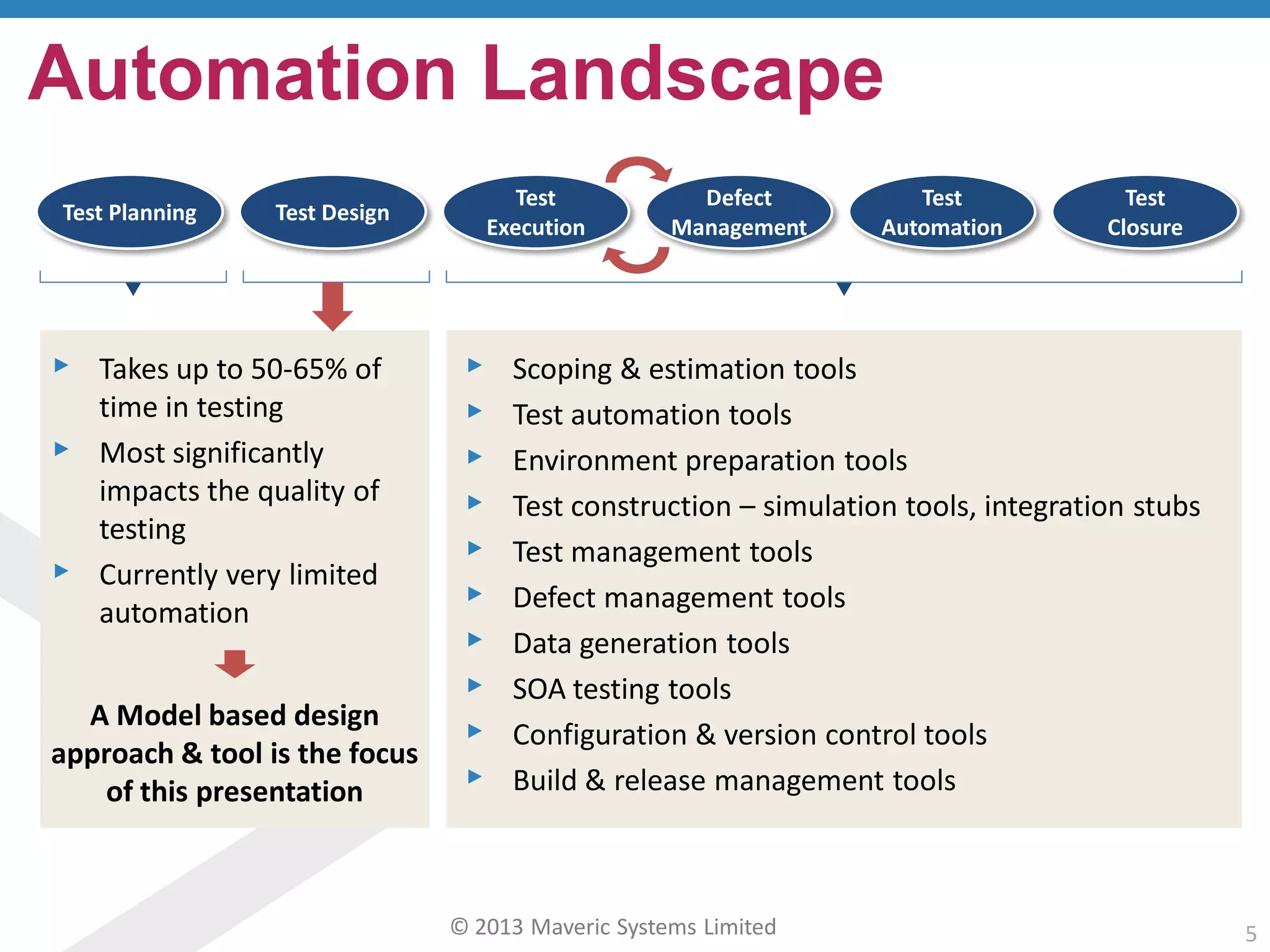
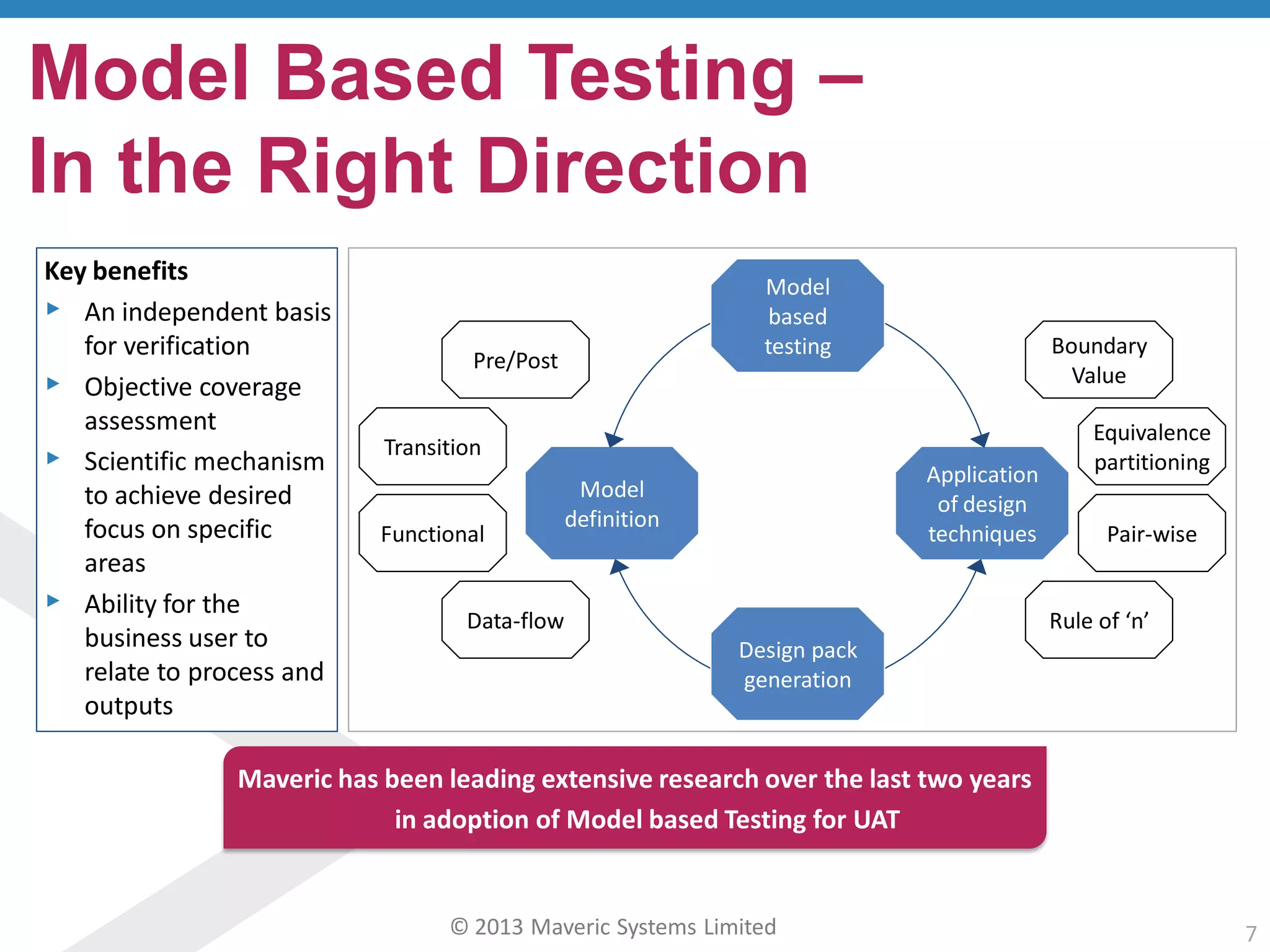
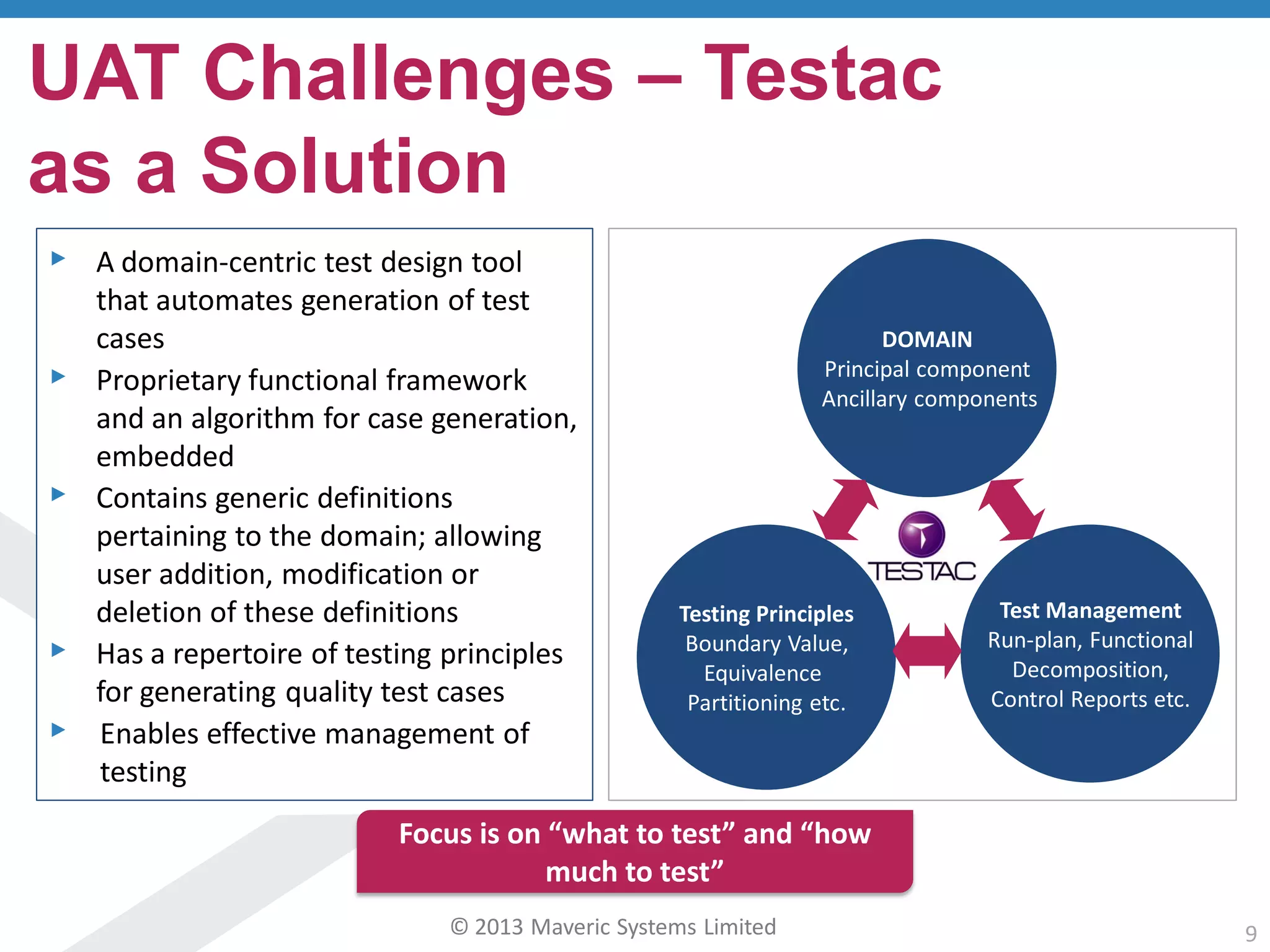
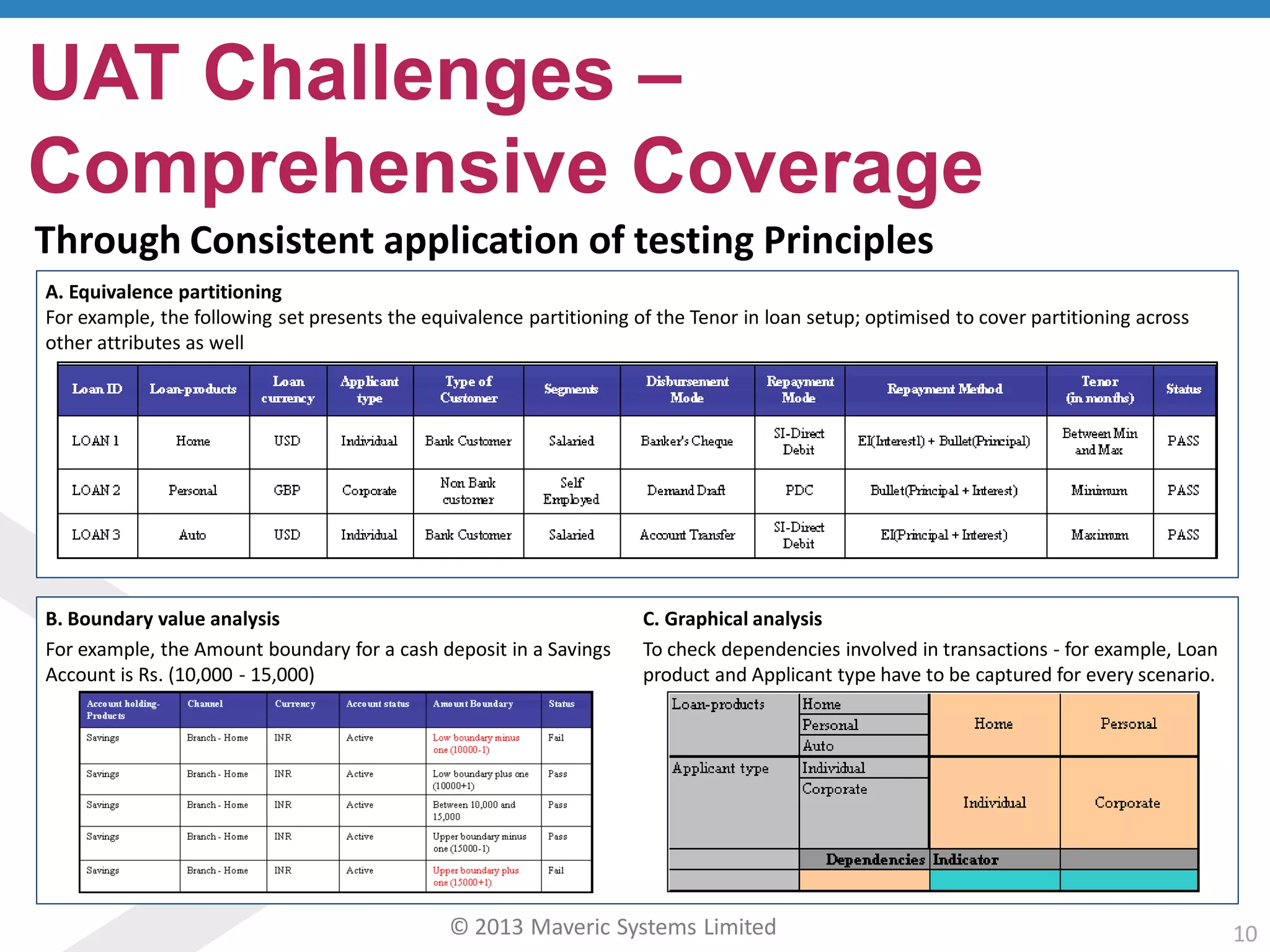
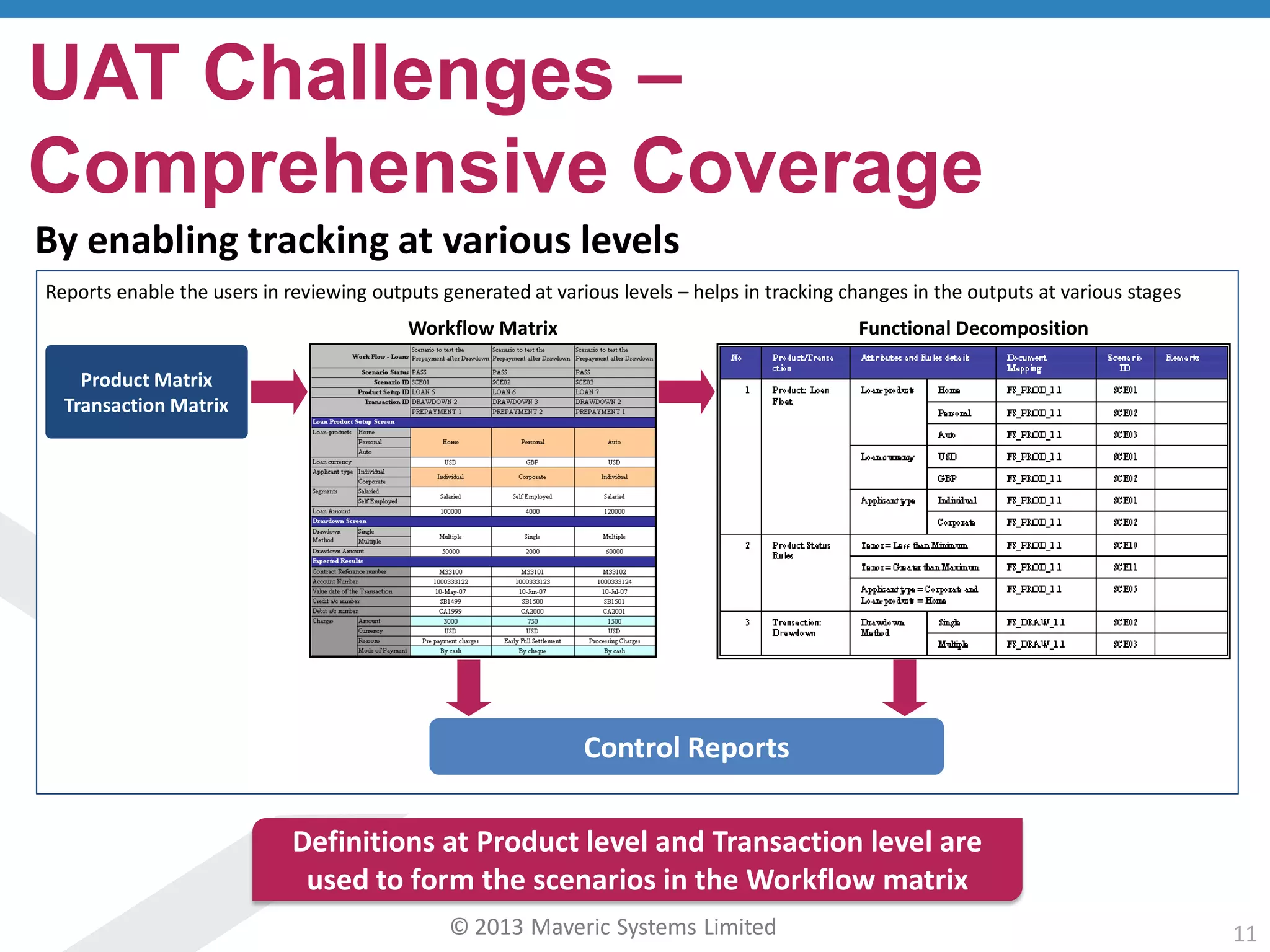
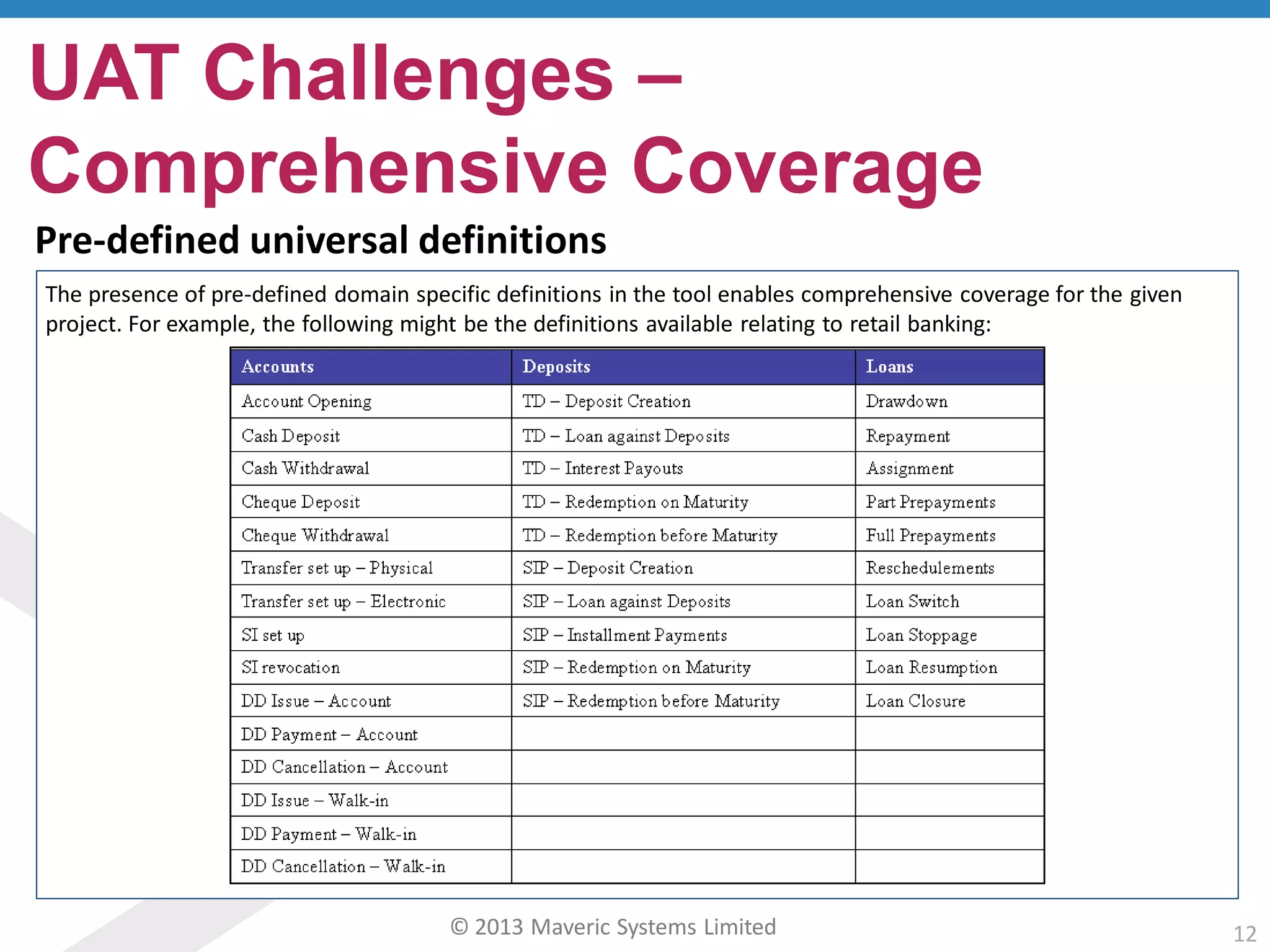
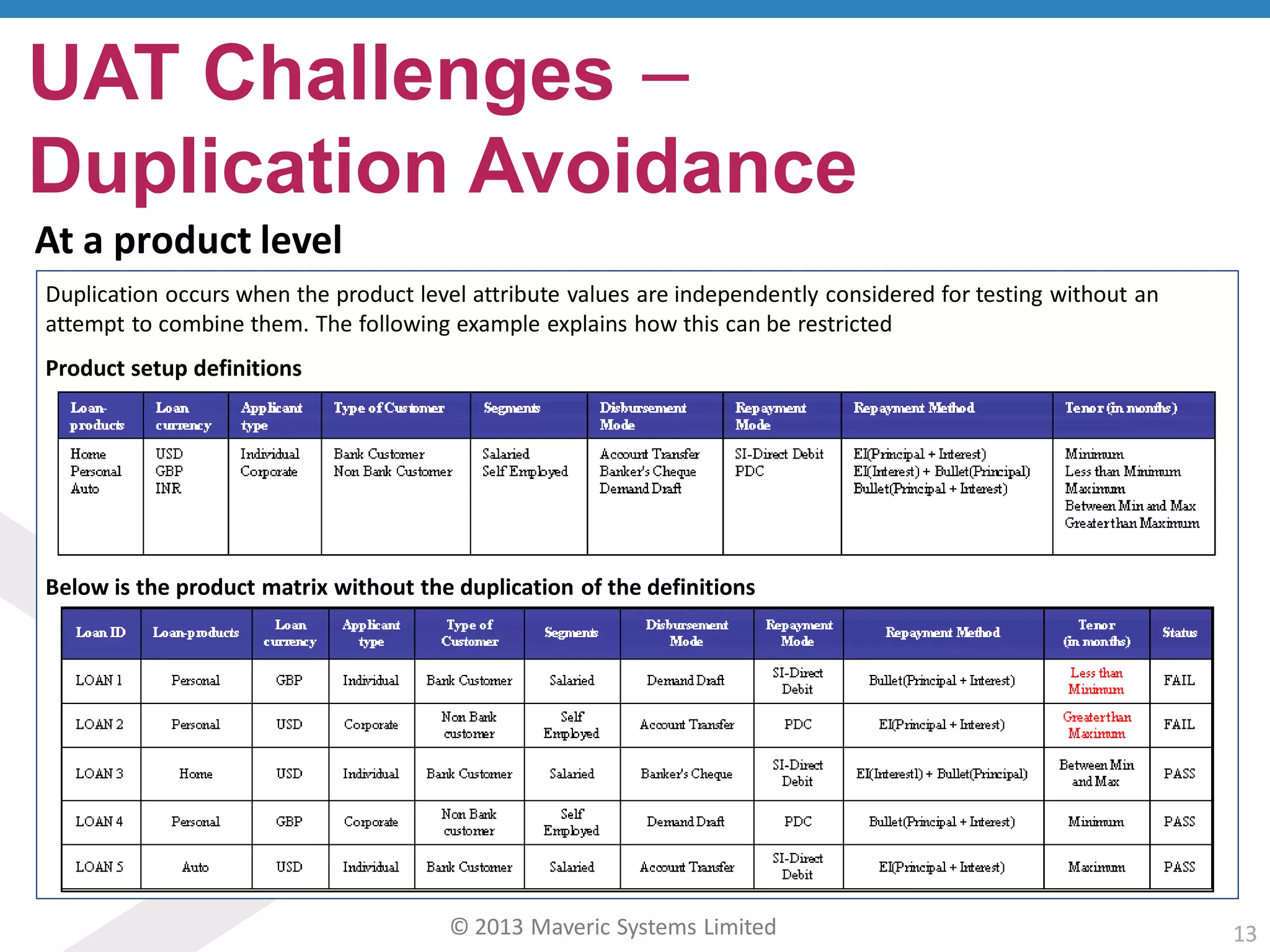
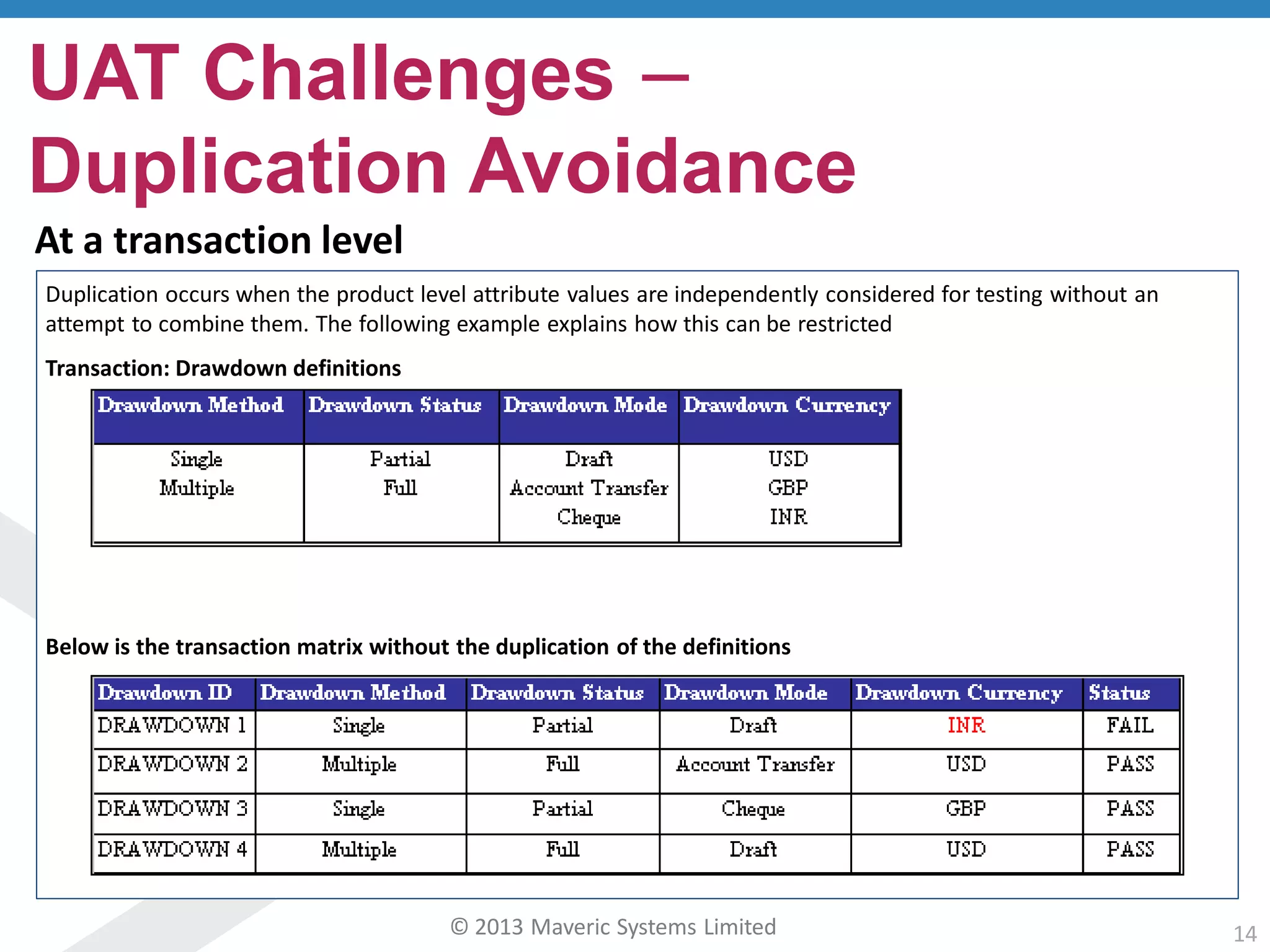
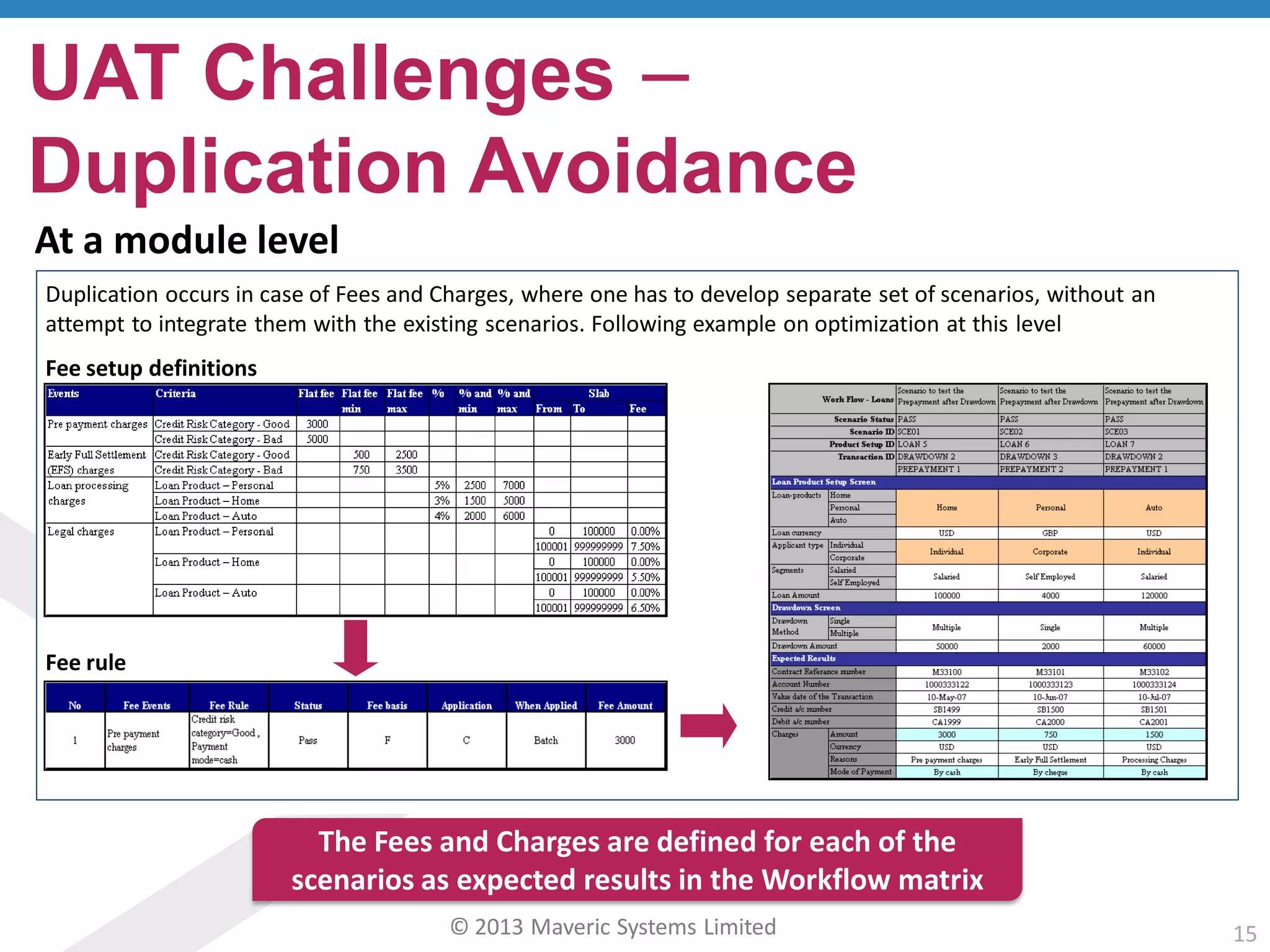
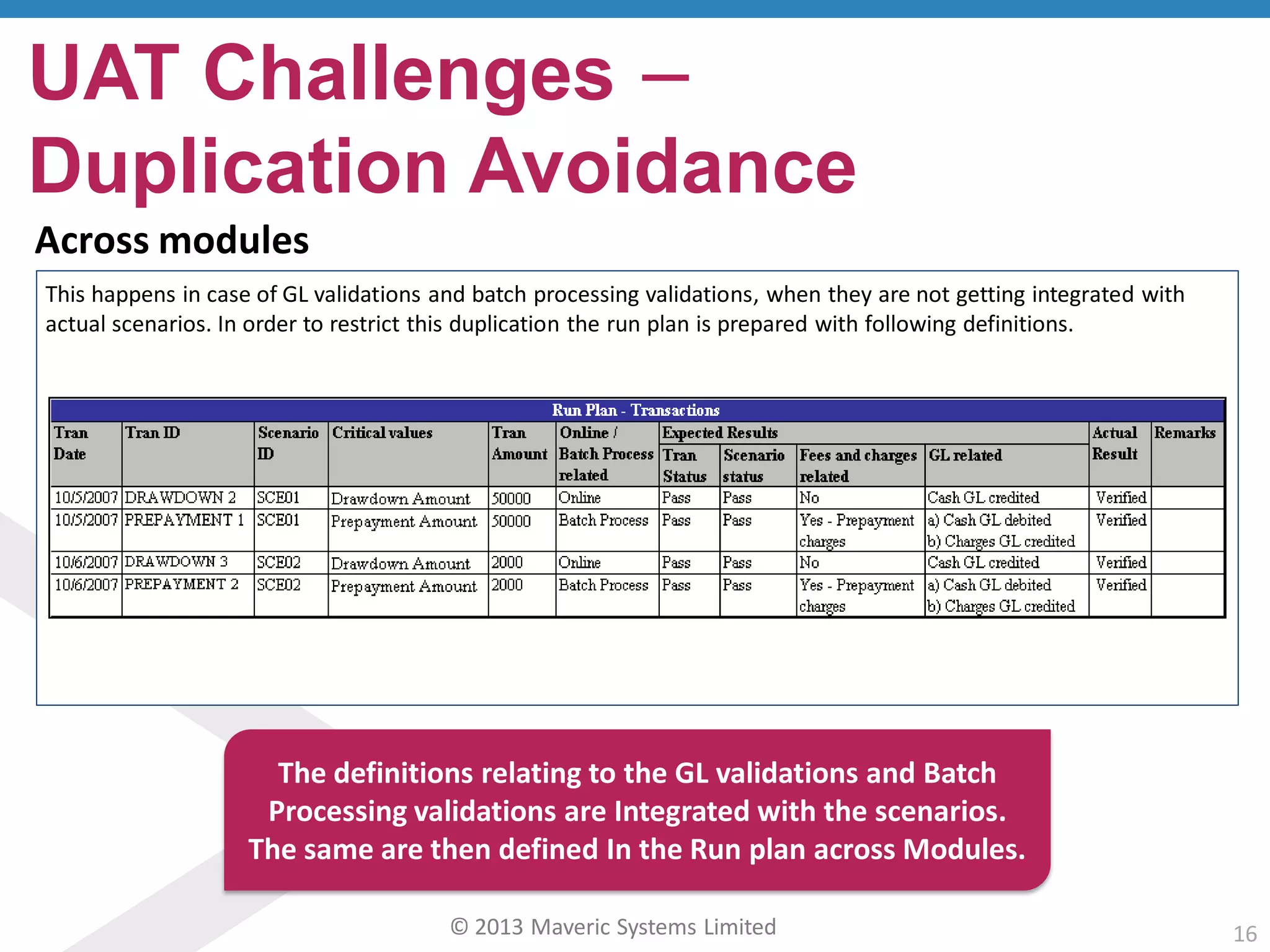
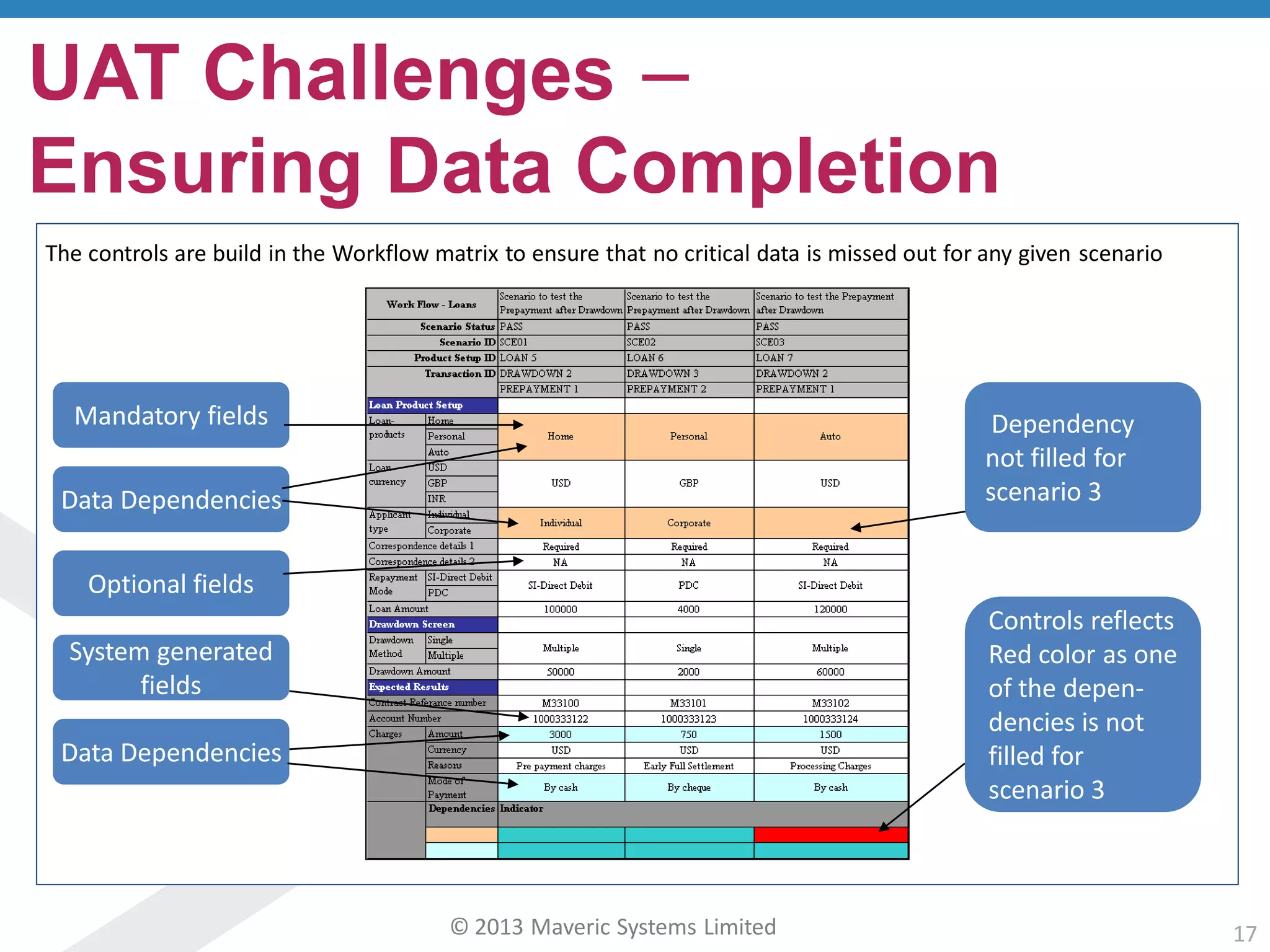
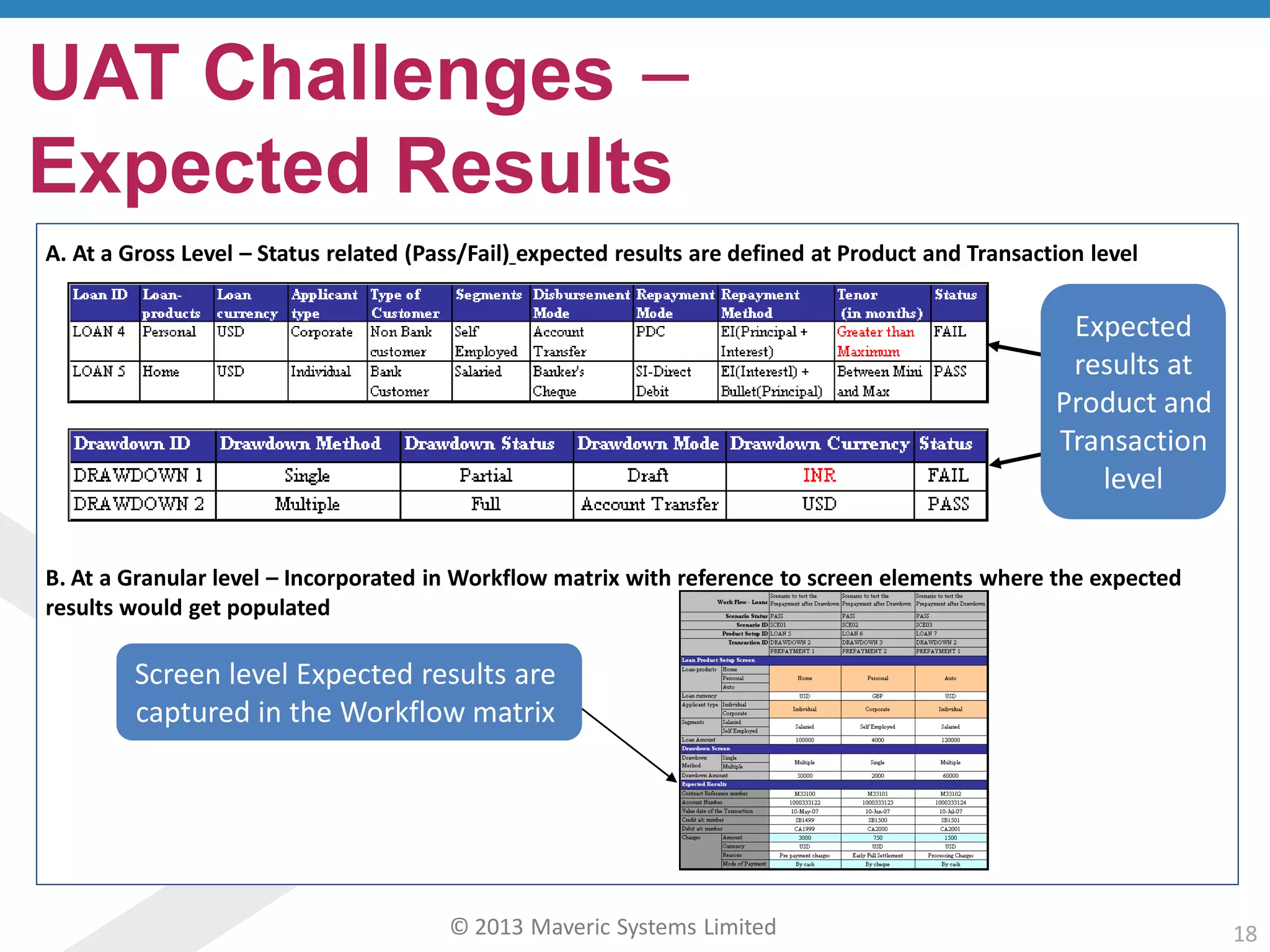
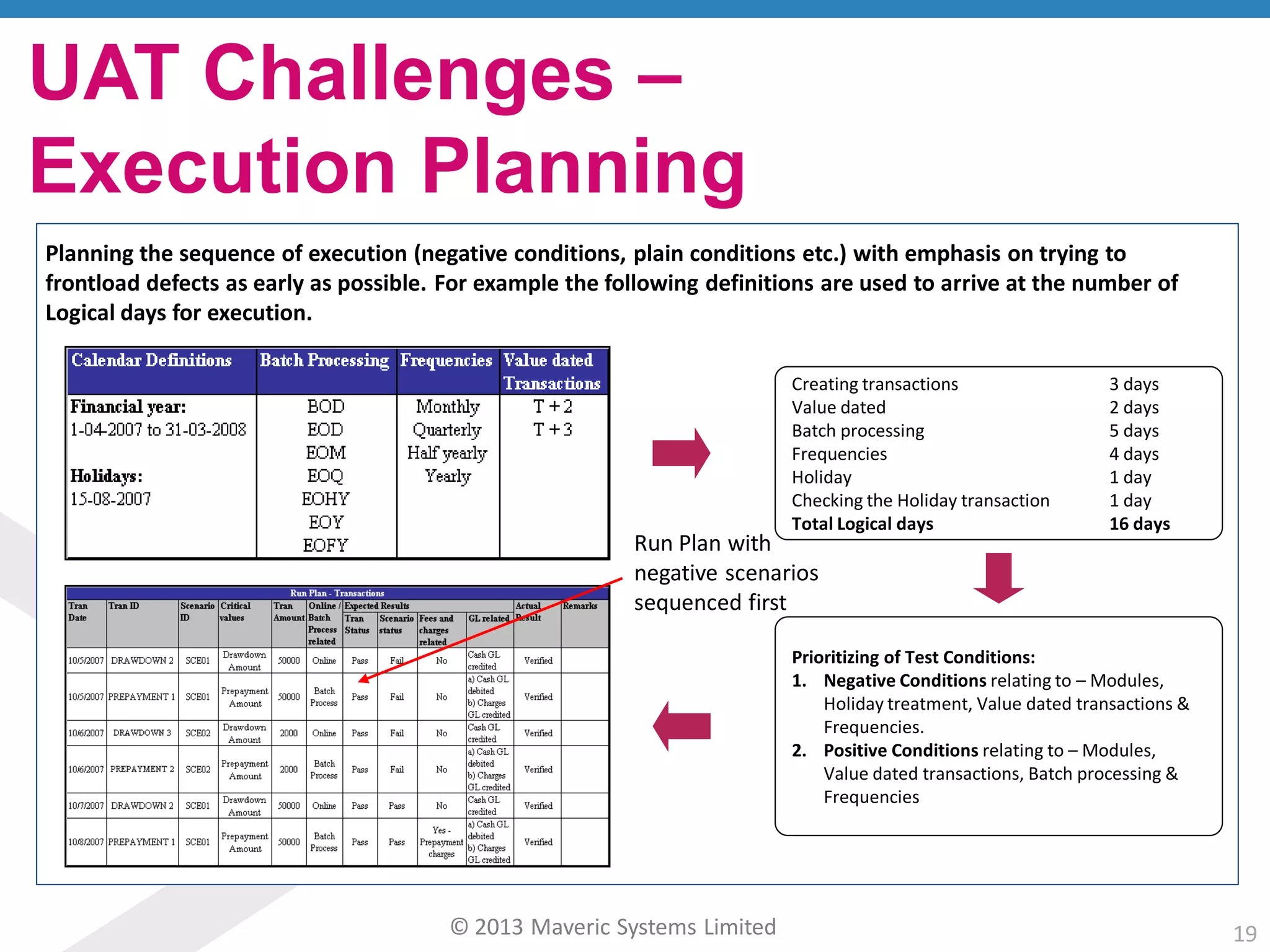
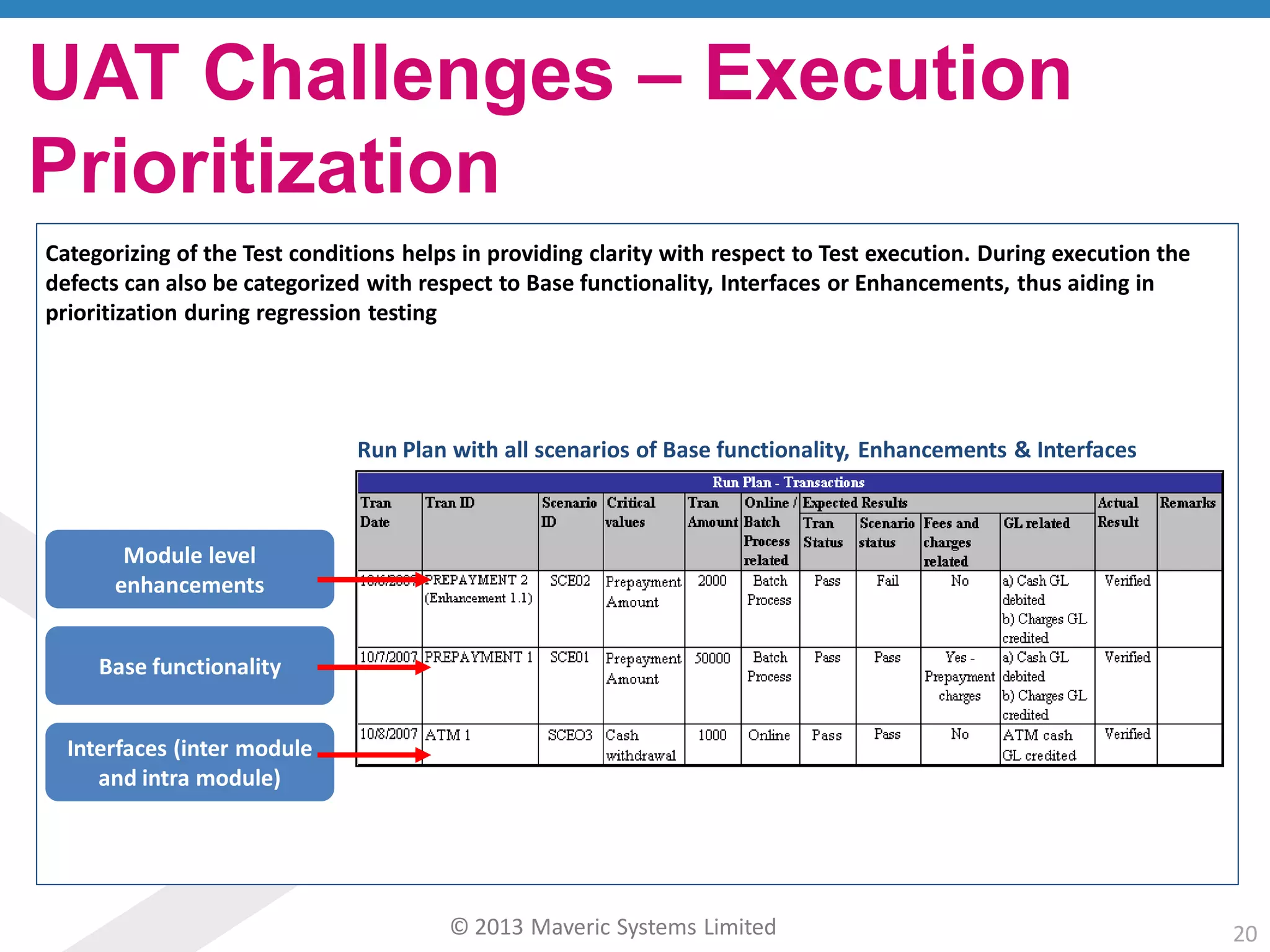
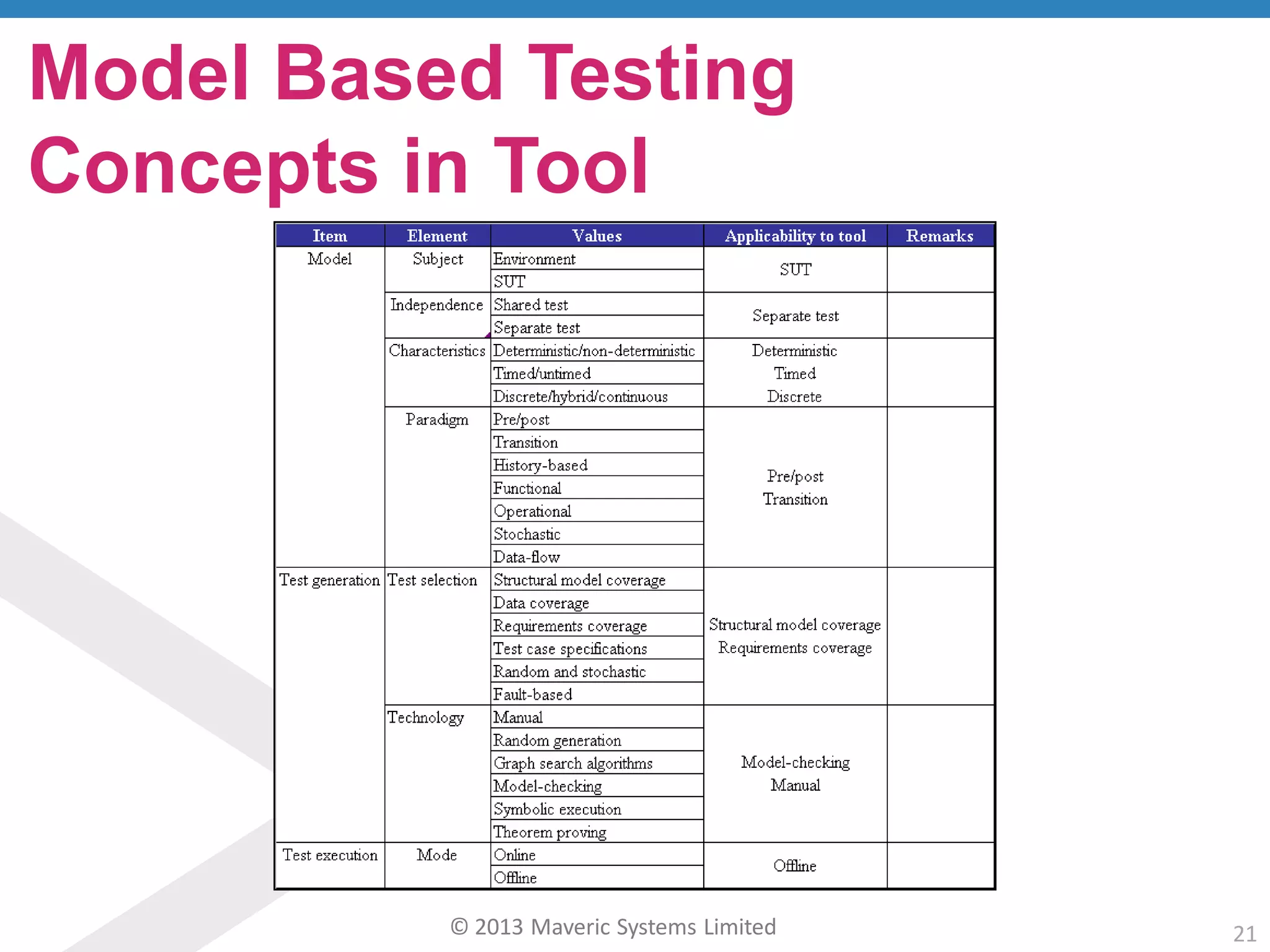
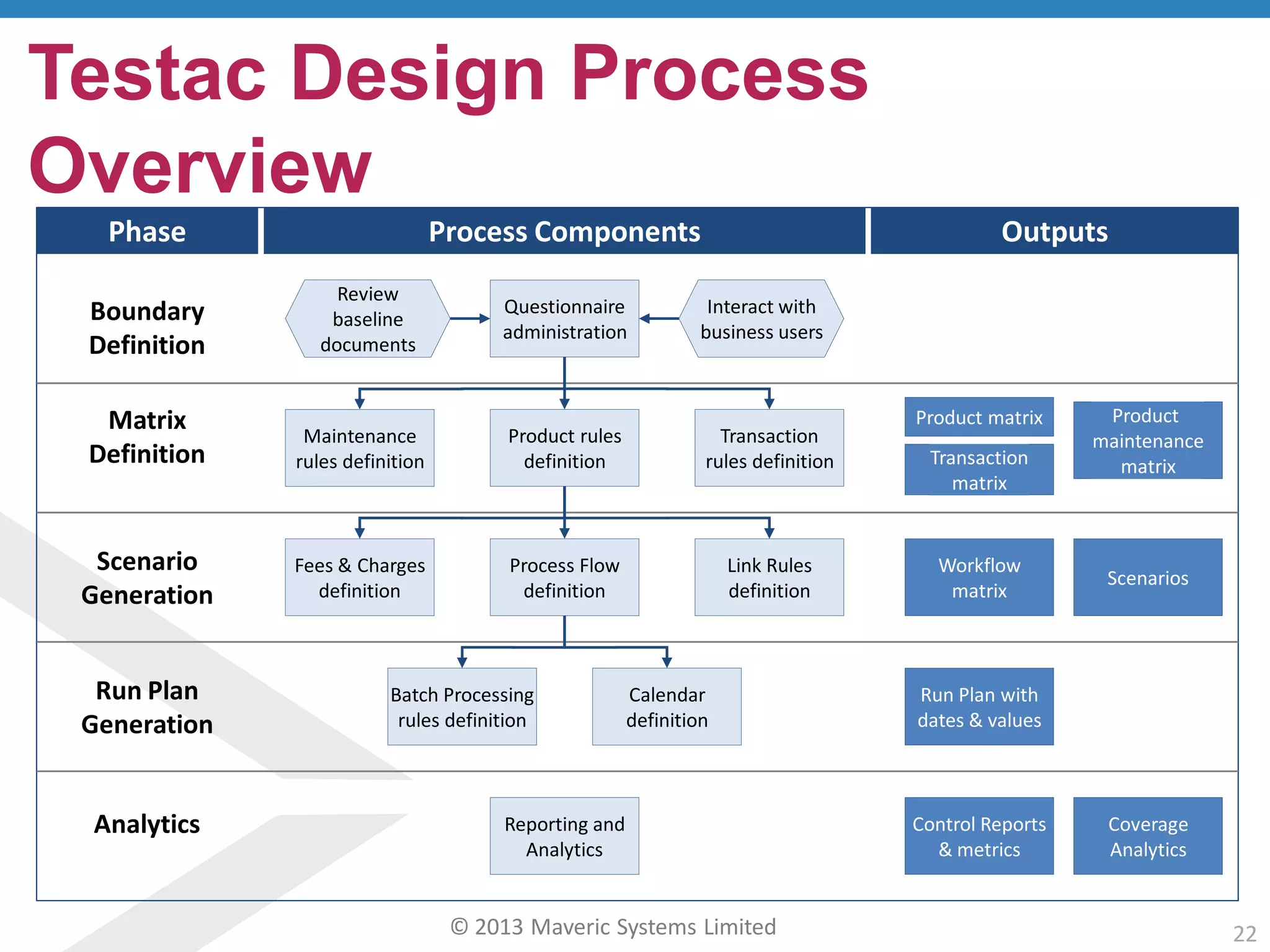
This document discusses challenges with user acceptance testing and how a model-based testing tool called Testac addresses these challenges. It provides an overview of the Testac design process, which involves defining product, transaction, and other rules from domain knowledge and then generating test scenarios and run plans from these rules through its scenario generation algorithm. This helps ensure comprehensive test coverage, eliminates duplication, and aids in execution planning and prioritization. The document outlines how Testac achieves benefits like an independent verification basis, objective coverage assessment, and a way for business users to engage with the testing process.