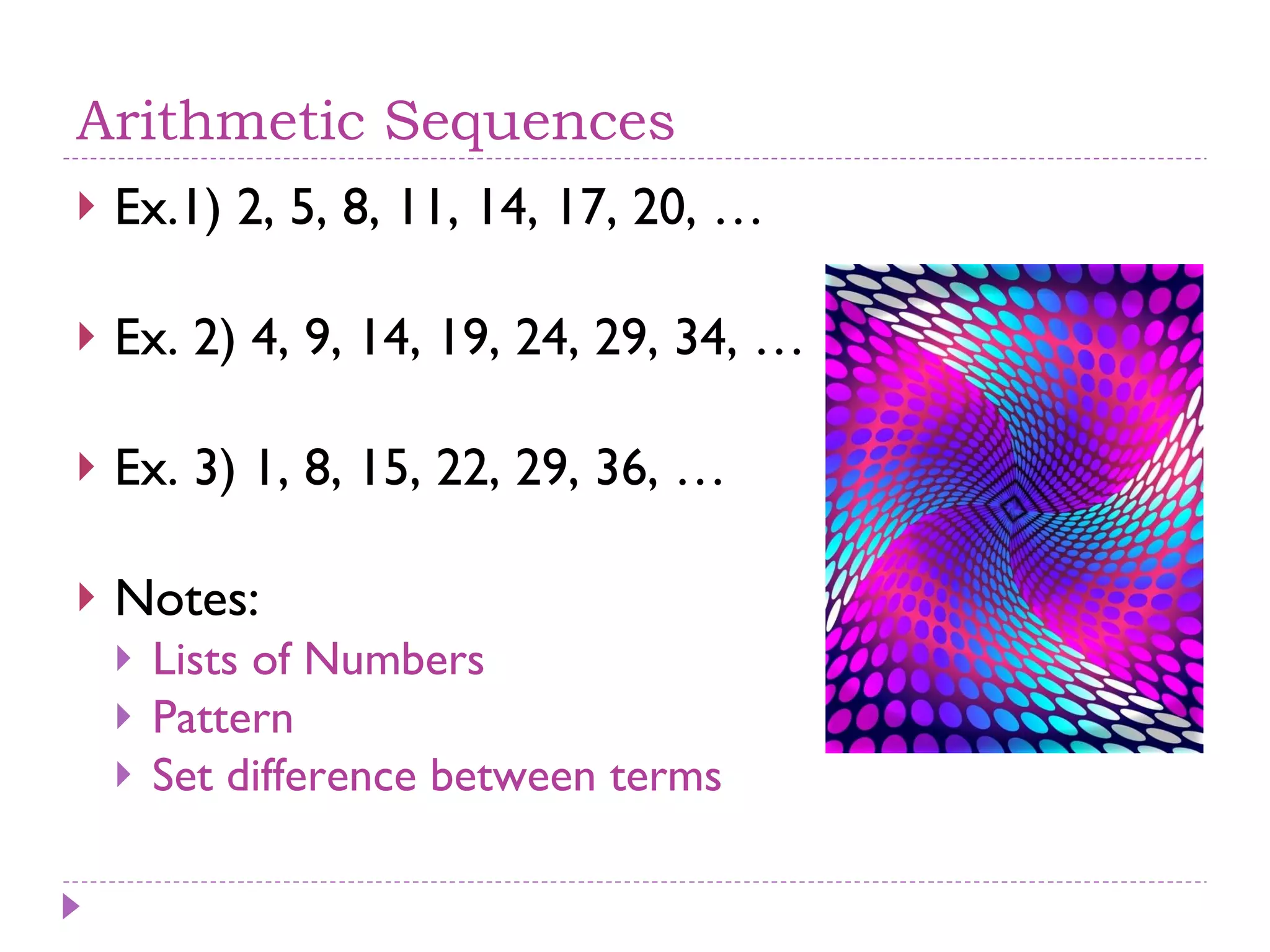
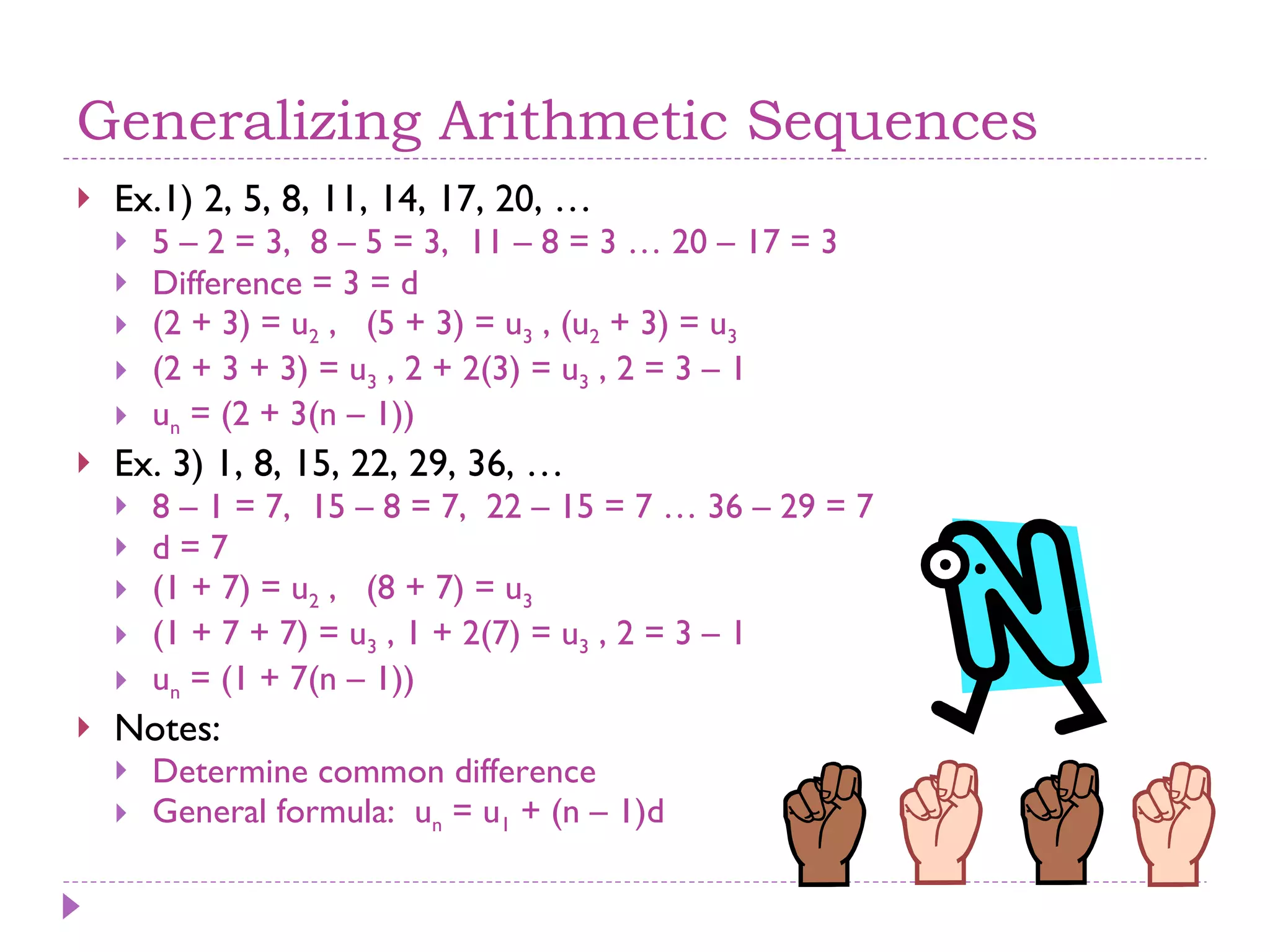
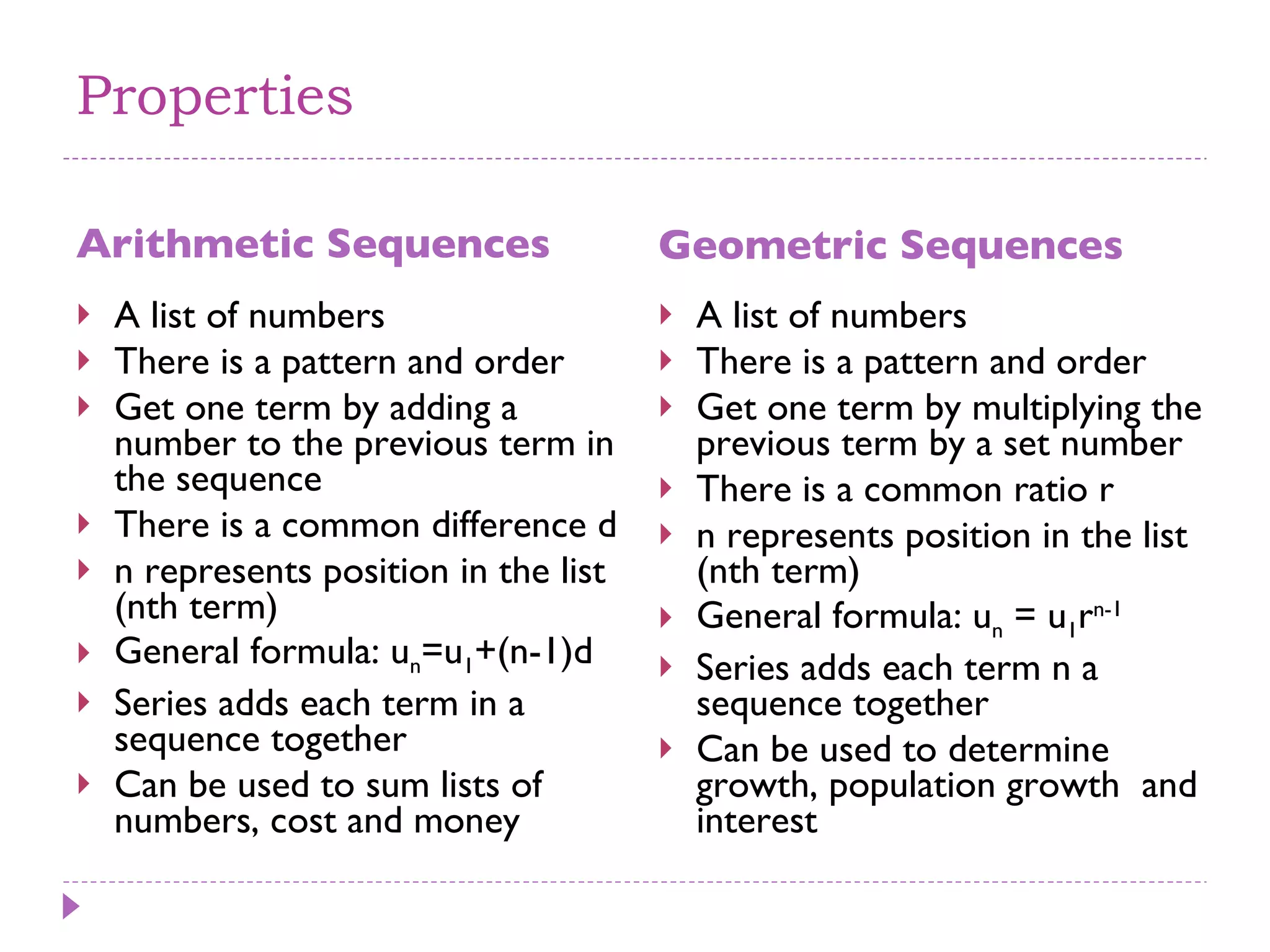
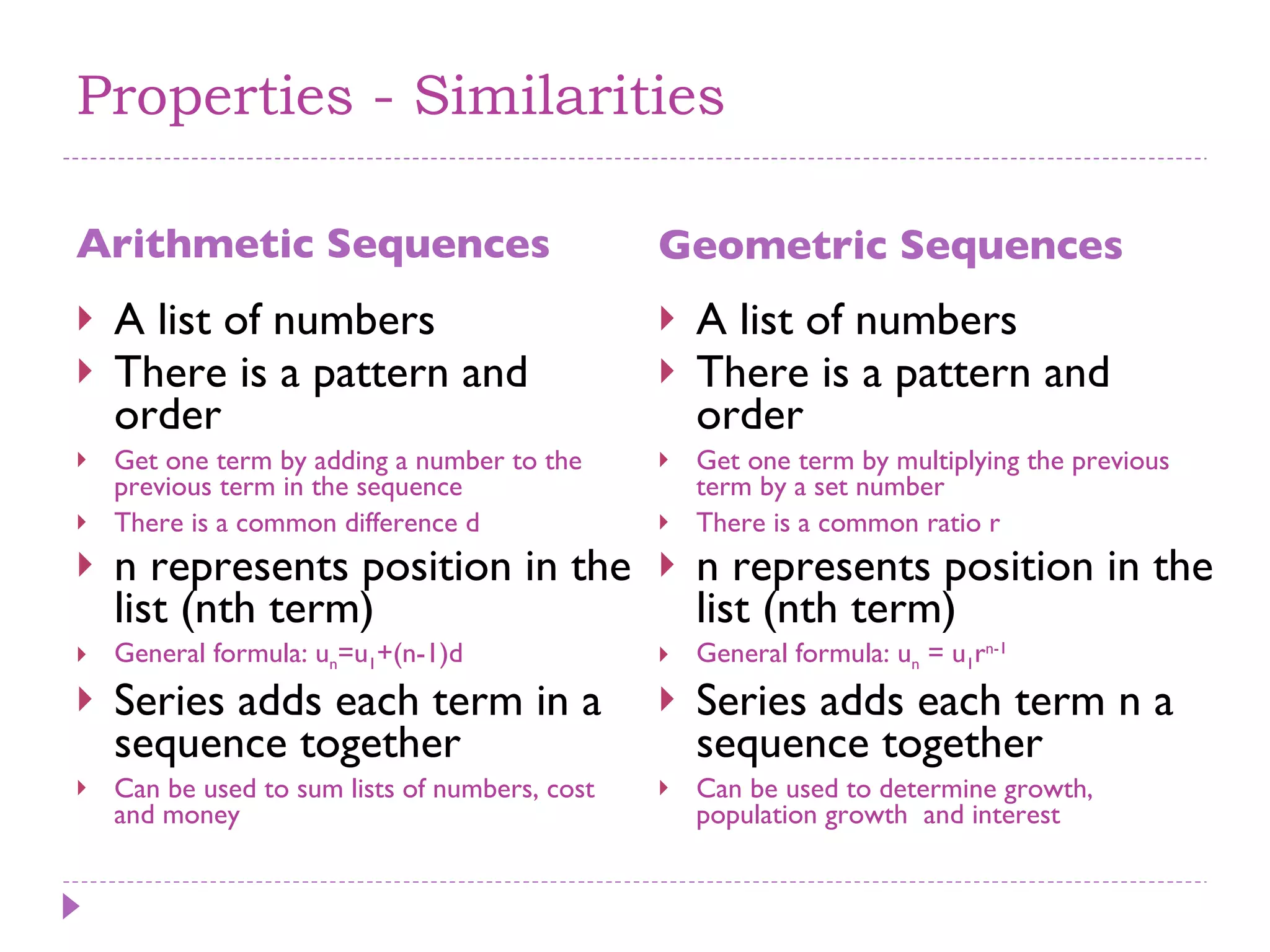
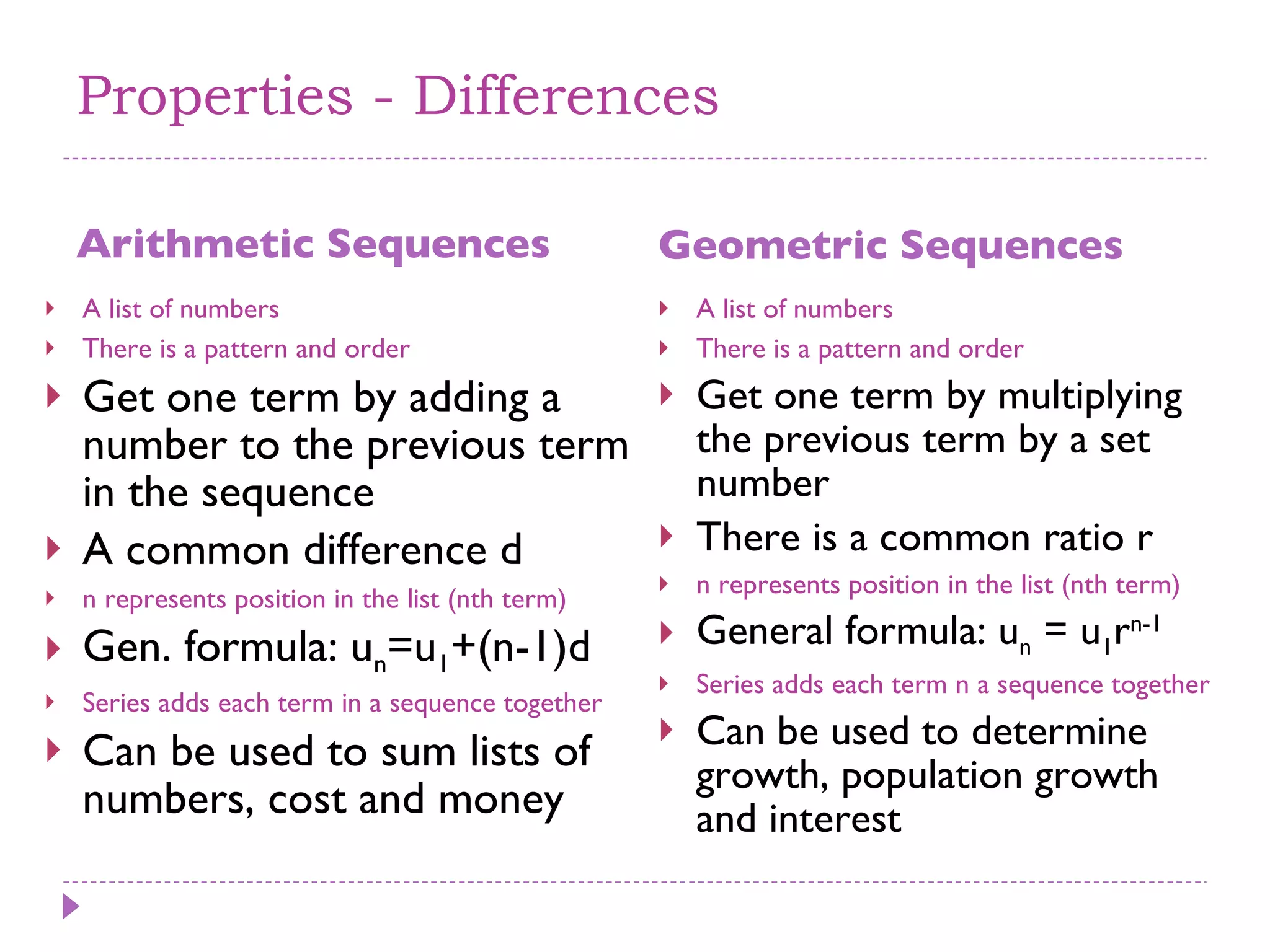
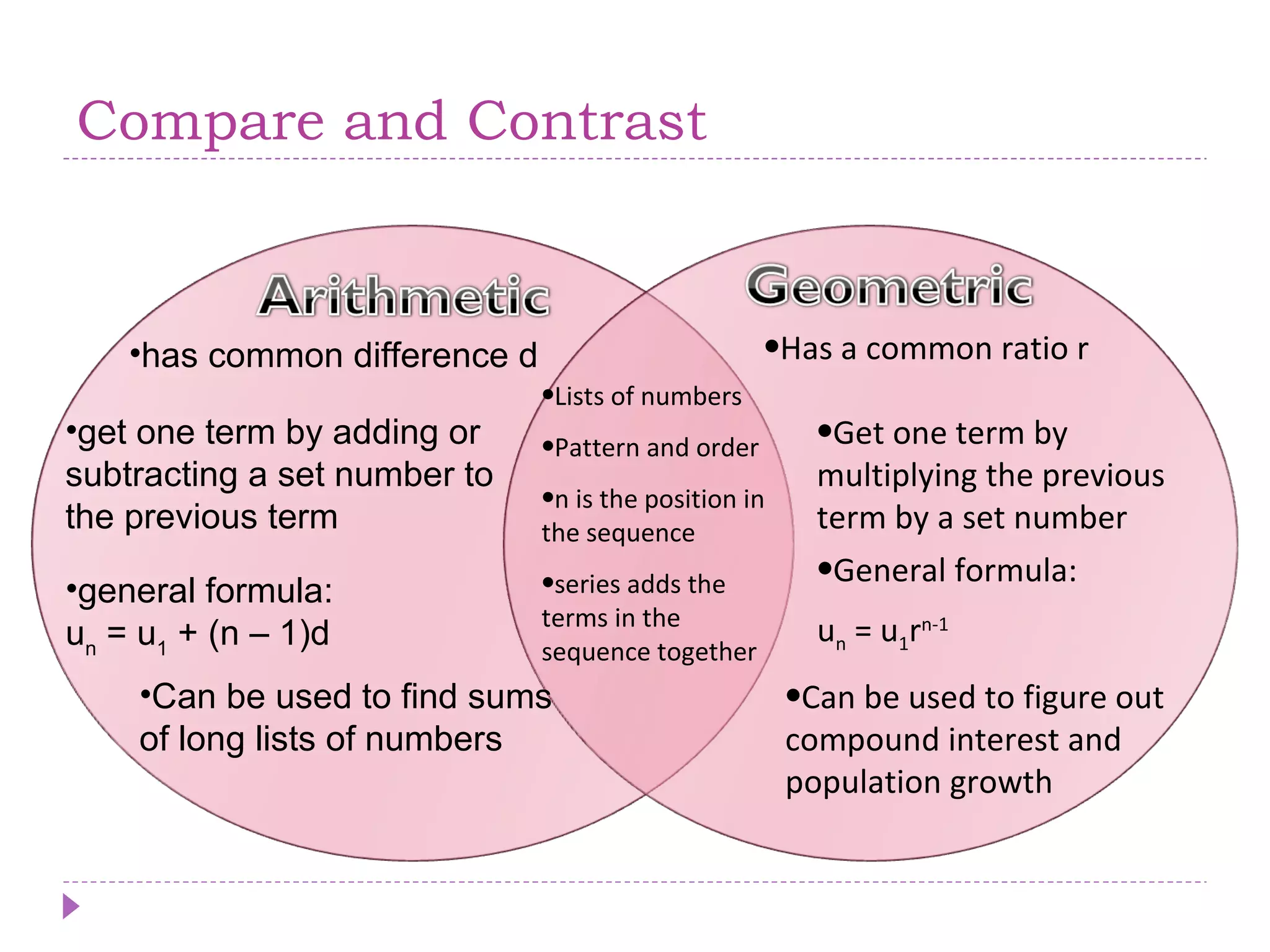
The document discusses arithmetic and geometric sequences and series. It provides examples of different sequences and explains how to determine the general formulas for finding any term in the sequence. Specifically, it explains that arithmetic sequences have a common difference and use the formula un = u1 + (n-1)d, while geometric sequences have a common ratio and use the formula un = u1rn-1. It also discusses how series are used to sum the terms of sequences and provides examples of applications for arithmetic and geometric sequences/series such as solving math problems, determining total costs or earnings, and calculating compound interest or population growth.

![Geometric Sequences Ex. 1) 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, … Ex. 2) 1000,100, 10, 1, 0.1, 0.01, … Ex.3) 3, 9, 27, 81, 243, 729, … Notes: List of numbers Pattern [Multiplication] Common ratio [r]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sequencesandseries-101212025005-phpapp02/75/Sequences-and-series-5-2048.jpg)
![Generalizing Geometric Sequences Ex. 1) 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, … 4÷2 = 2, 8÷4 = 2, … 64÷32 = 2 Common ratio r = 2 u 1 ×2 = u 2 , u 2 ×2 = u 3 , (u 1 ×2)×2 = u 3 u 3 = u 1 ×(2 2 ) , thus u n = u 1 (2 n-1 ) Ex. 2) 1000,100, 10, 1, 0.1, 0.01, … 100÷1000 = 1 / 10 , 10÷100 = 1 / 10 Common ratio r = 1 / 10 1 / 10 × u 1 = u 2 , 1 / 10 × u 2 = u 3 , 1 / 10 × ( 1 / 10 × u 1 )= u 3 u 3 = u 1 ×( 1 / 10 ) 2 , thus u n = u 1 ( 1 / 10 ) n-1 Notes: Find common ration r [dividing one term by previous term] General formula: u n = u 1 (r n-1 )](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sequencesandseries-101212025005-phpapp02/75/Sequences-and-series-6-2048.jpg)
![Applications What are Arithmetic Sequences used for? Solving Math Problems Used in conjunction with Series [Arithmetic Series] Can be used to sum up long lists of numbers Can be used to sum up prices Ex. Theater tickets are sold for $60 for odd numbered tickets and $40 for even numbered tickets. There are 50 seats in the theater, how much money do even tickets bring in if all are sold? What are Geometric Sequences used for? Solving Compound Interest When money is put into a bank it gains a percentage interest. At any given point in time geometric series can determine how much money is in the bank, with interest. To calculate population growth, often in biology.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sequencesandseries-101212025005-phpapp02/75/Sequences-and-series-8-2048.jpg)

![Now for Review Get into groups of four Review information presented in class Write helpful information on index cards [keep it on the lines – one side] 5 minutes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sequencesandseries-101212025005-phpapp02/75/Sequences-and-series-14-2048.jpg)