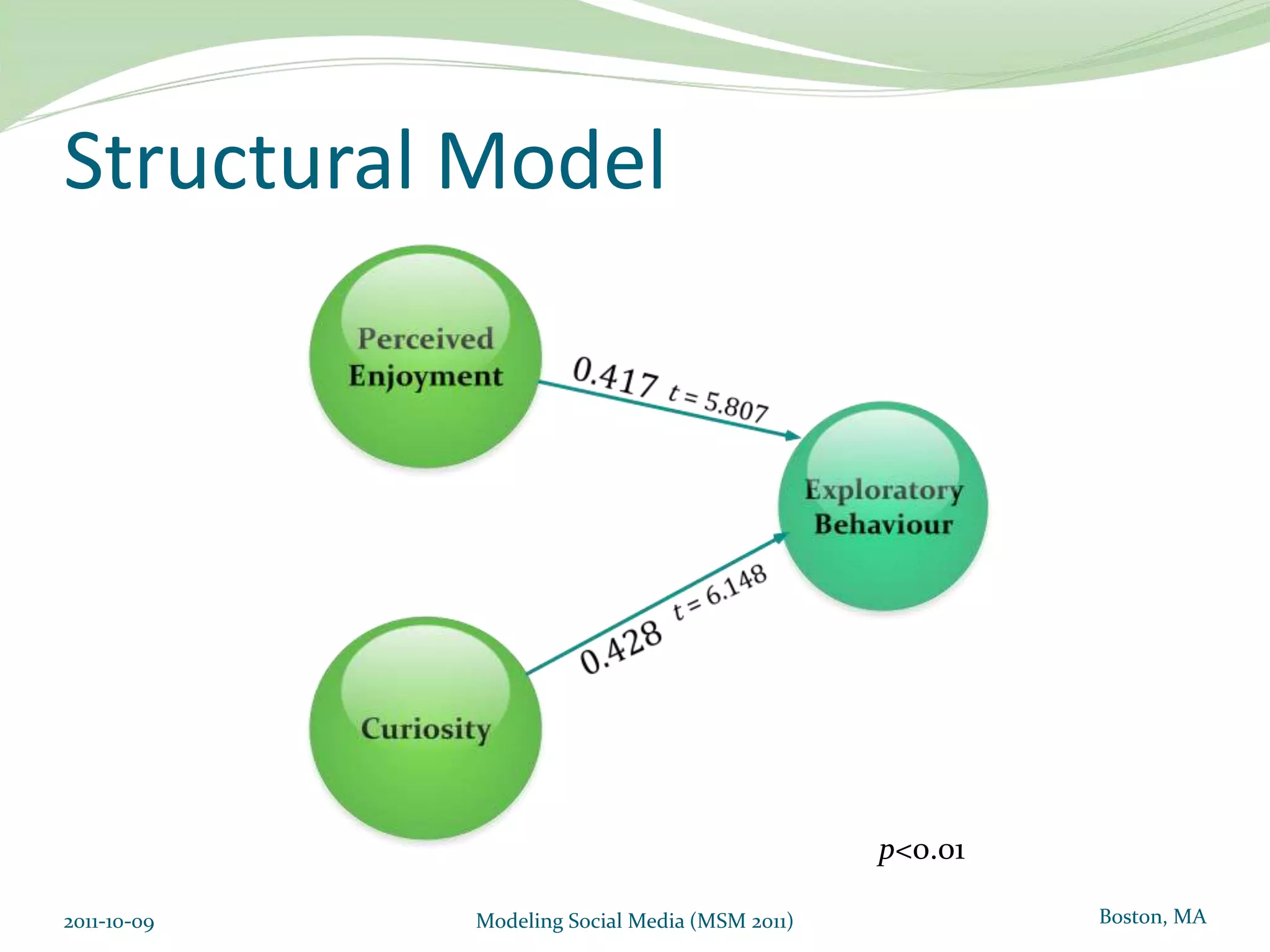
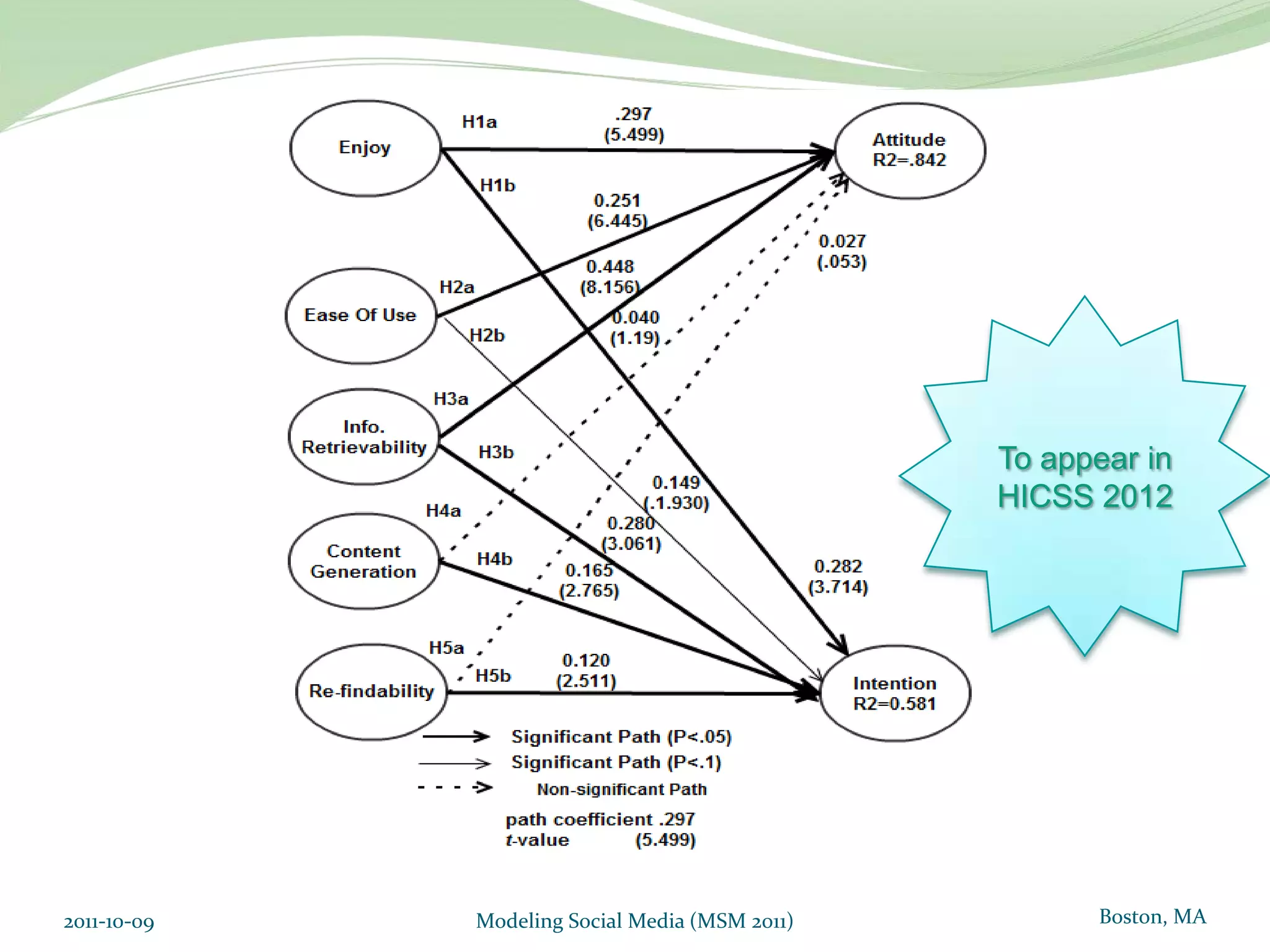
This document proposes a model of hedonic browsing to enhance exploratory search using social tagging tools. It suggests that perceived enjoyment and curiosity have a positive impact on exploratory behavior in social tagging systems. An exploratory study of 38 respondents was conducted using structural equation modeling to identify relationships between measured explorability and latent variables of enjoyment and curiosity. Results found a strong positive association between exploratory behavior and experiences of enjoyment and curiosity when using social tagging. However, the study had limitations as a small pilot test and future research could further test the composite hedonic factors.