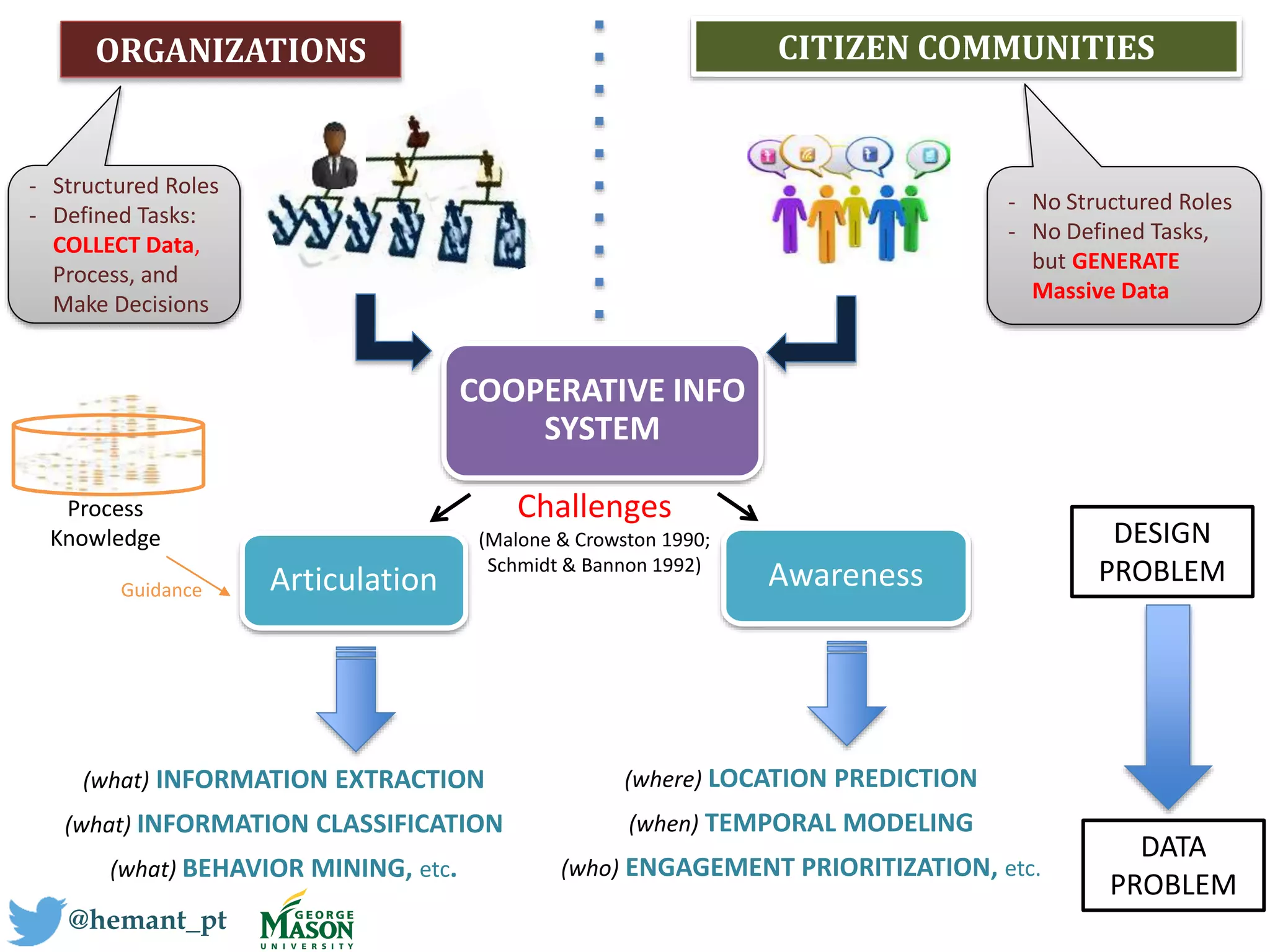
This document discusses using a humanitarian informatics approach to facilitate cooperation between citizens and organizational decision makers during crisis situations. It proposes mining and managing social data generated by citizens to address organizations' information needs and challenges of articulation and awareness. Specifically, it involves extracting, classifying, and modeling social data to provide actionable information aligned with organizations' process-driven needs for decision making during disasters and other humanitarian efforts. The approach aims to leverage citizens' massive social media data generation to help organizations that have more defined roles and information needs but less direct access to data.