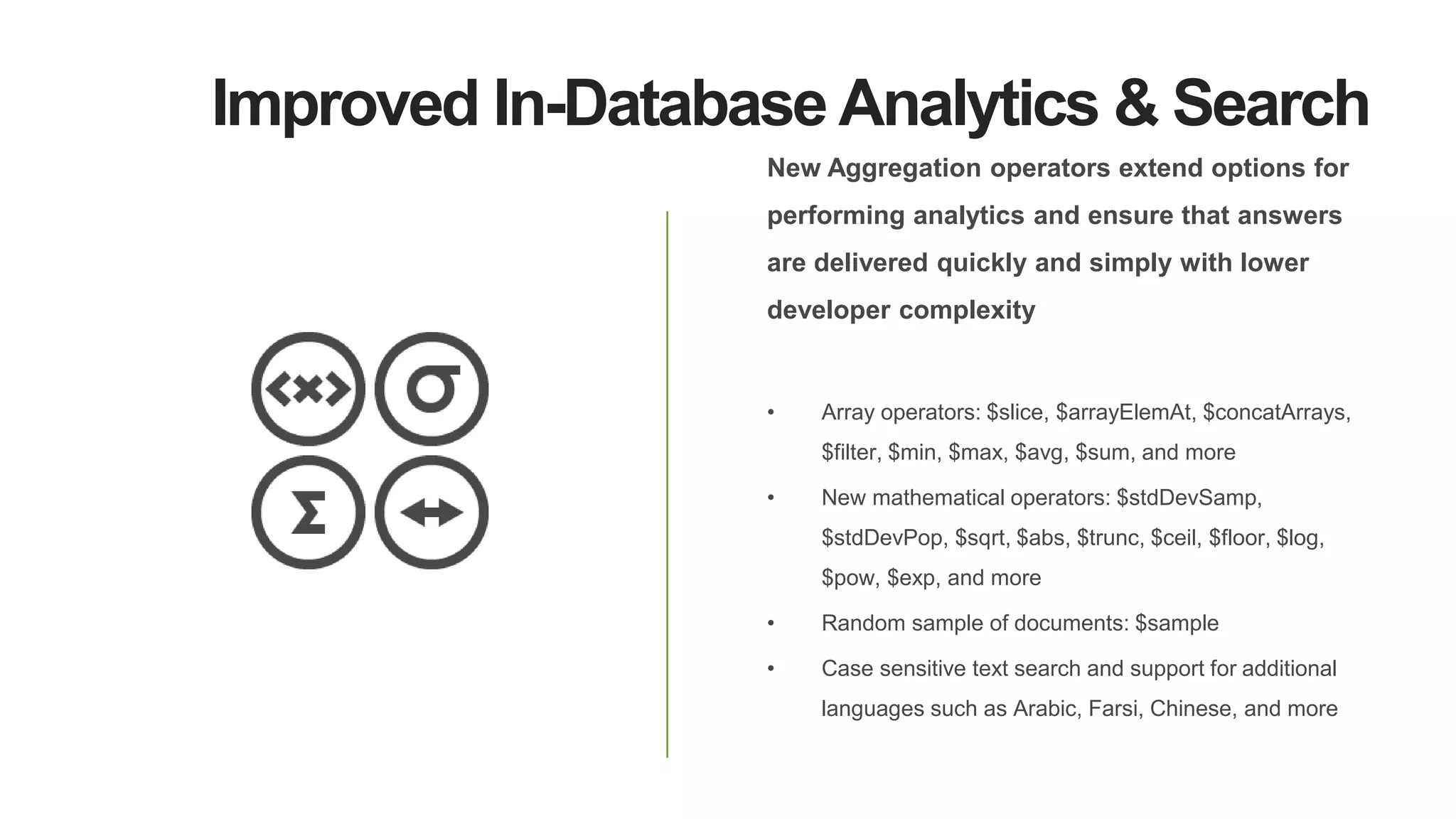
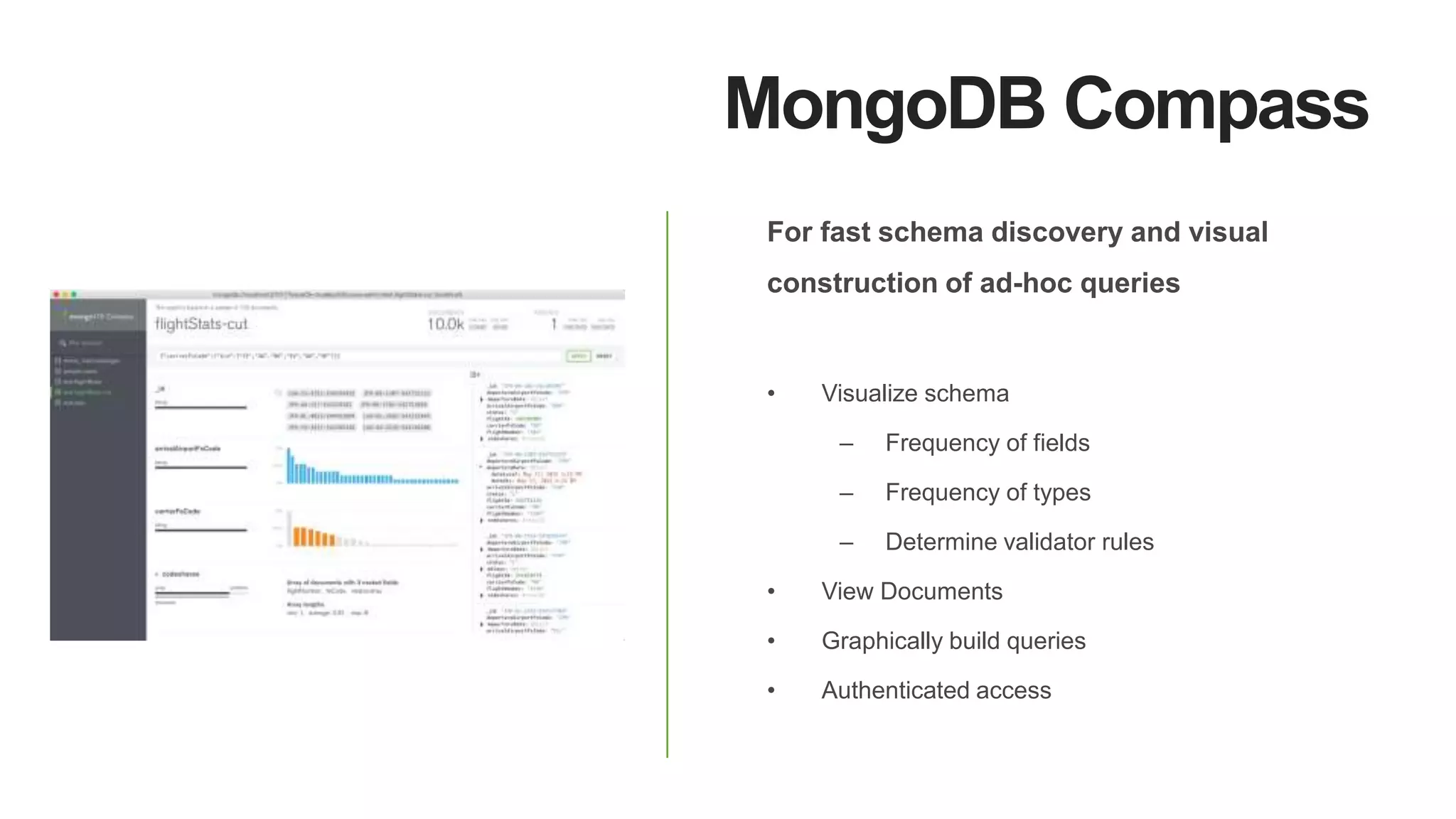
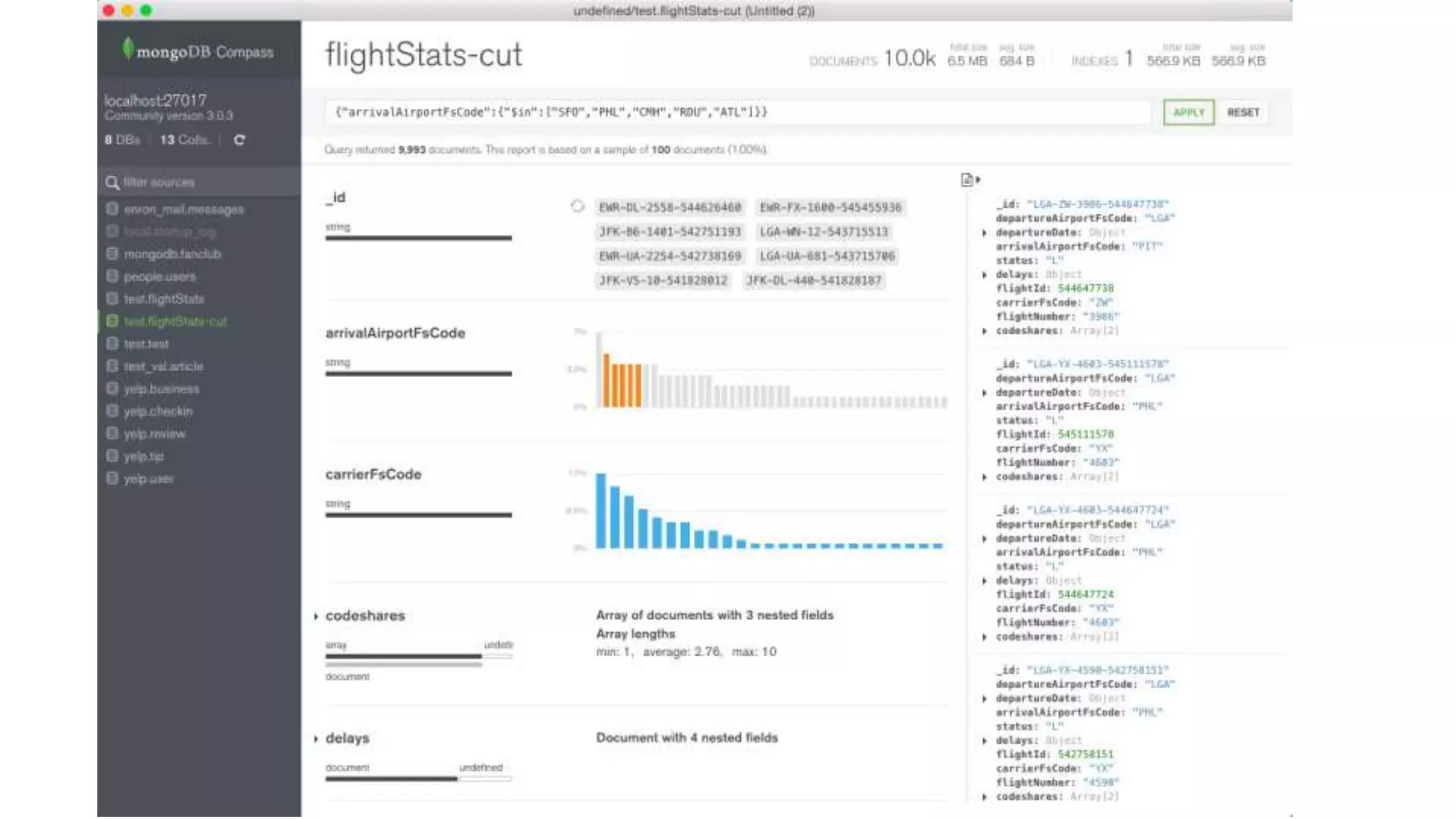
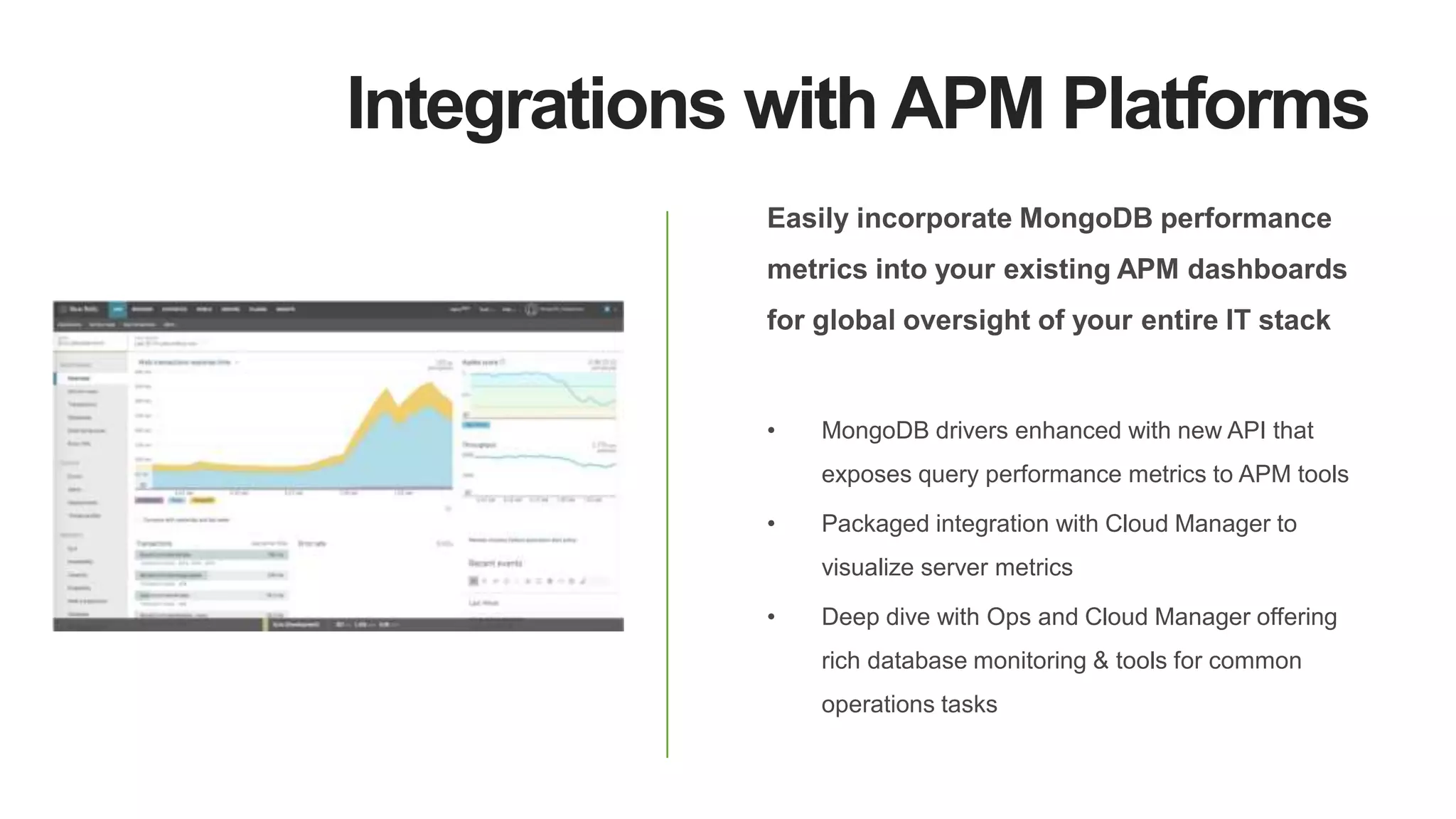
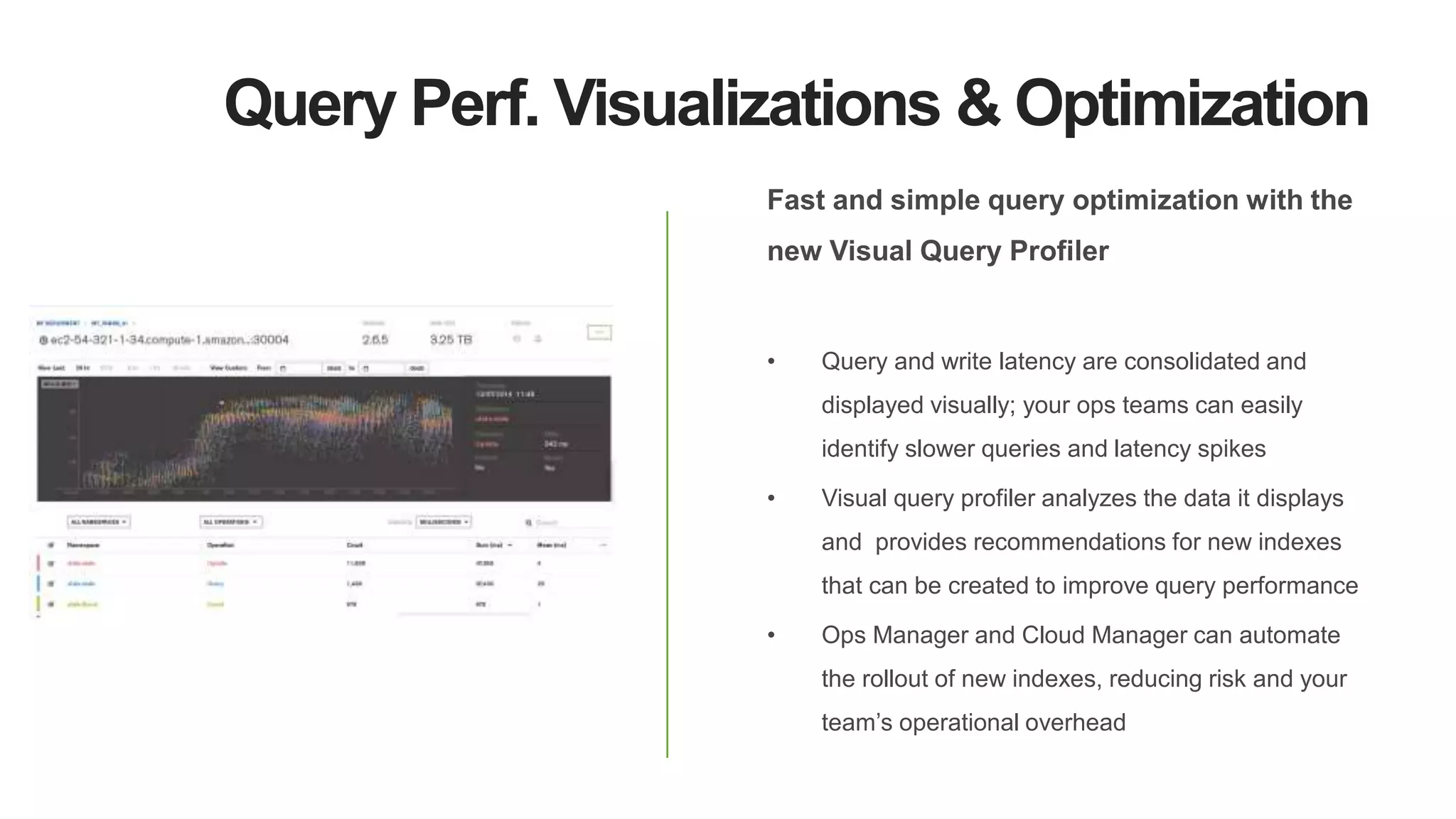
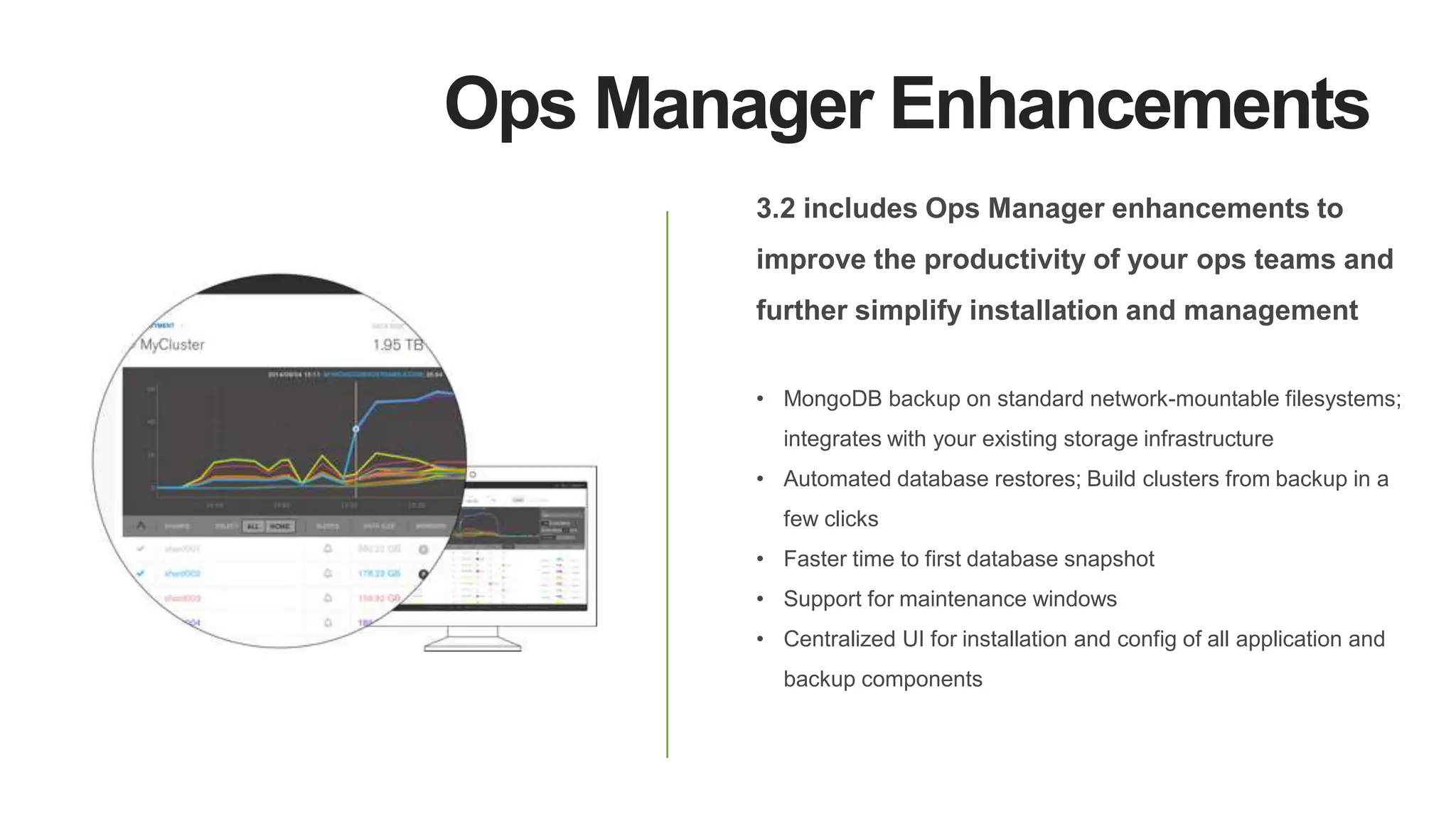
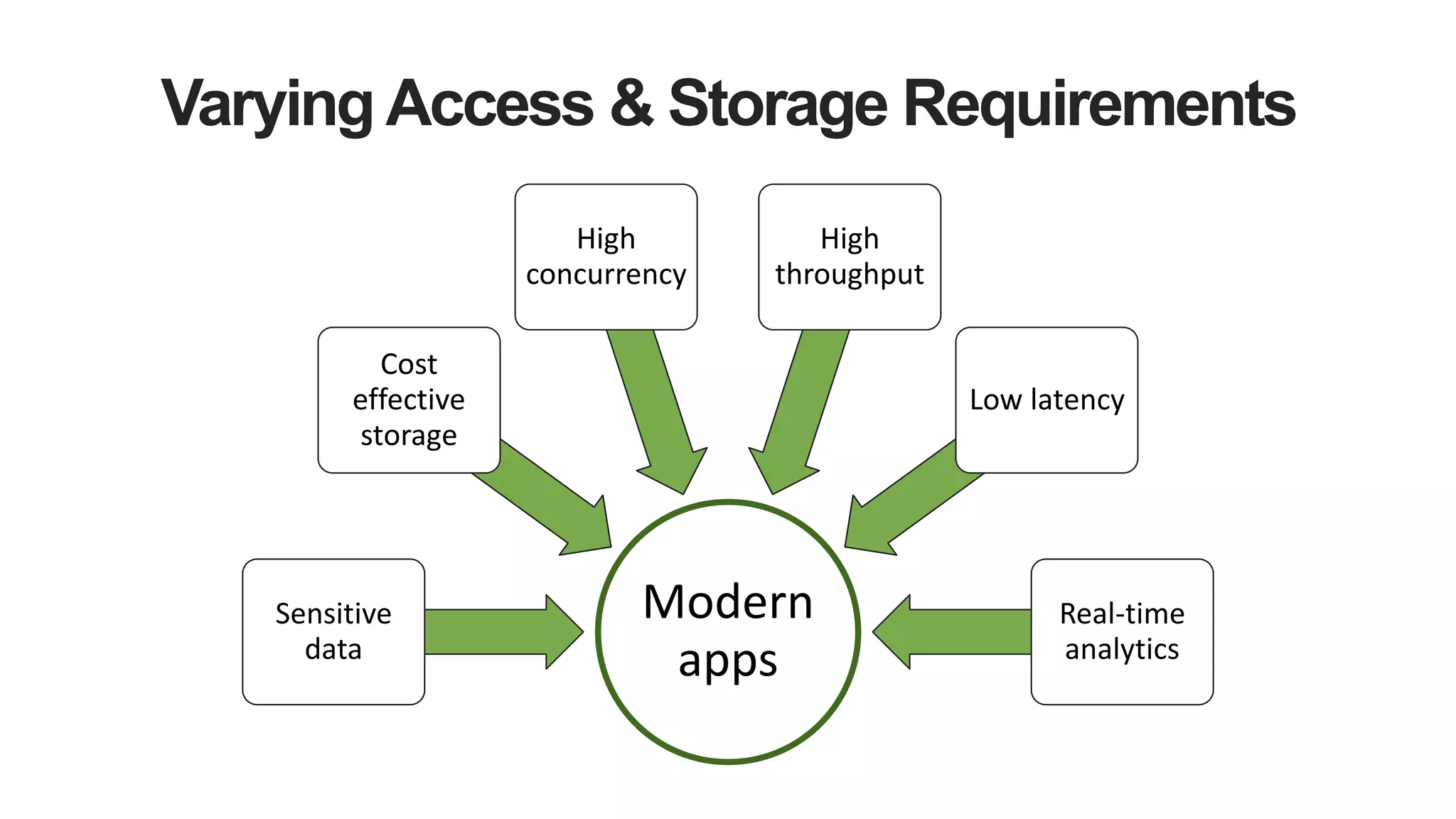
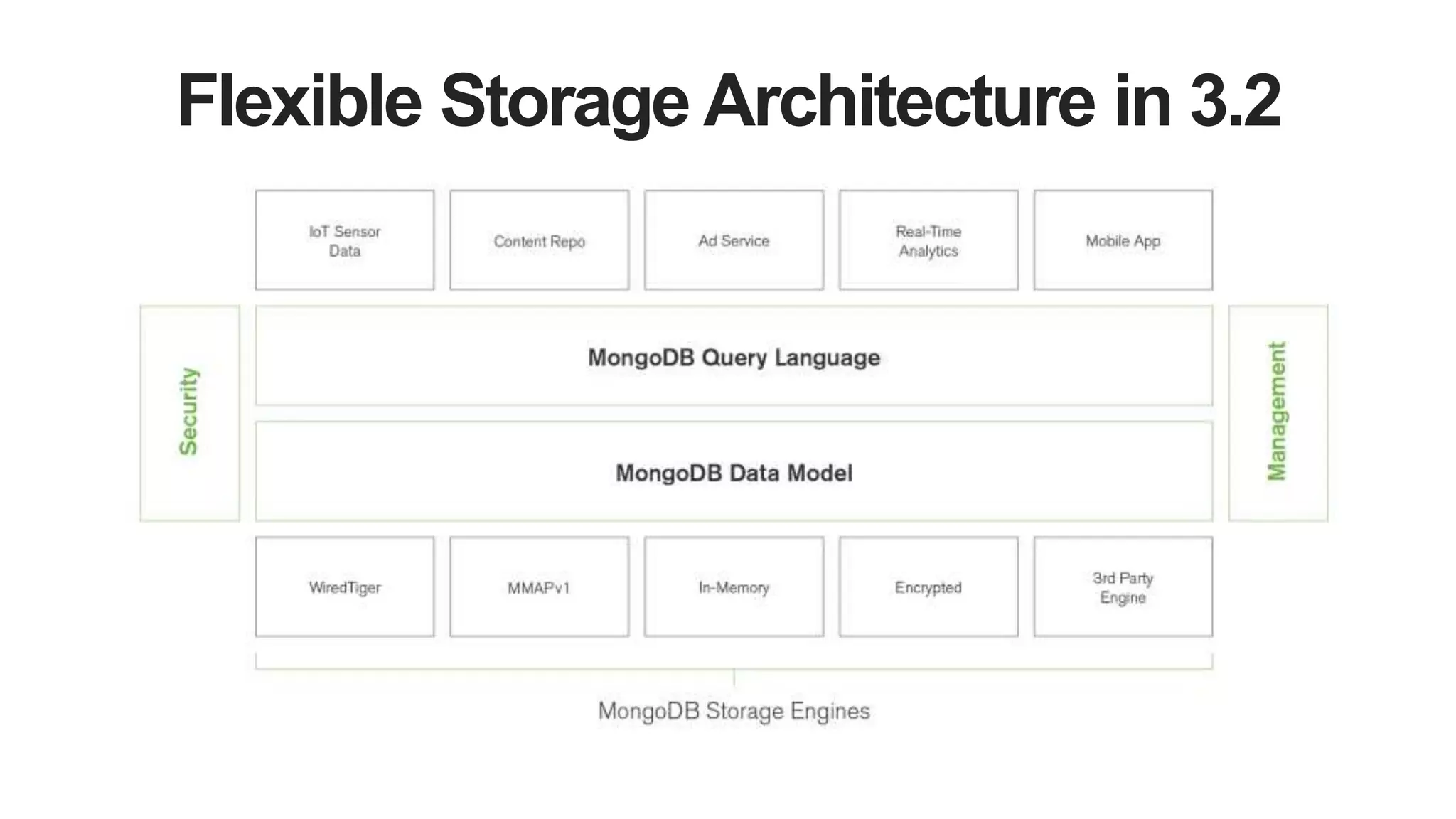
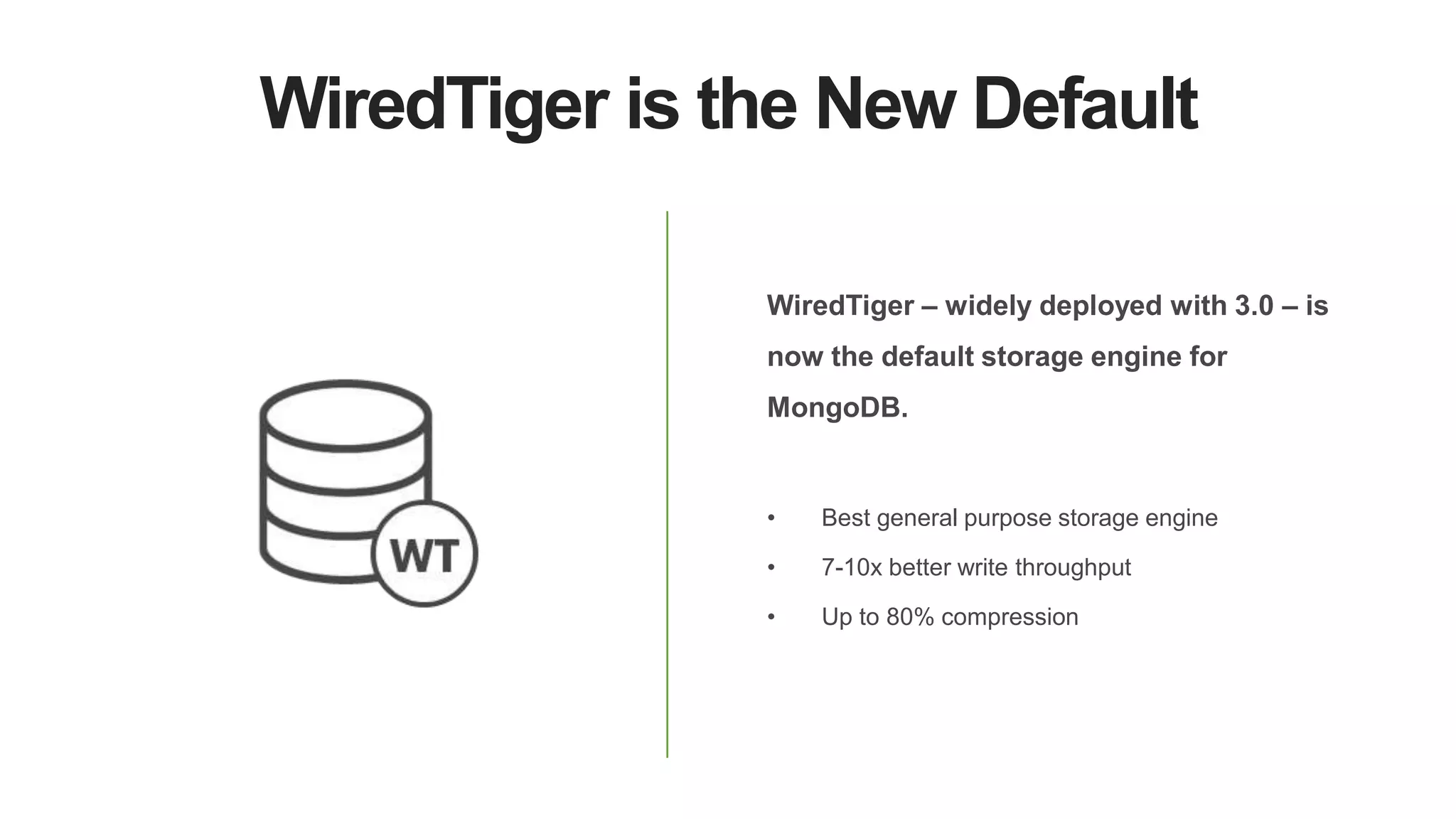
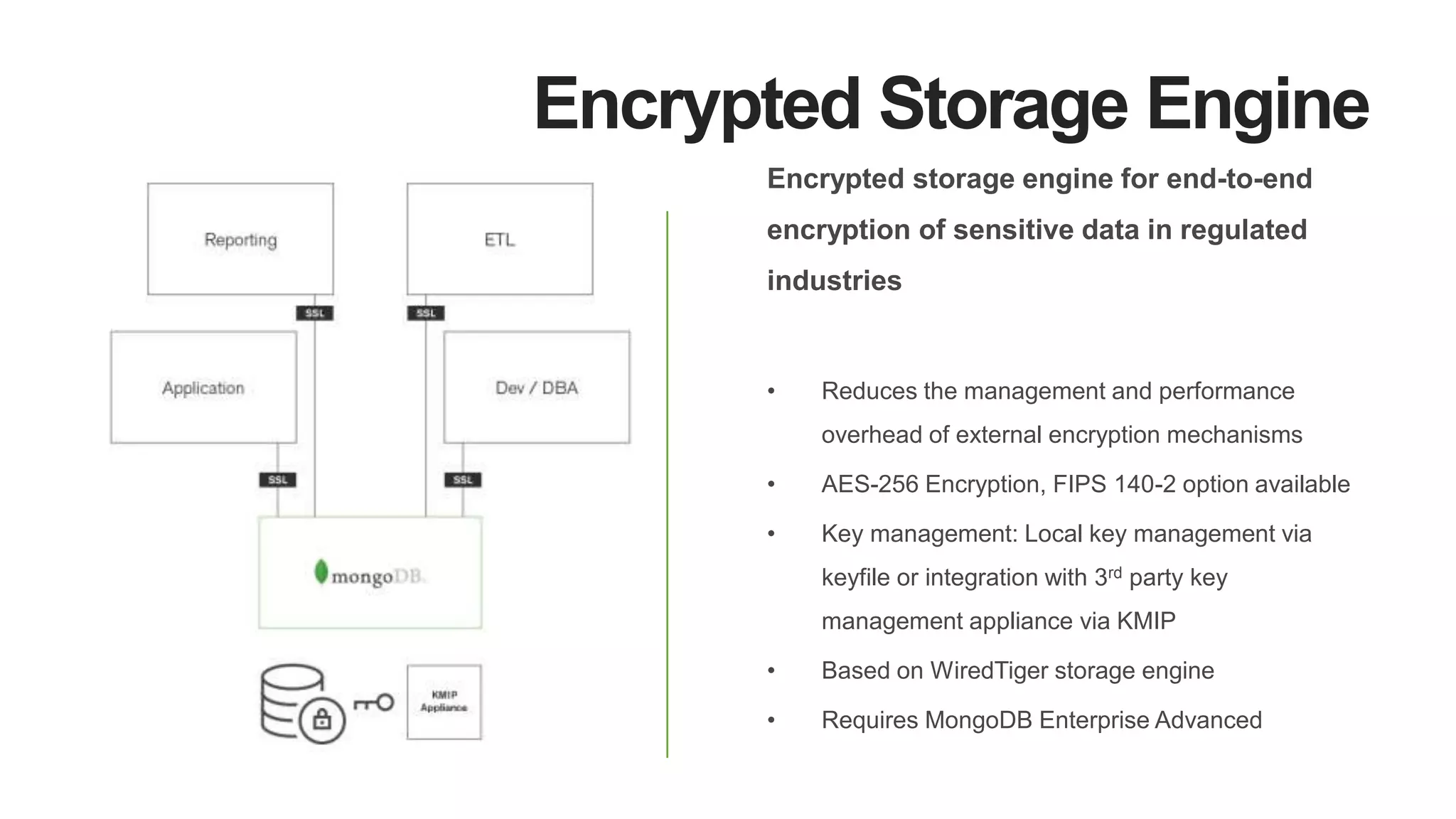
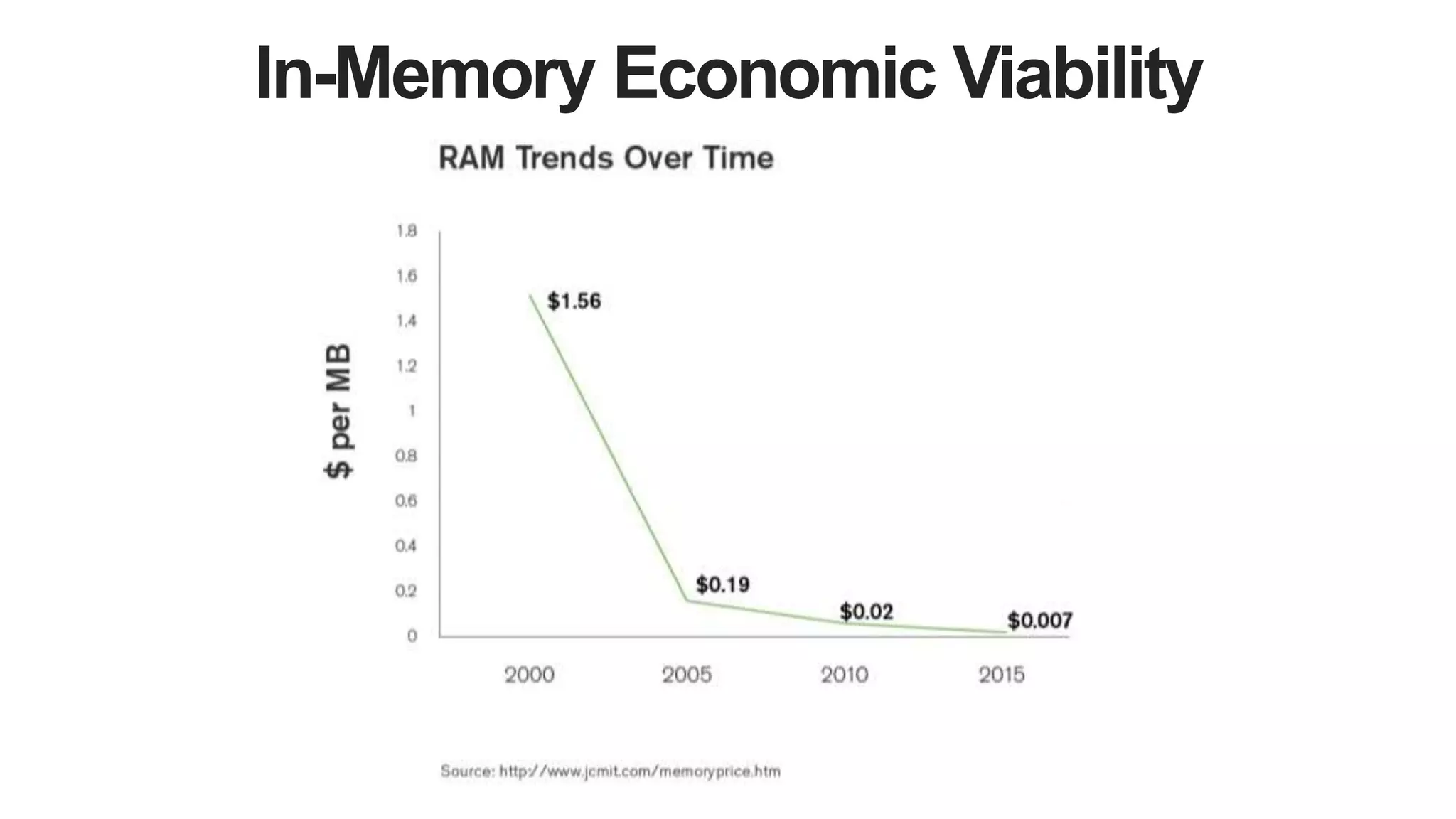
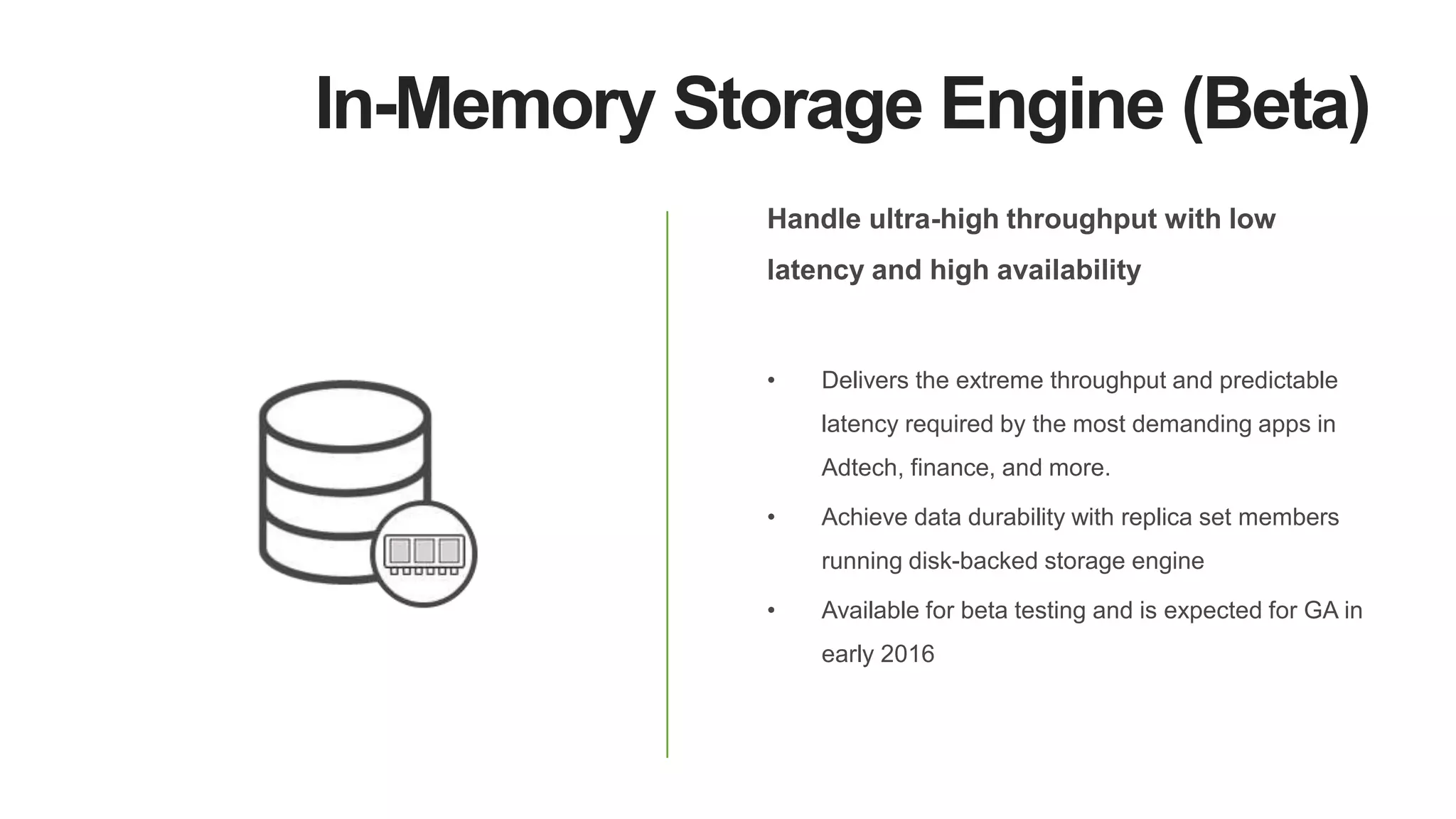
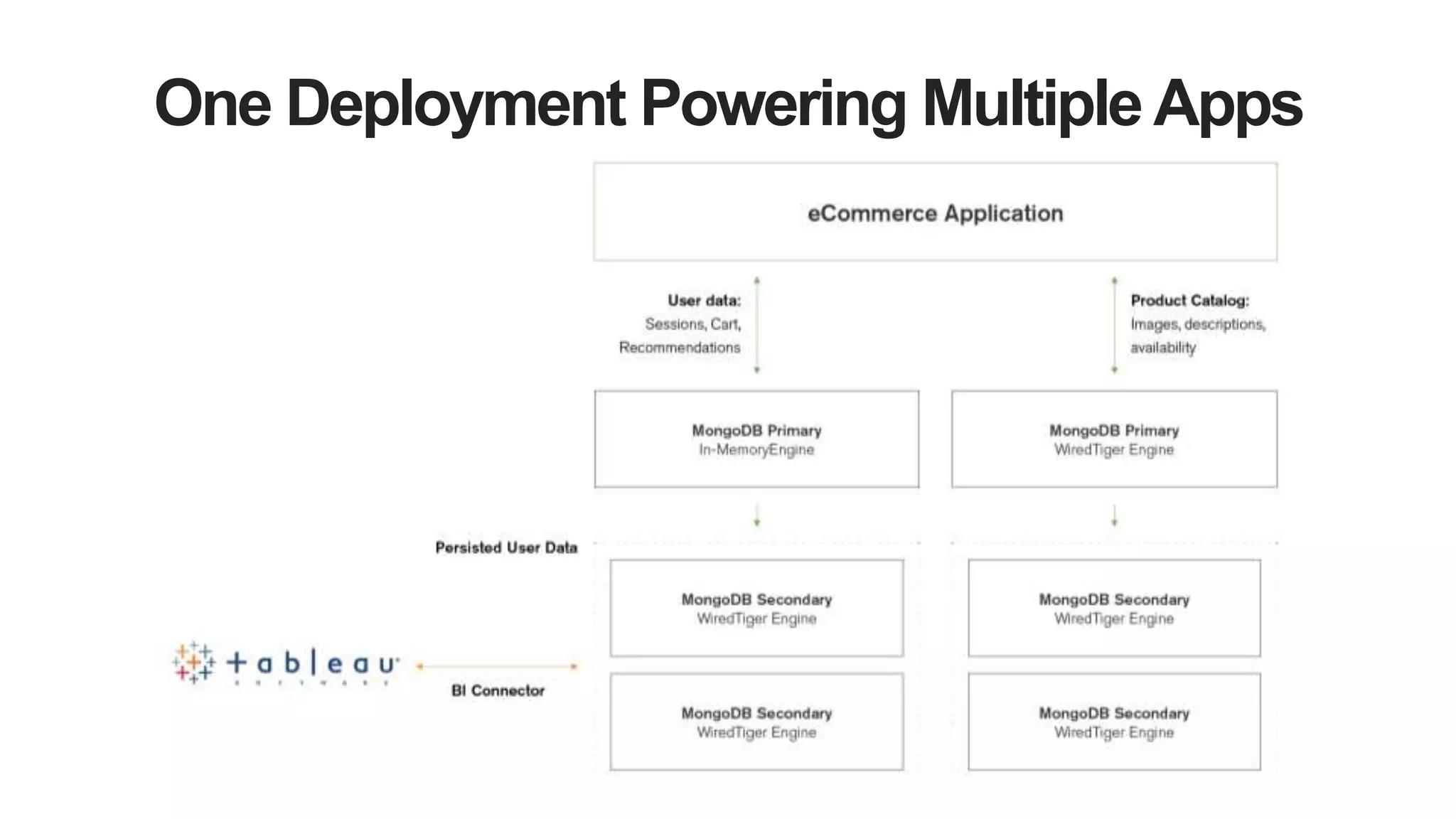
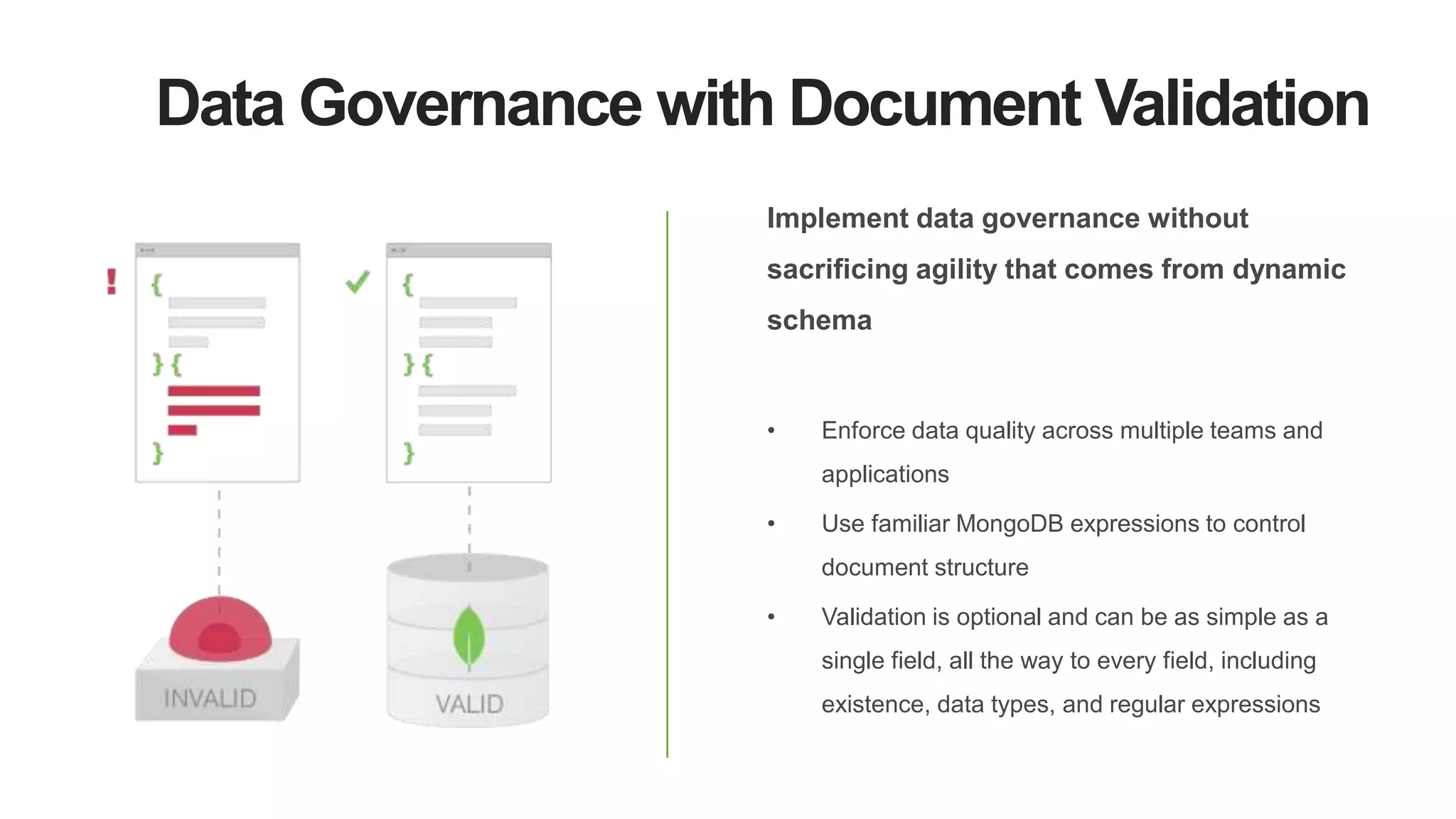
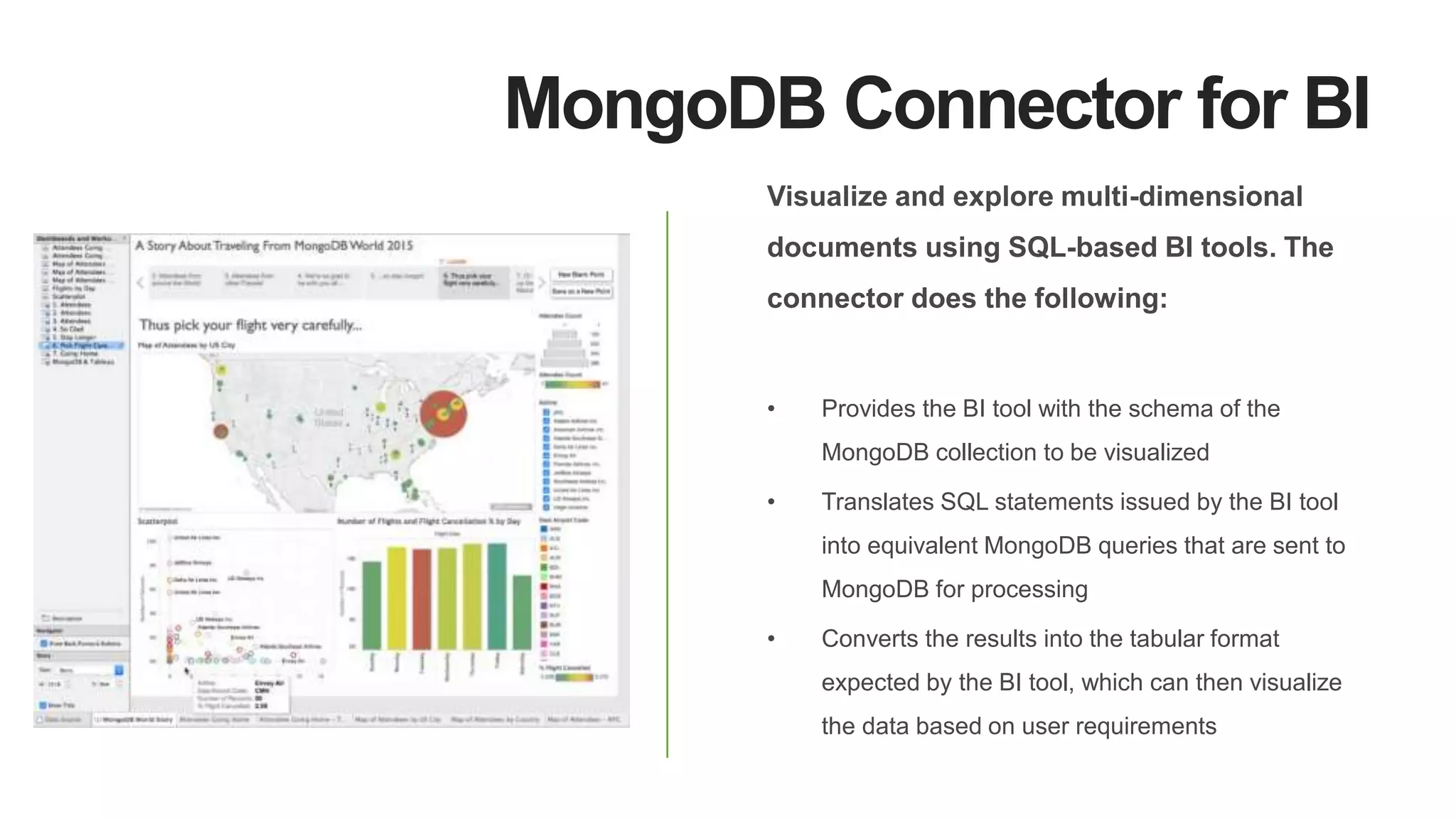
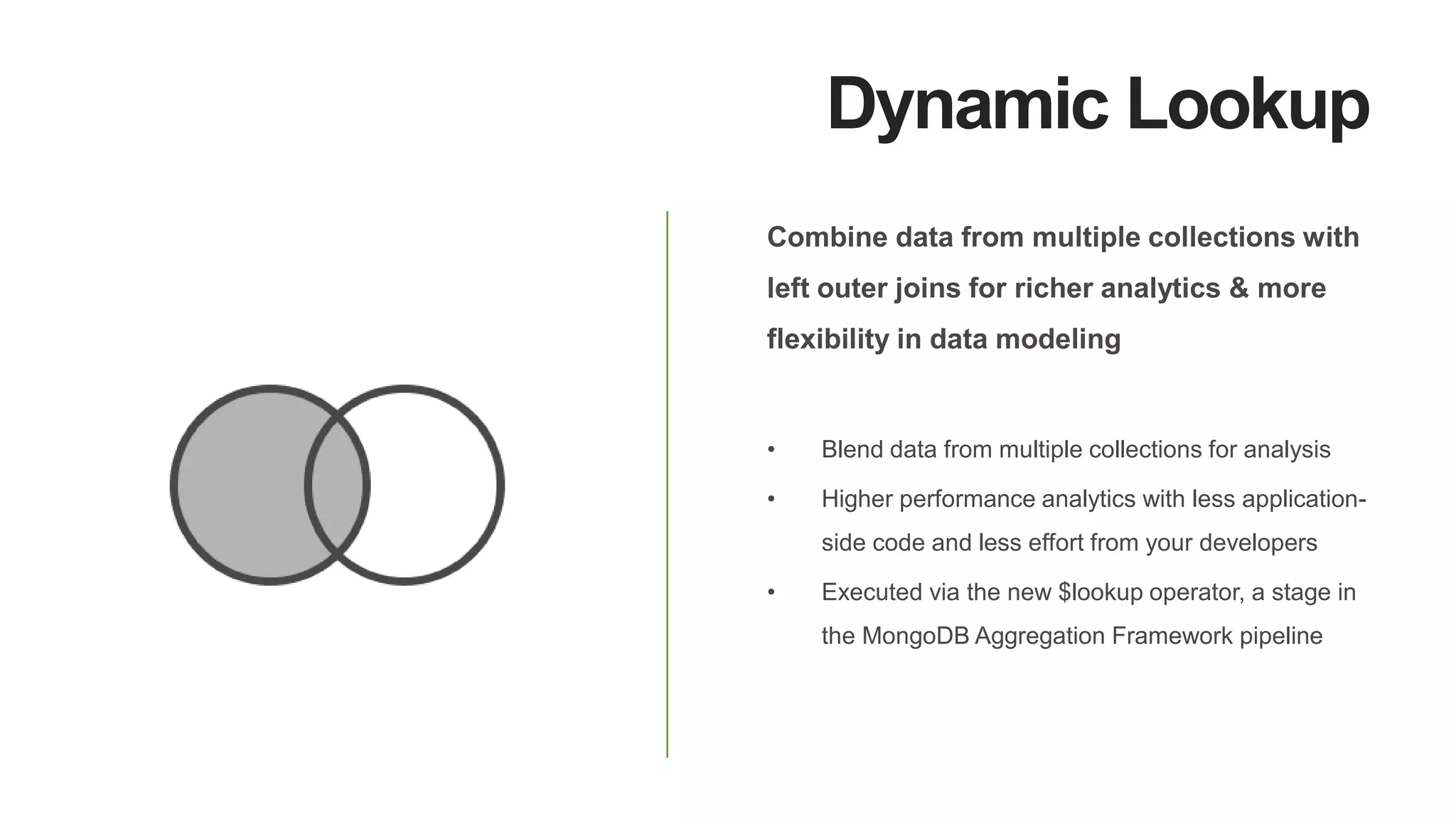
MongoDB 3.2 introduces significant features such as hash-based sharding, enhanced encryption, a new default storage engine (WiredTiger), and improved in-memory capabilities aimed at high concurrency and low latency. It facilitates better data governance with document validation, enhanced analytics via new aggregation operators, and tools for business analysts, making it integral for modern applications. Additional improvements include faster failover algorithms, simplified cluster management, and enhanced performance diagnostics for operations teams.















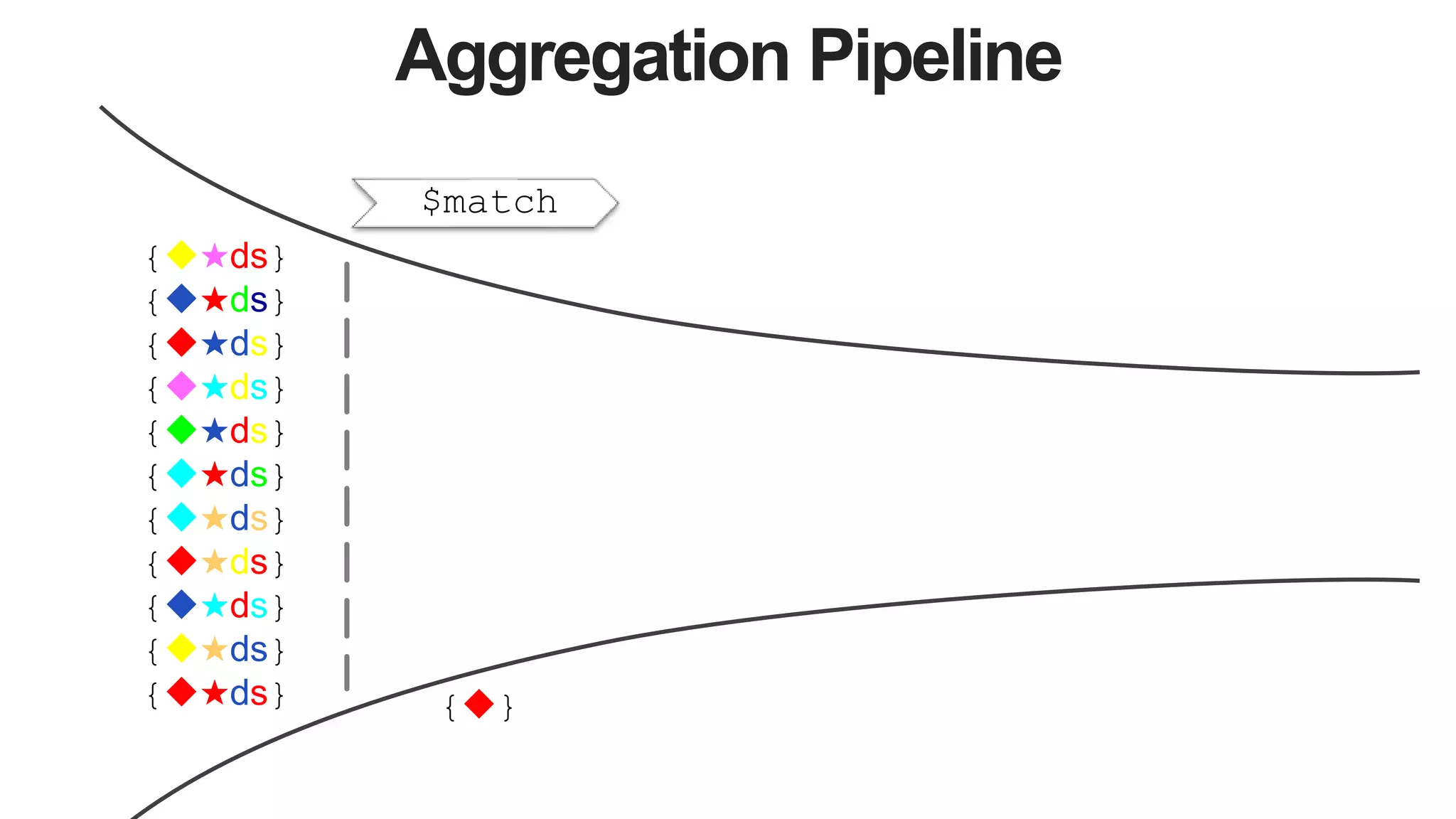
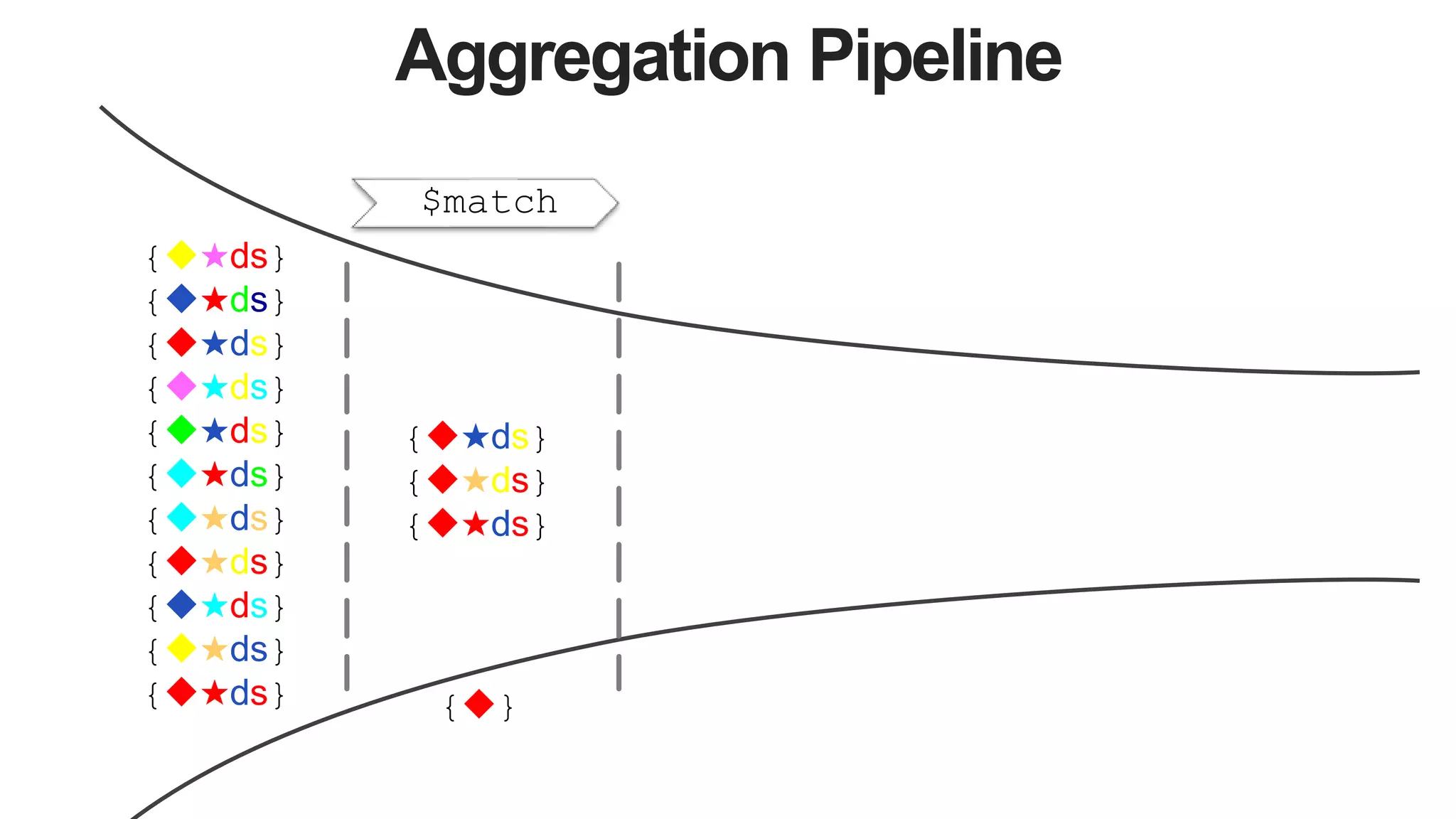
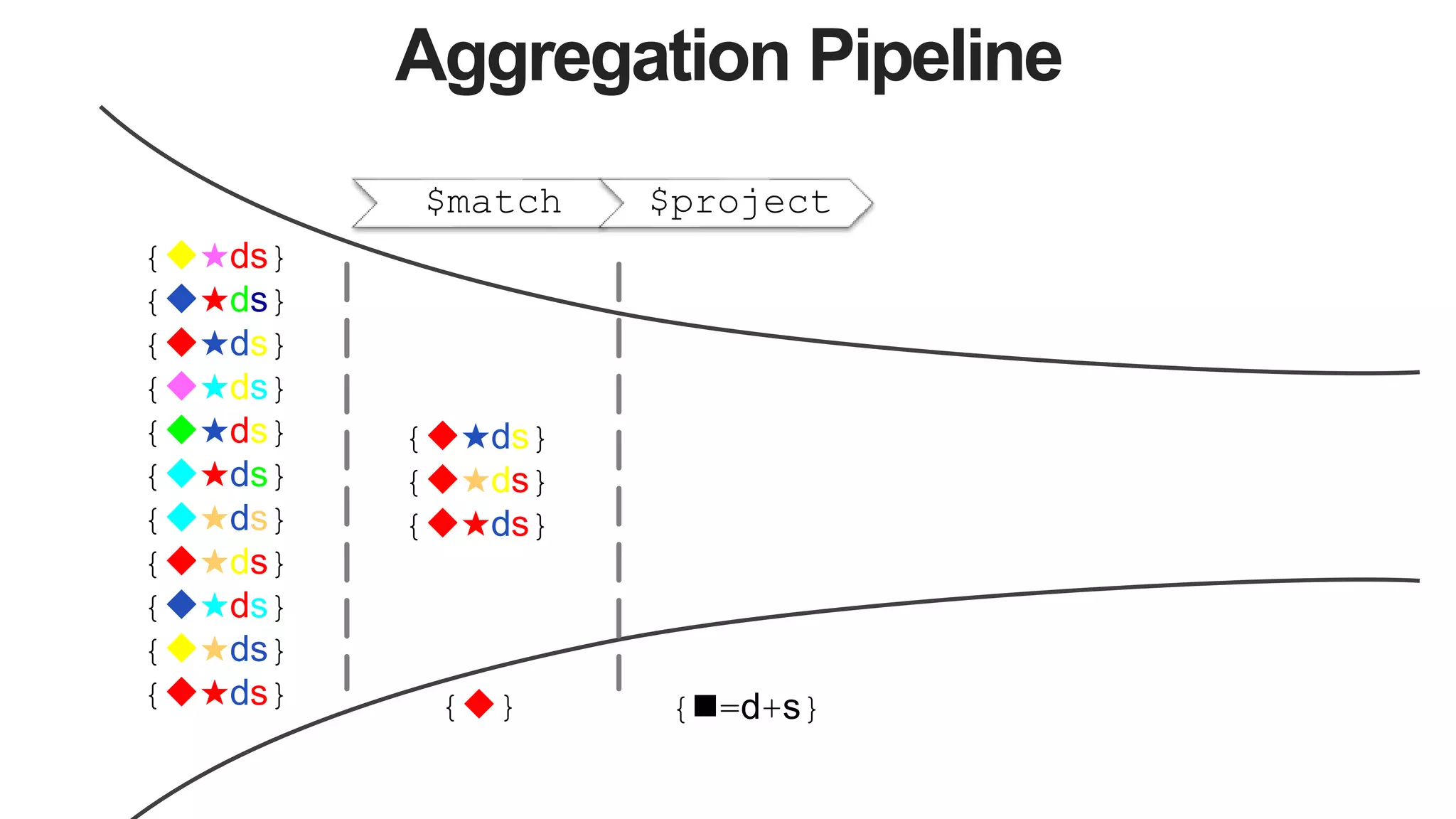
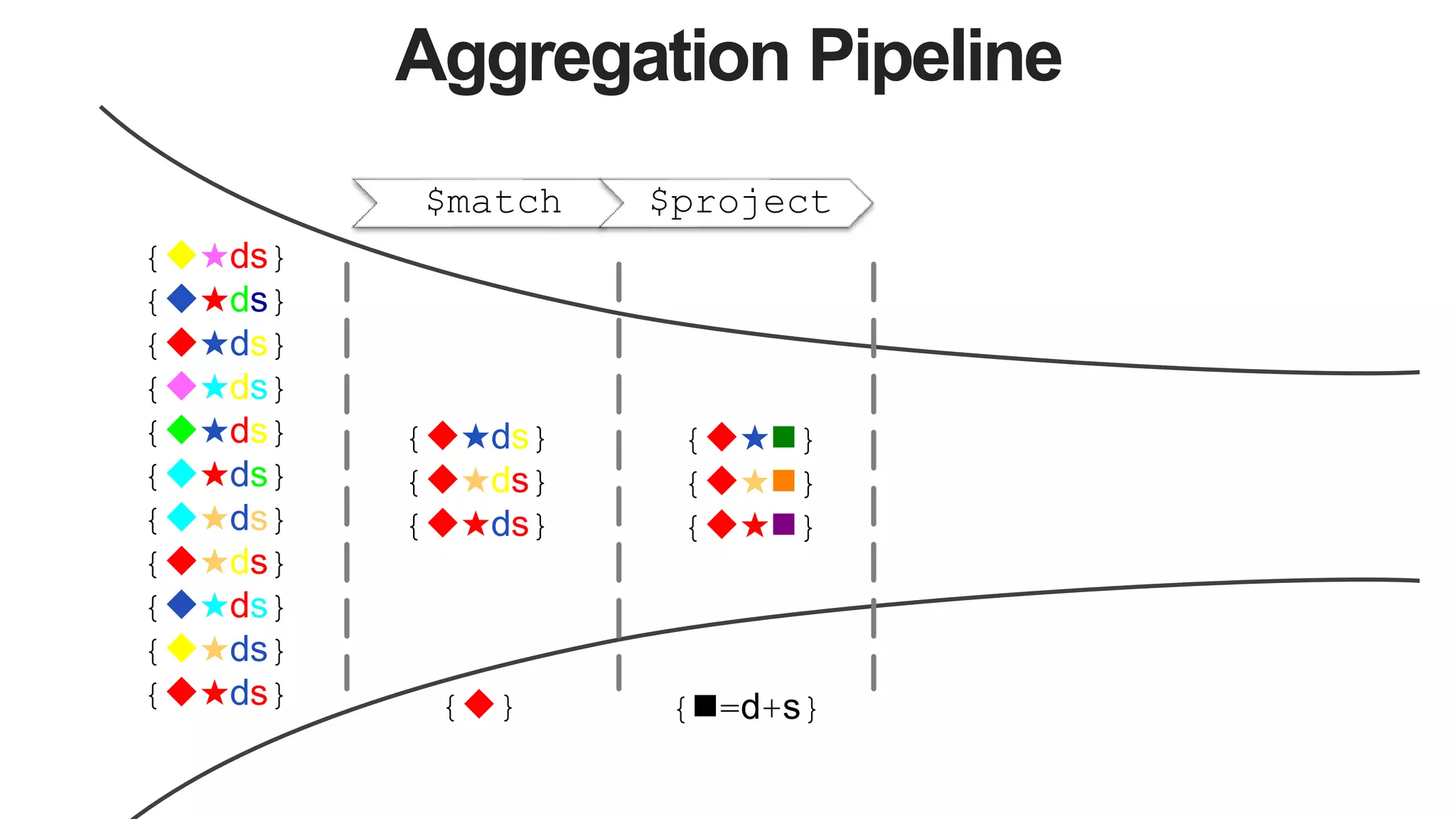
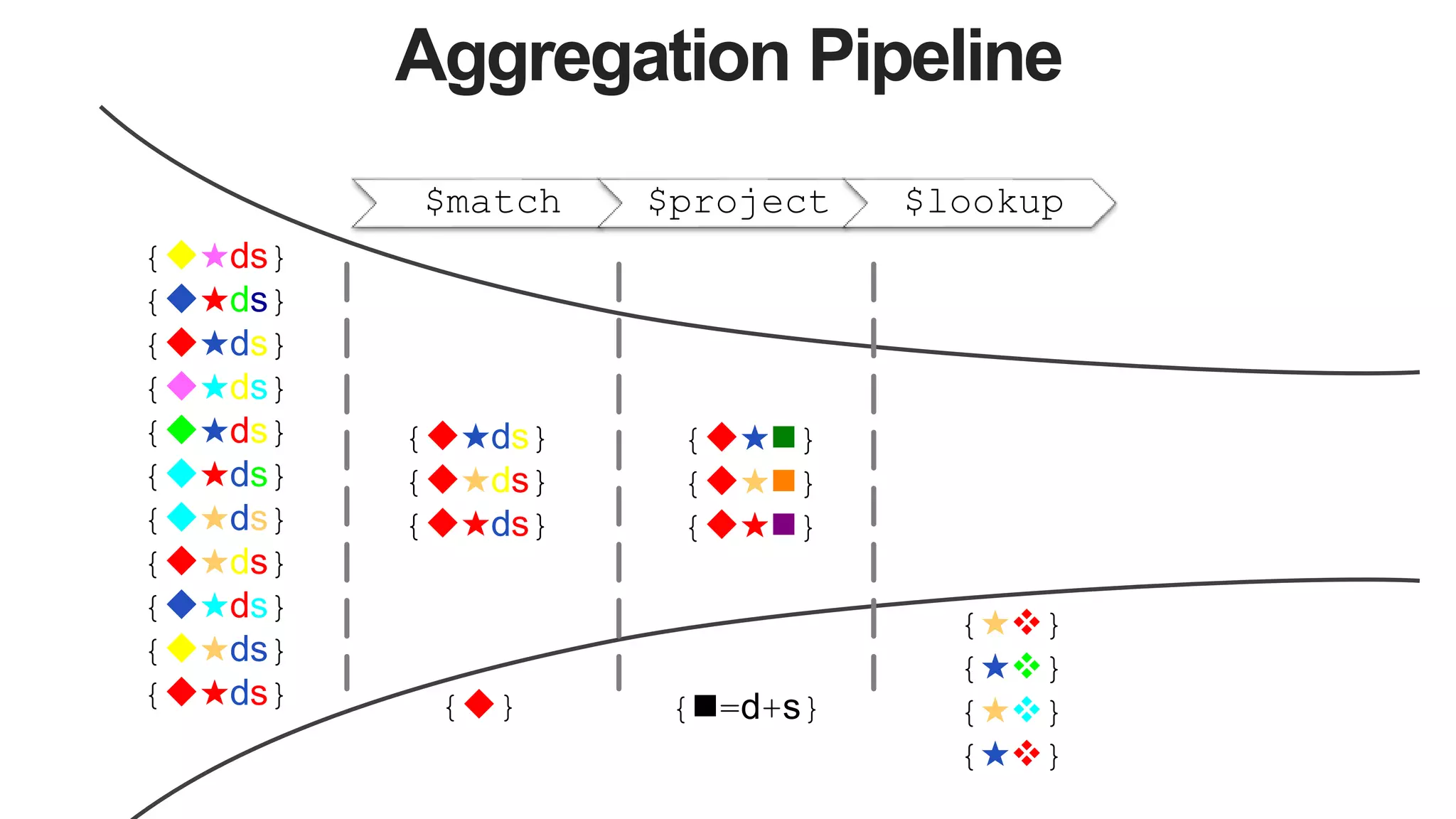
![Aggregation Pipeline
$match $project $lookup
{★ds}
{★ds}
{★ds}
{★ds}
{★ds}
{★ds}
{★ds}
{★ds}
{★ds}
{★ds}
{★ds} {}
{★ds}
{★ds}
{★ds}
{★}
{★}
{★}
{★}
{★}
{★}
{★}
{=d+s}
{★[]}
{★[]}
{★}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatsnewin3-151118172341-lva1-app6891/75/Webinar-What-s-New-in-MongoDB-3-2-33-2048.jpg)
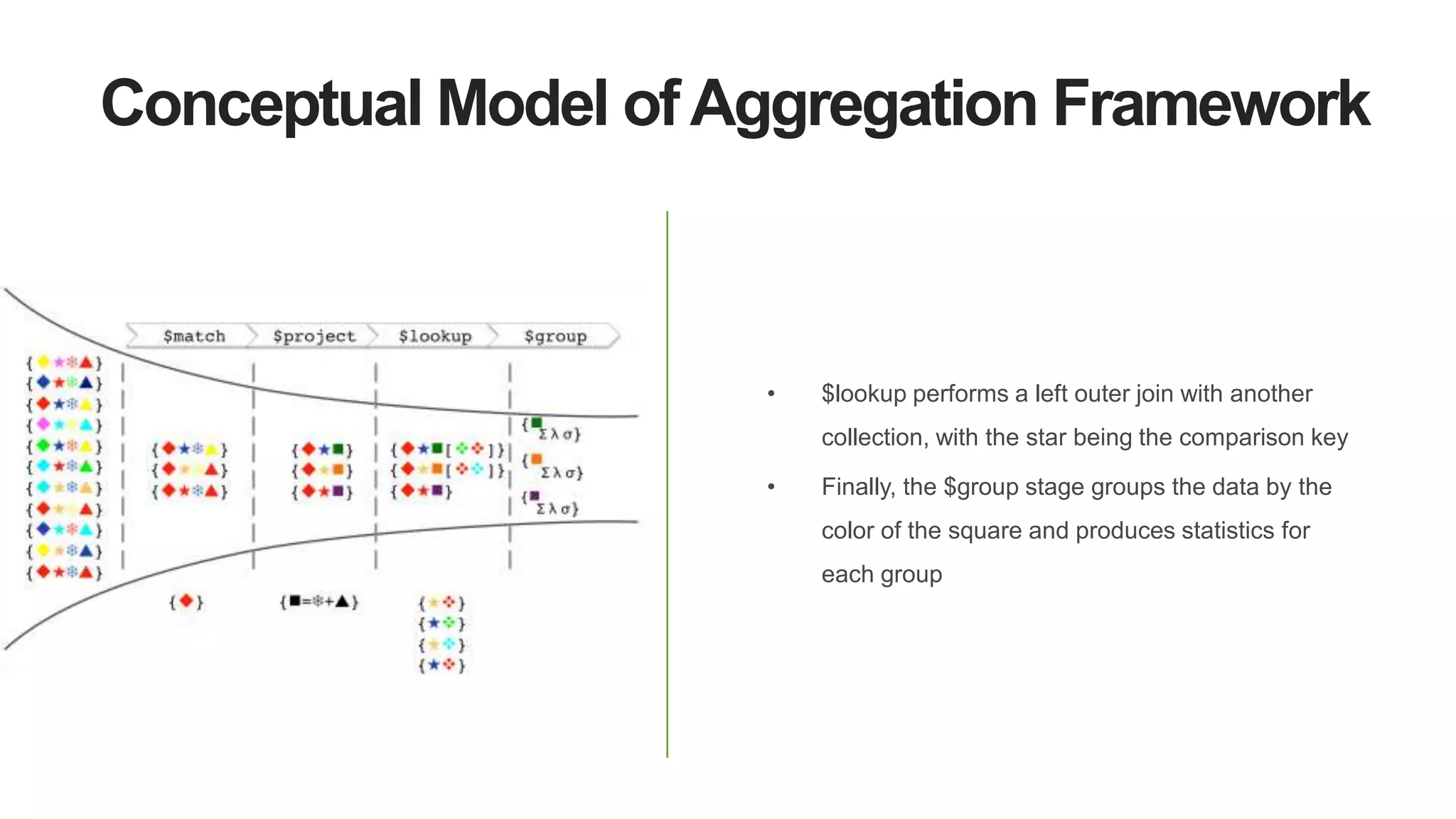
![Aggregation Pipeline
$match $project $lookup $group
{★ds}
{★ds}
{★ds}
{★ds}
{★ds}
{★ds}
{★ds}
{★ds}
{★ds}
{★ds}
{★ds} {}
{★ds}
{★ds}
{★ds}
{★}
{★}
{★}
{★}
{★}
{★}
{★}
{=d+s}
{
Σ λ σ}
{
Σ λ σ}
{
Σ λ σ}
{★[]}
{★[]}
{★}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/whatsnewin3-151118172341-lva1-app6891/75/Webinar-What-s-New-in-MongoDB-3-2-34-2048.jpg)