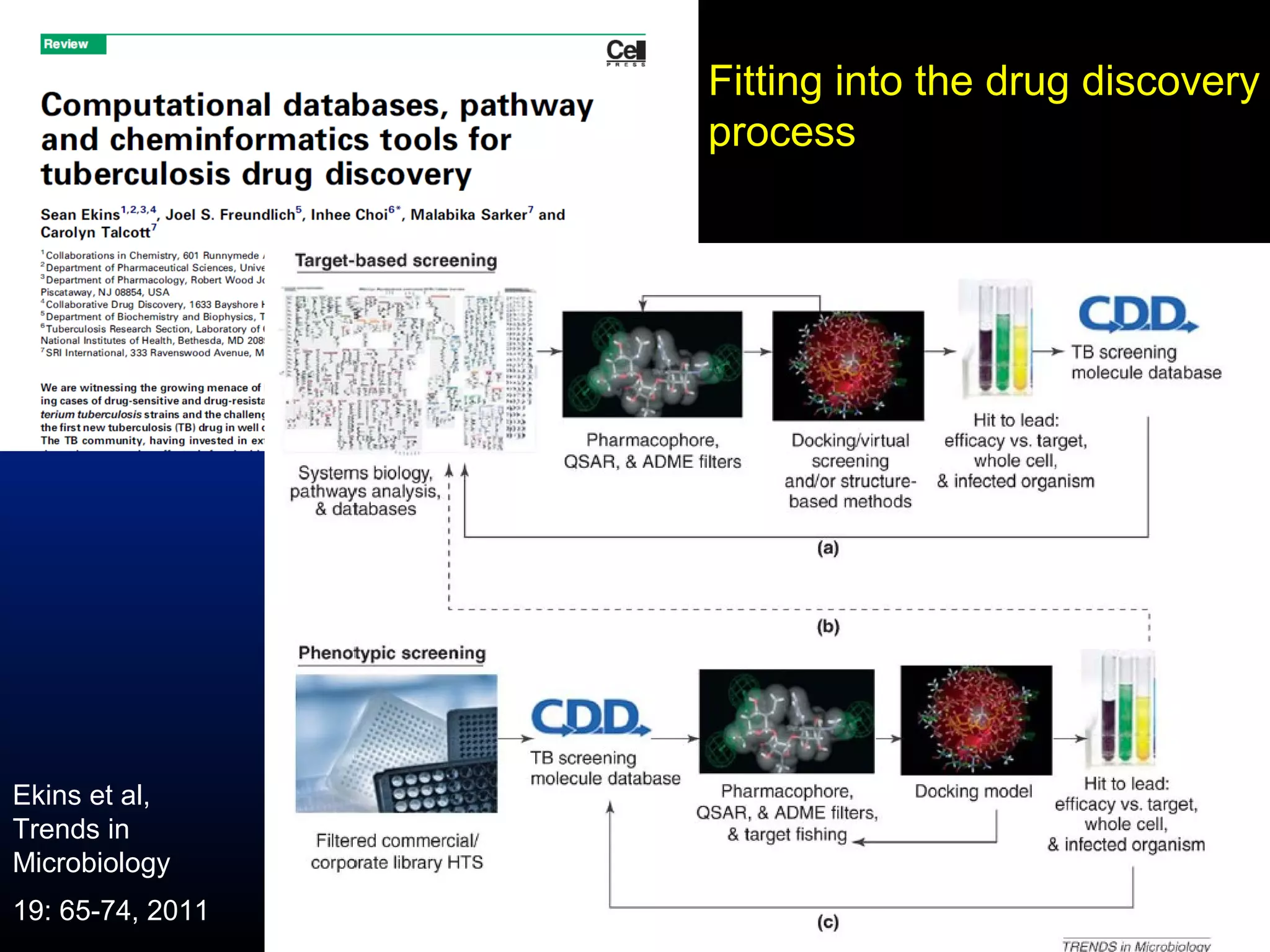
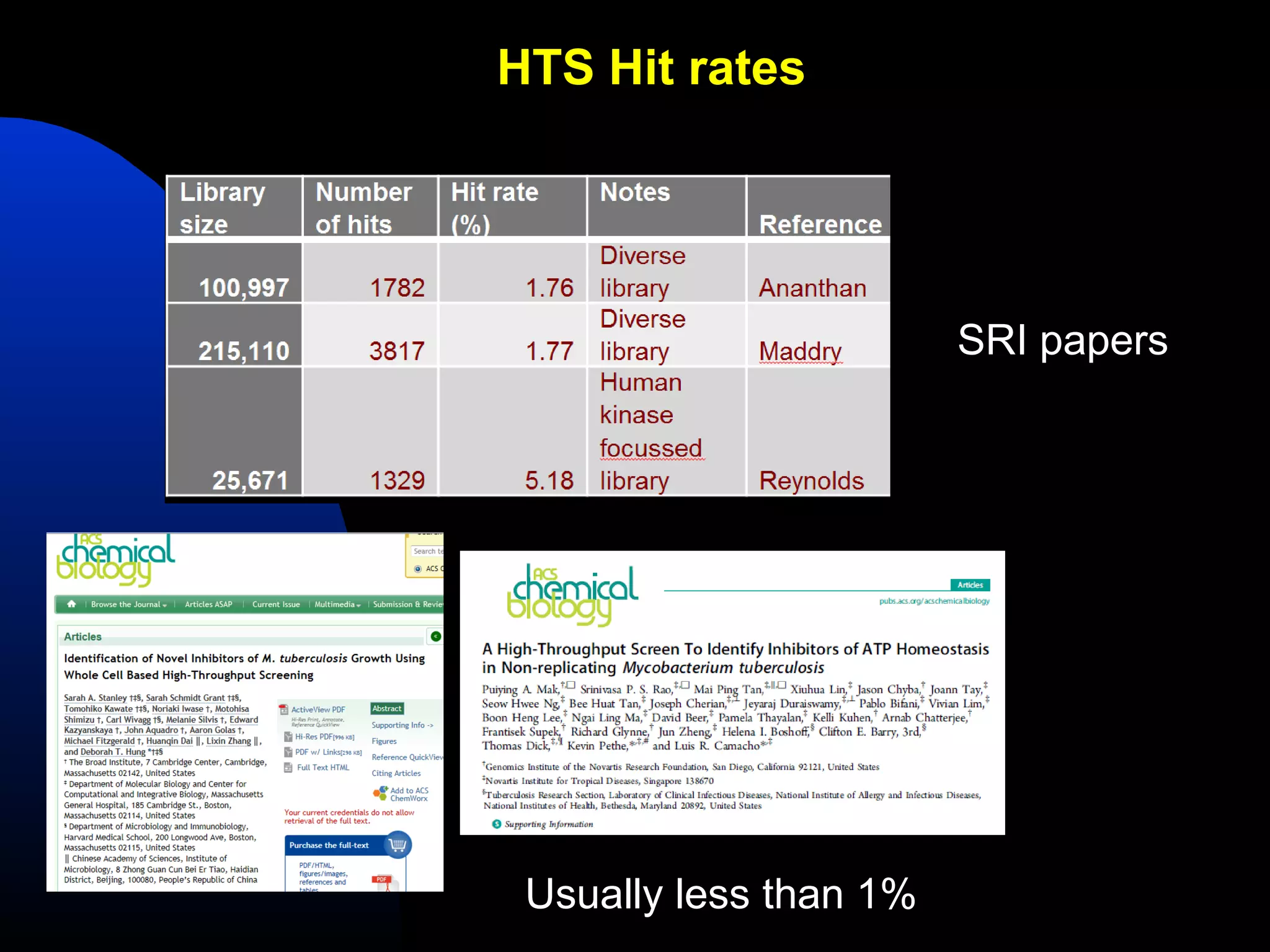
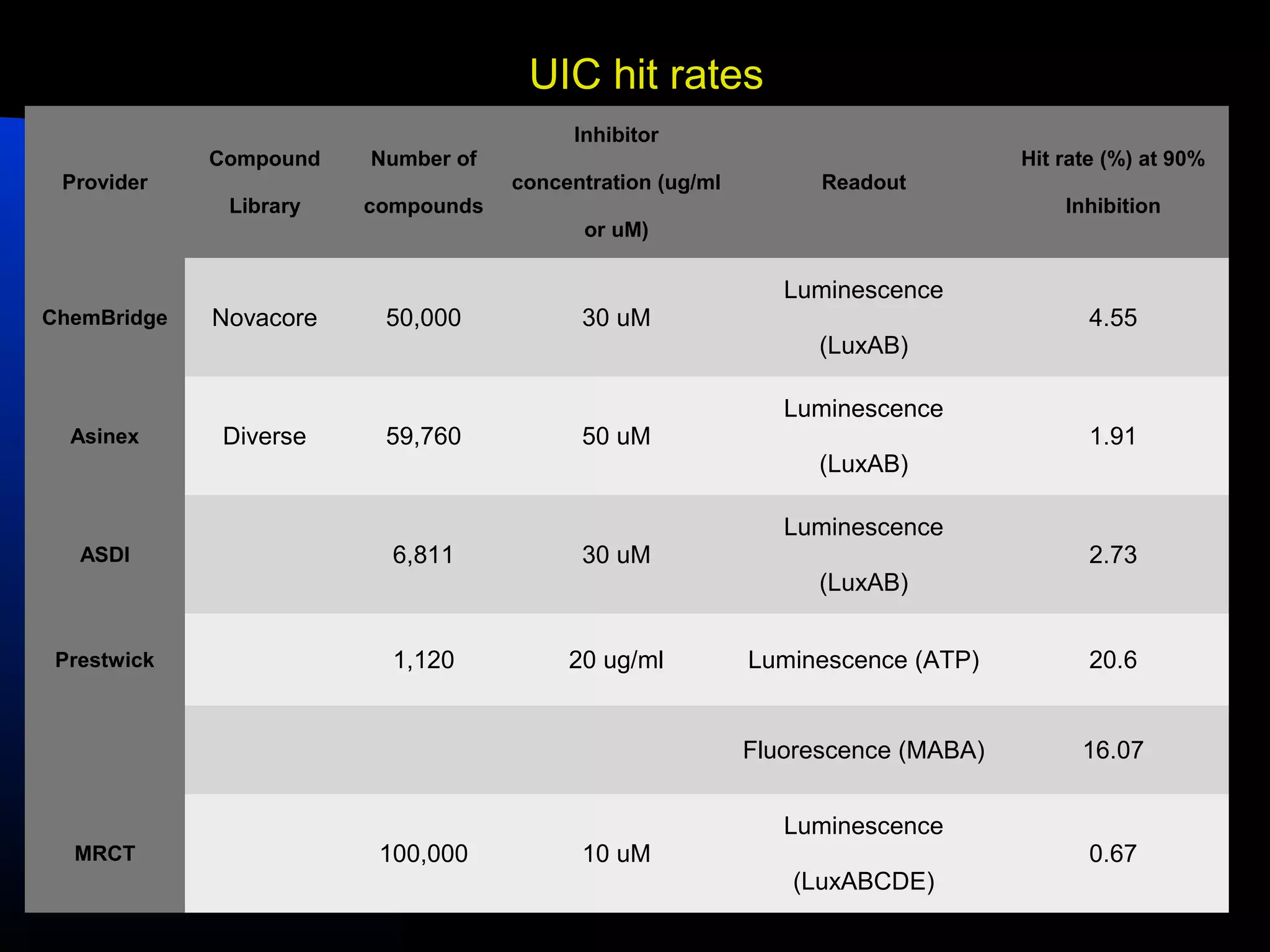
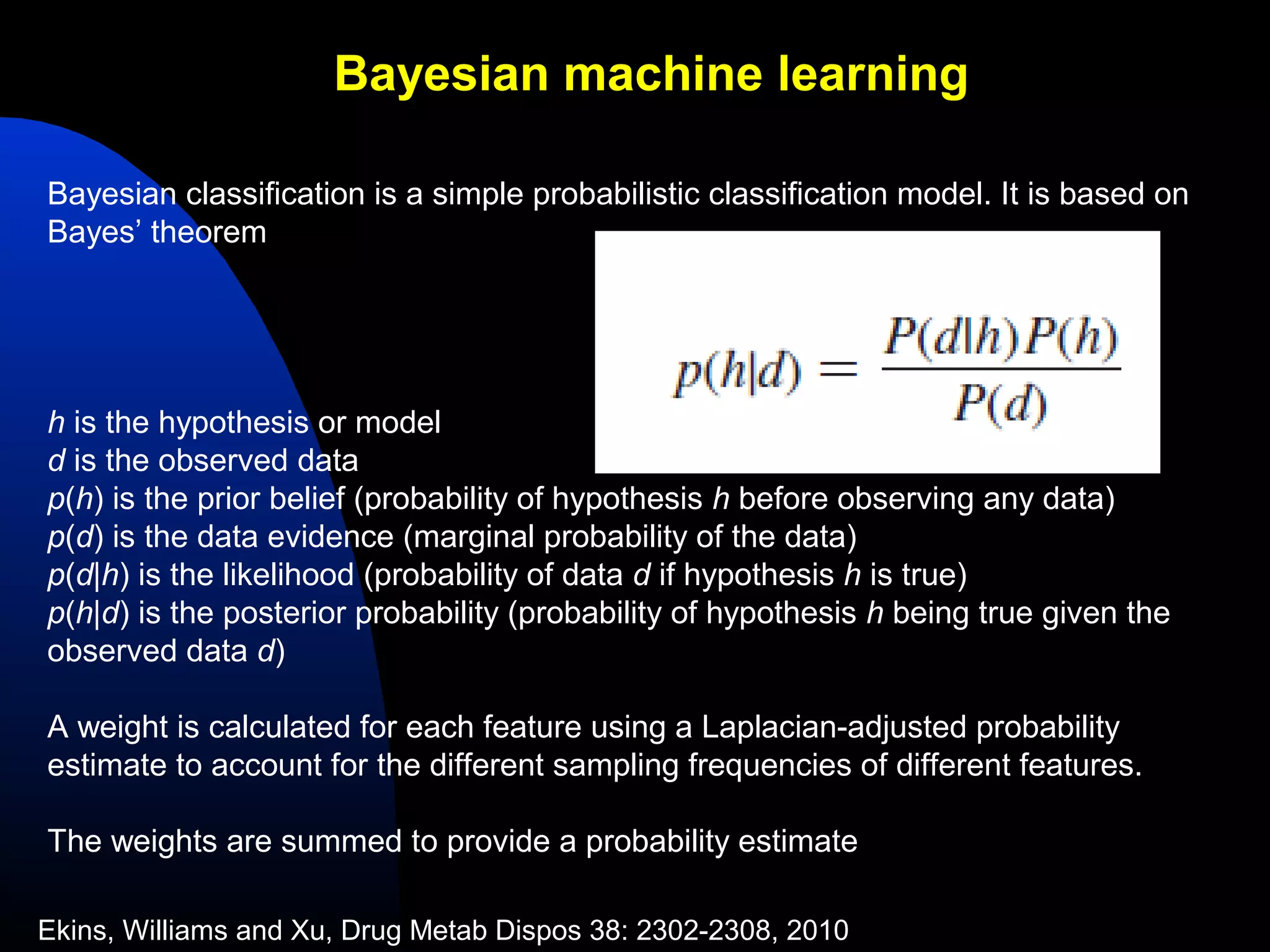
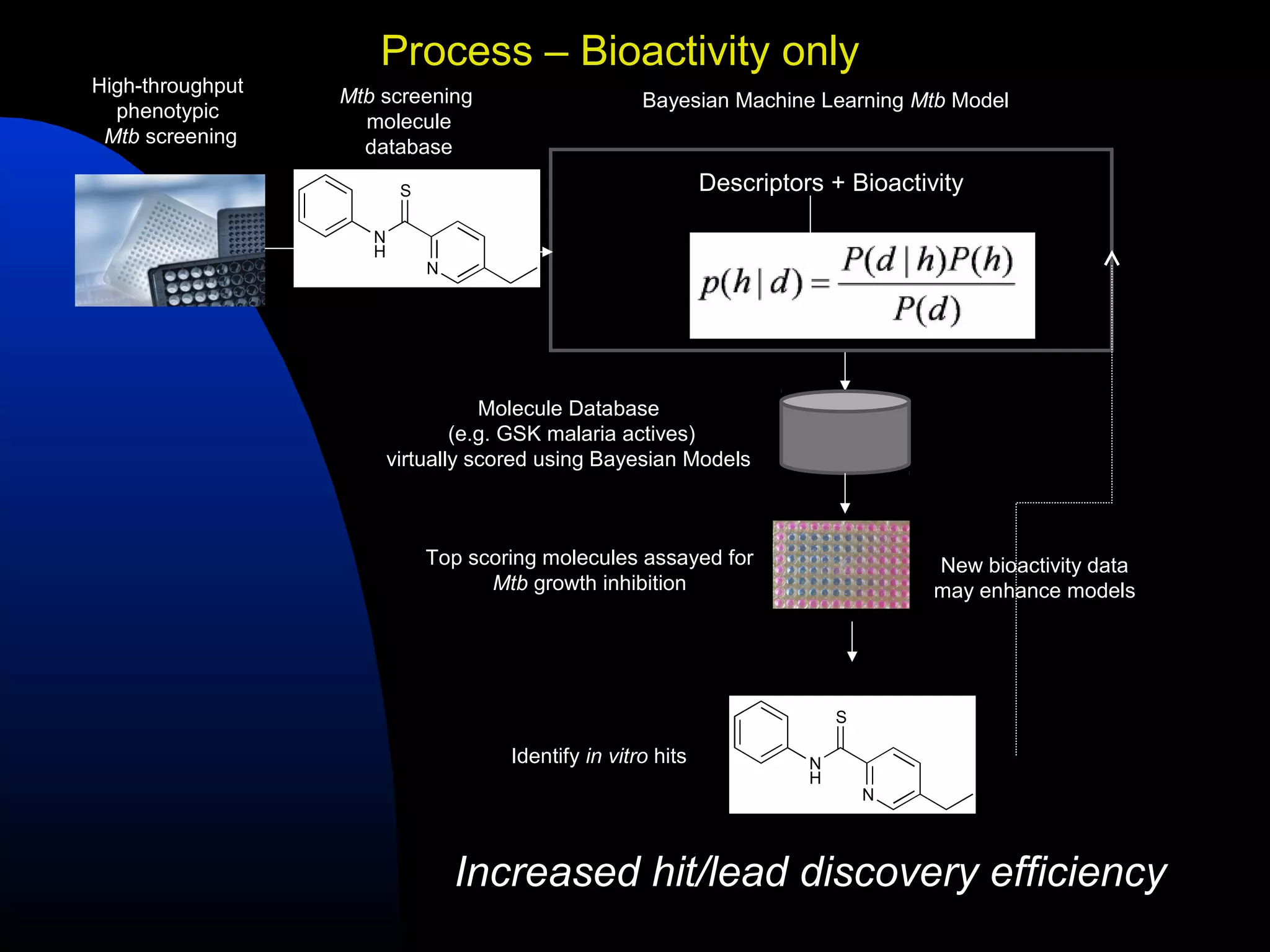
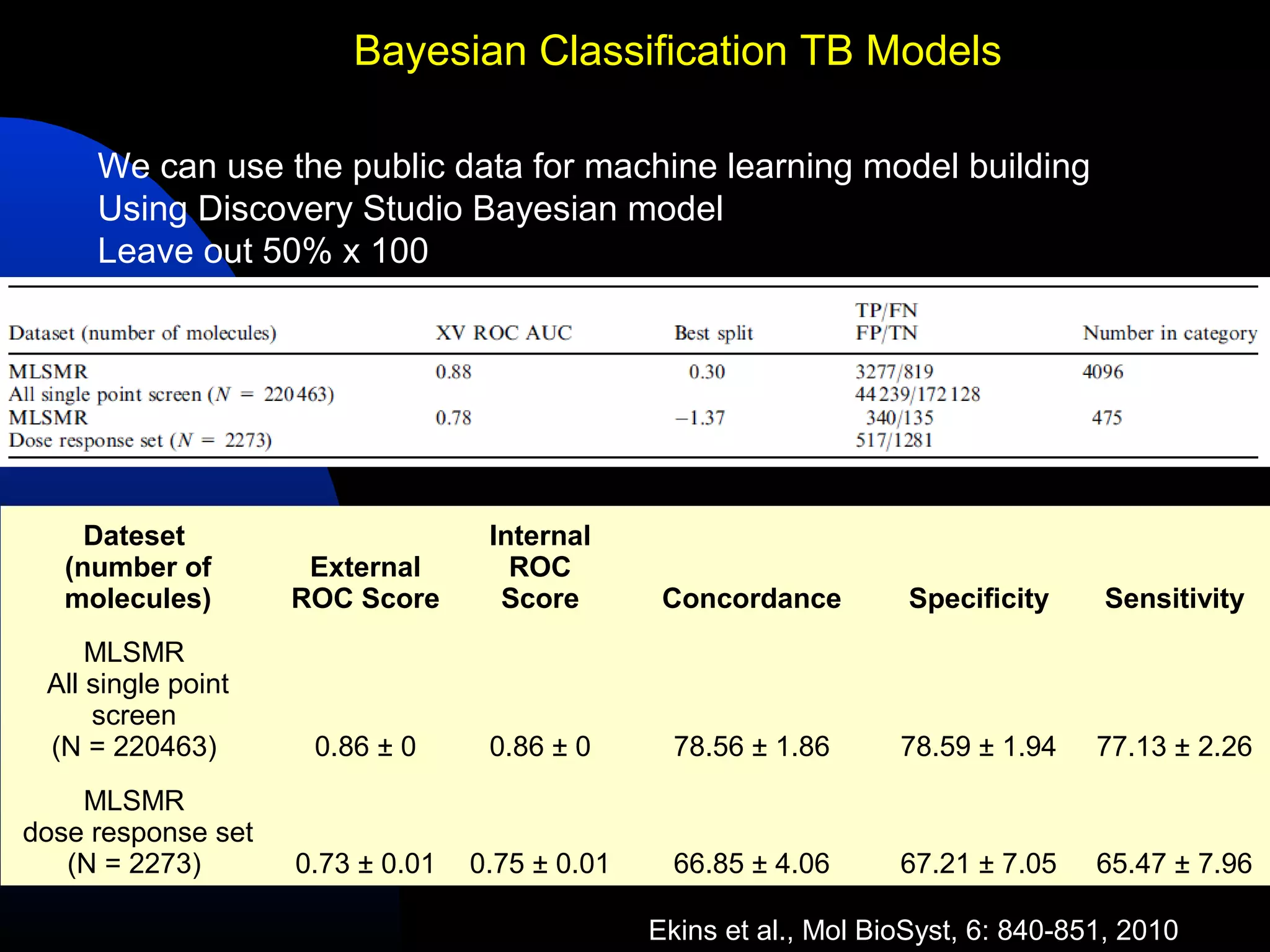
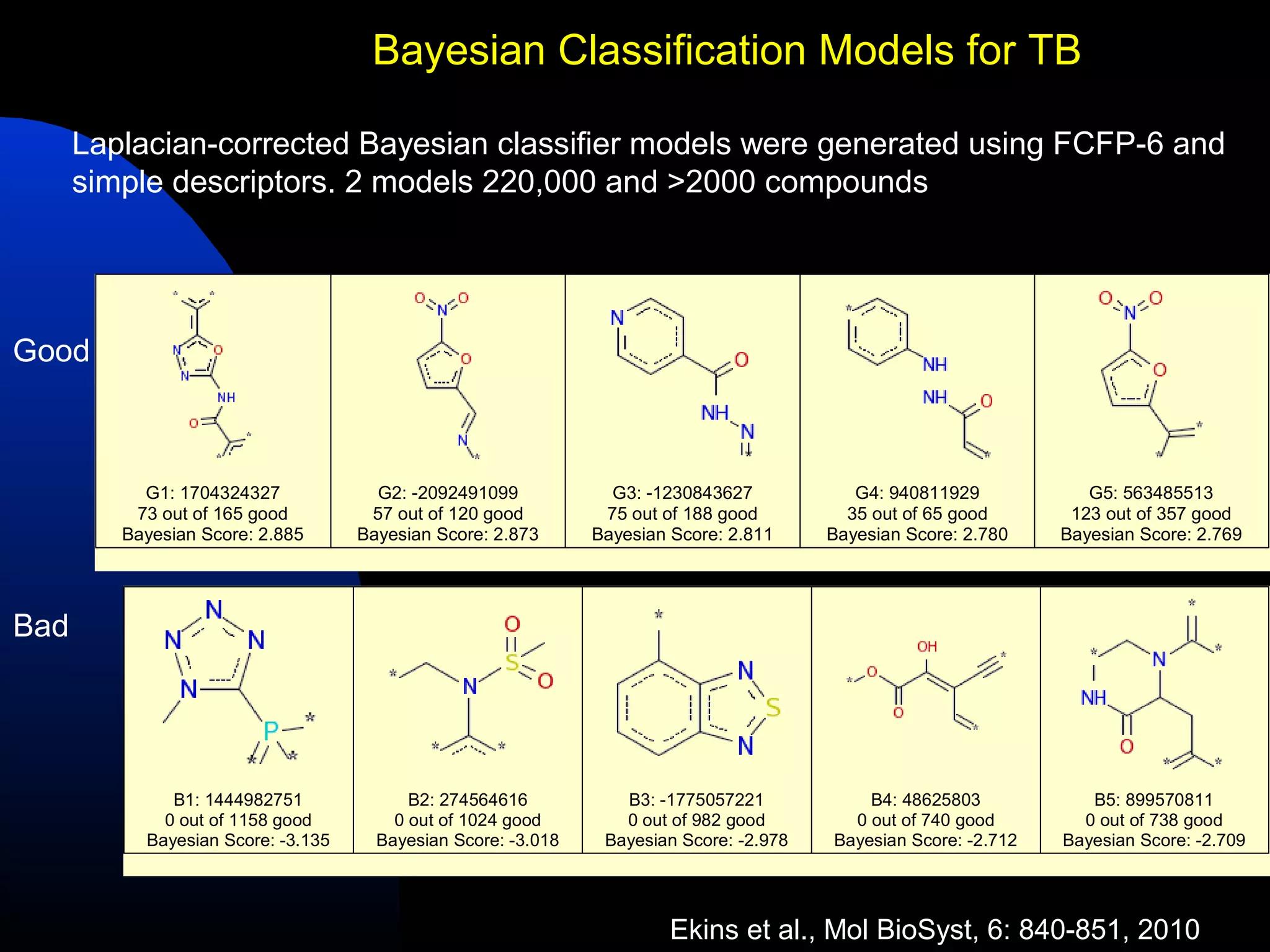
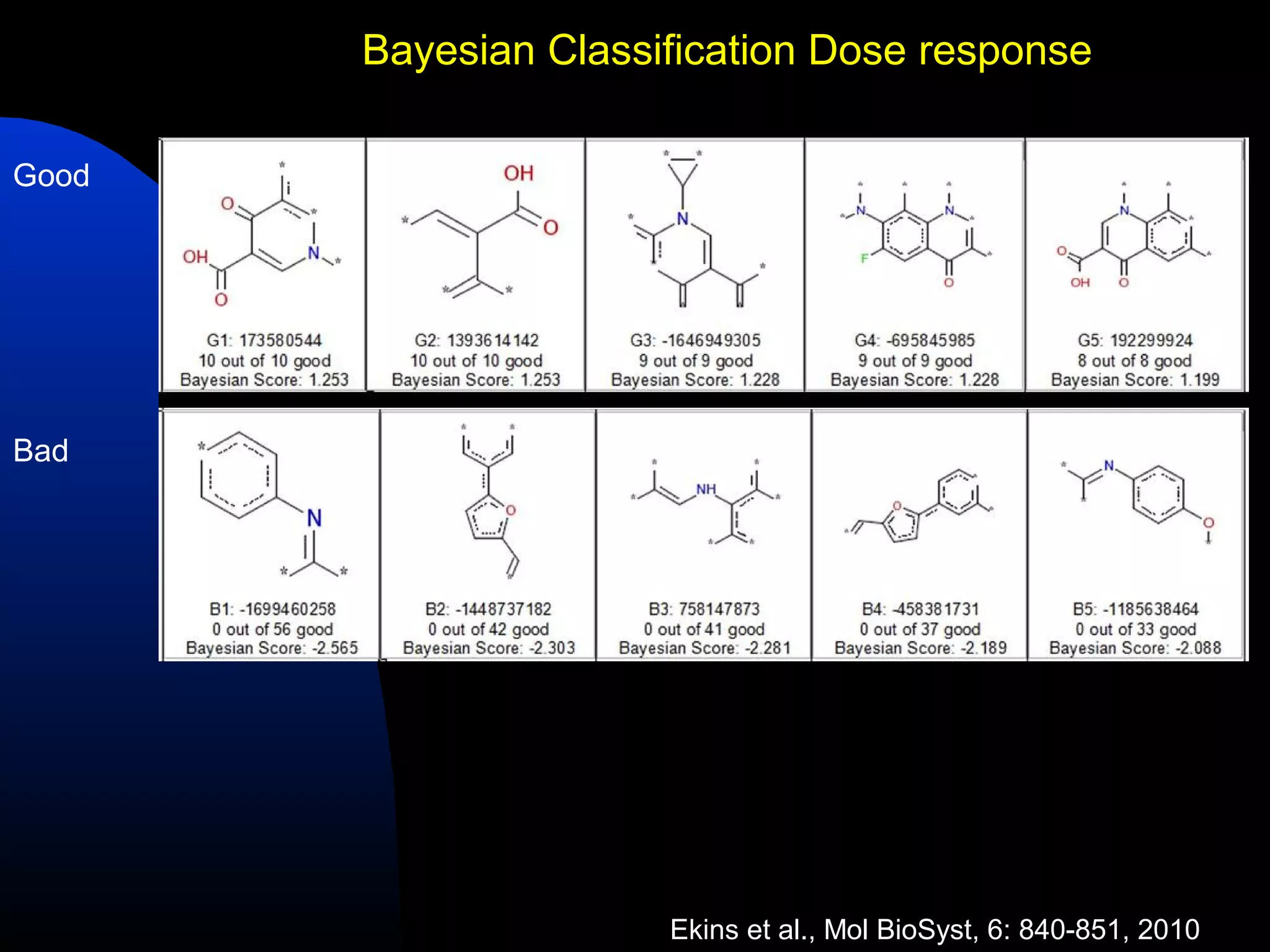
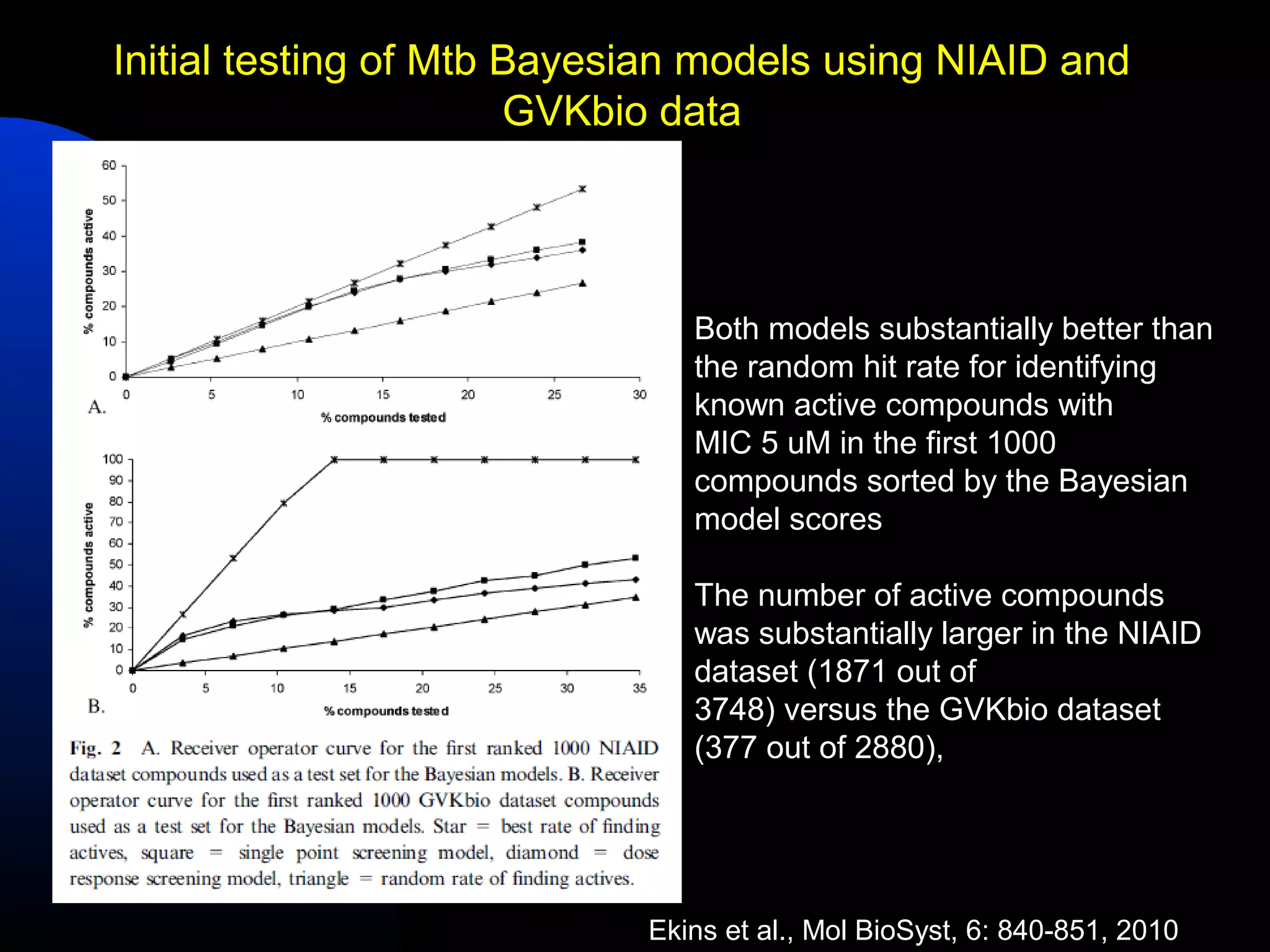
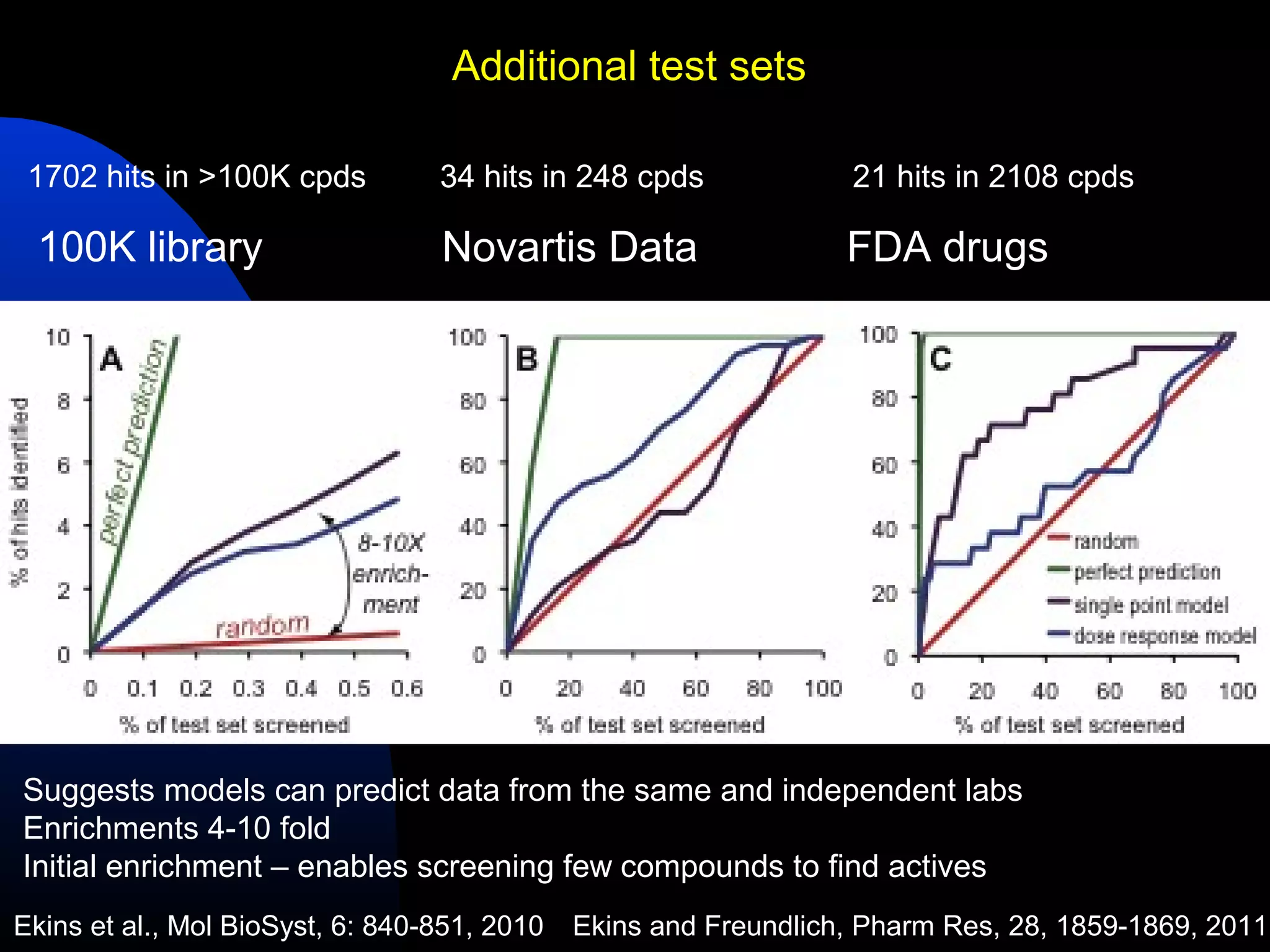
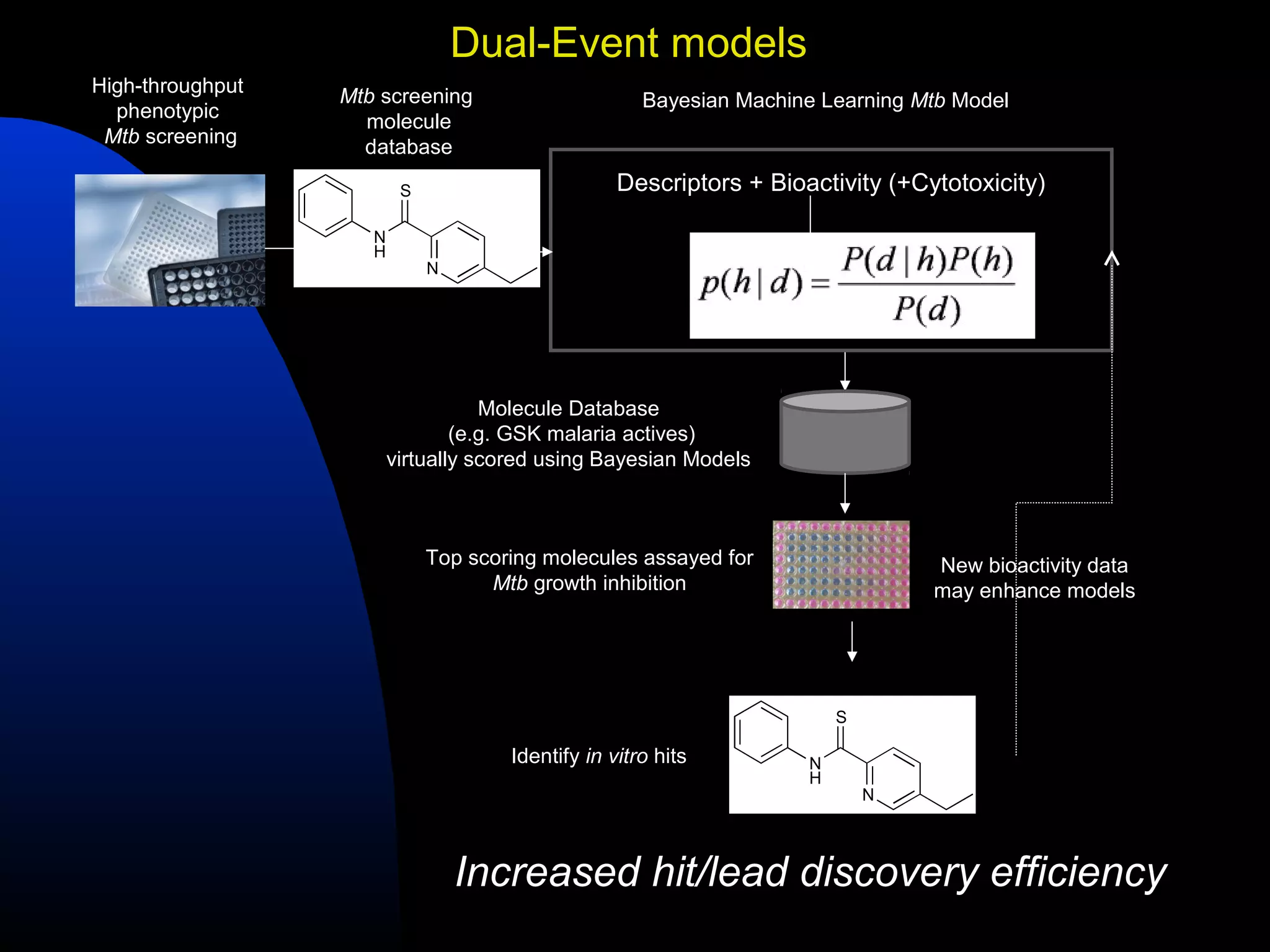
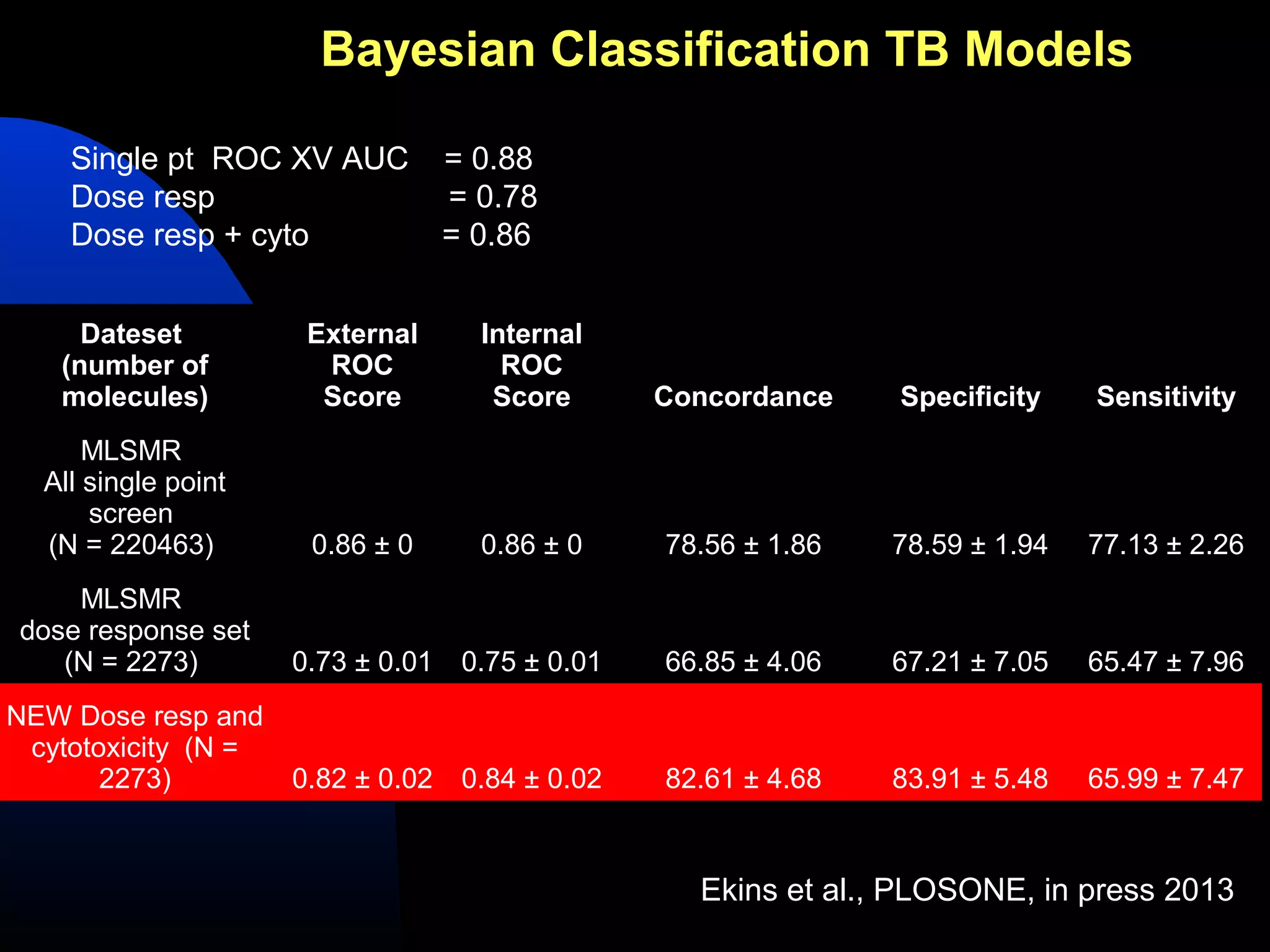
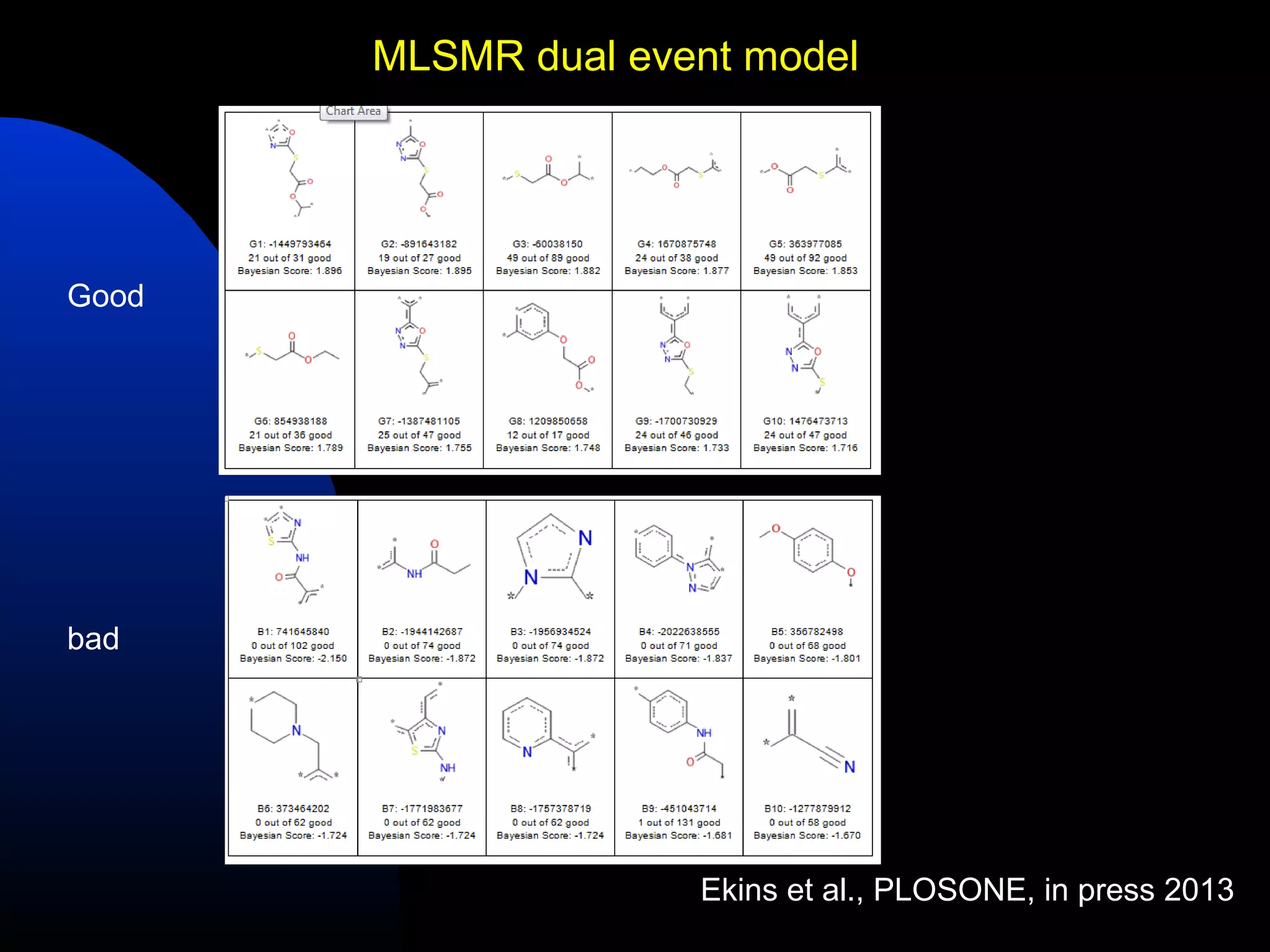
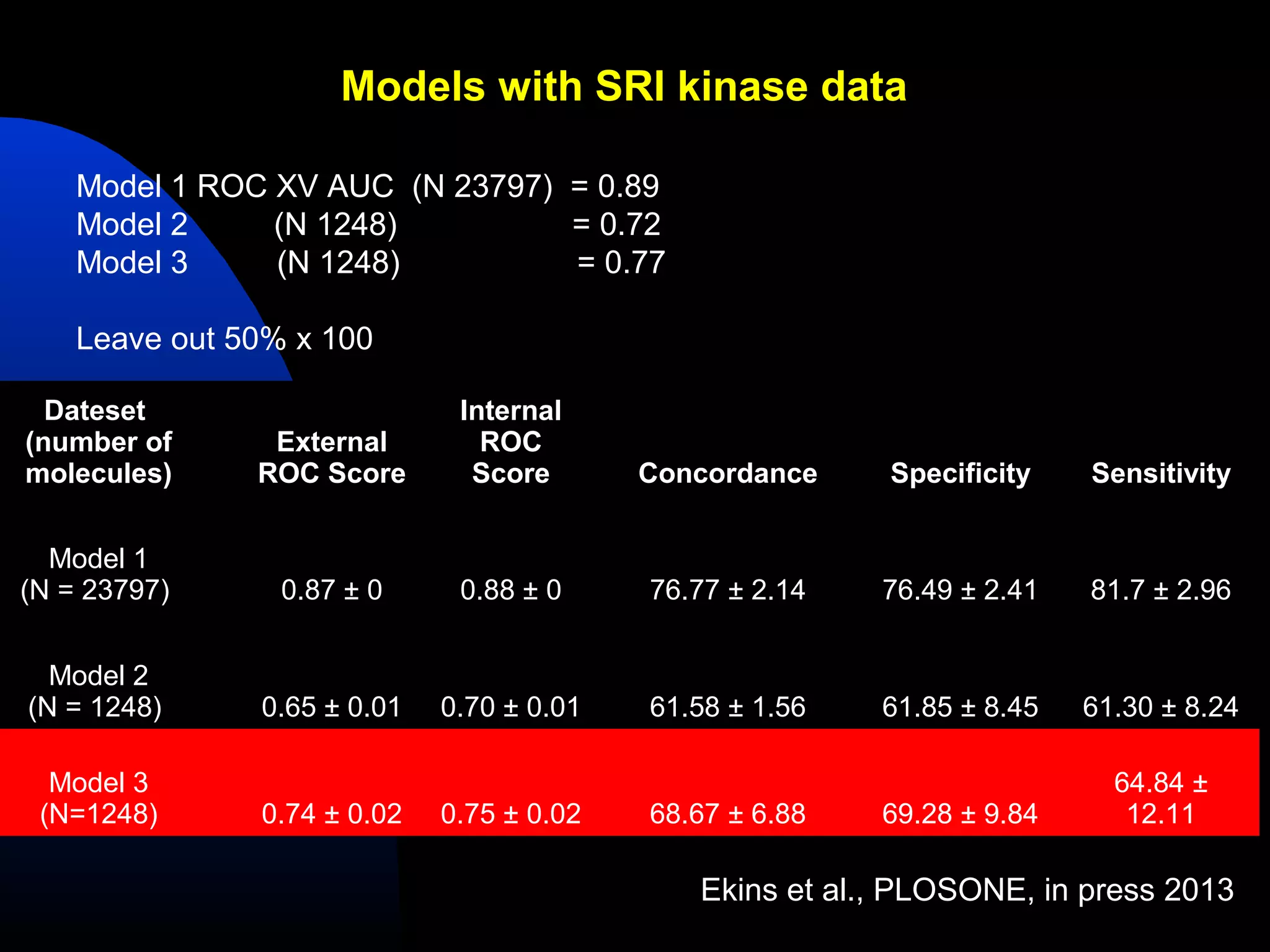
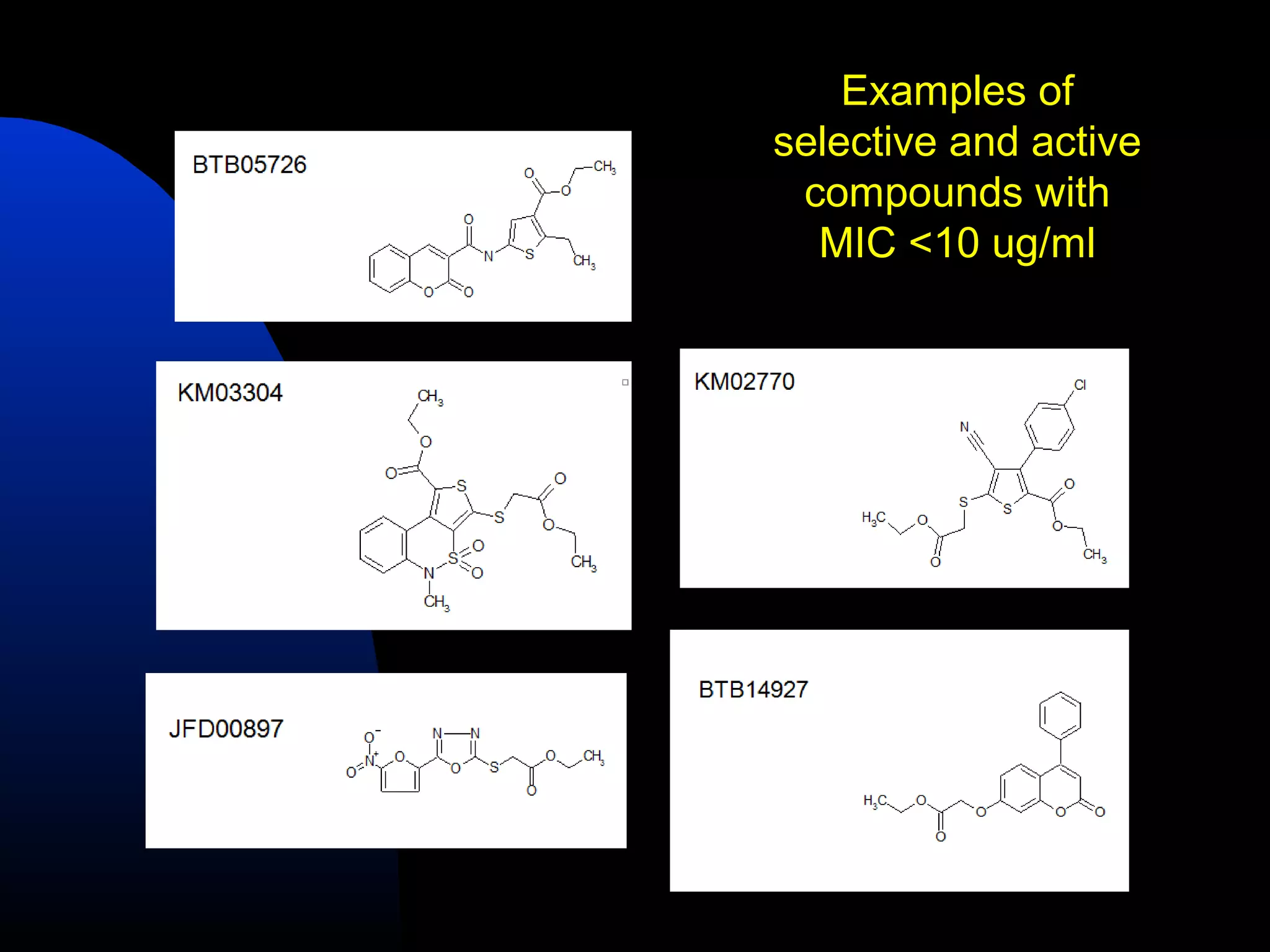
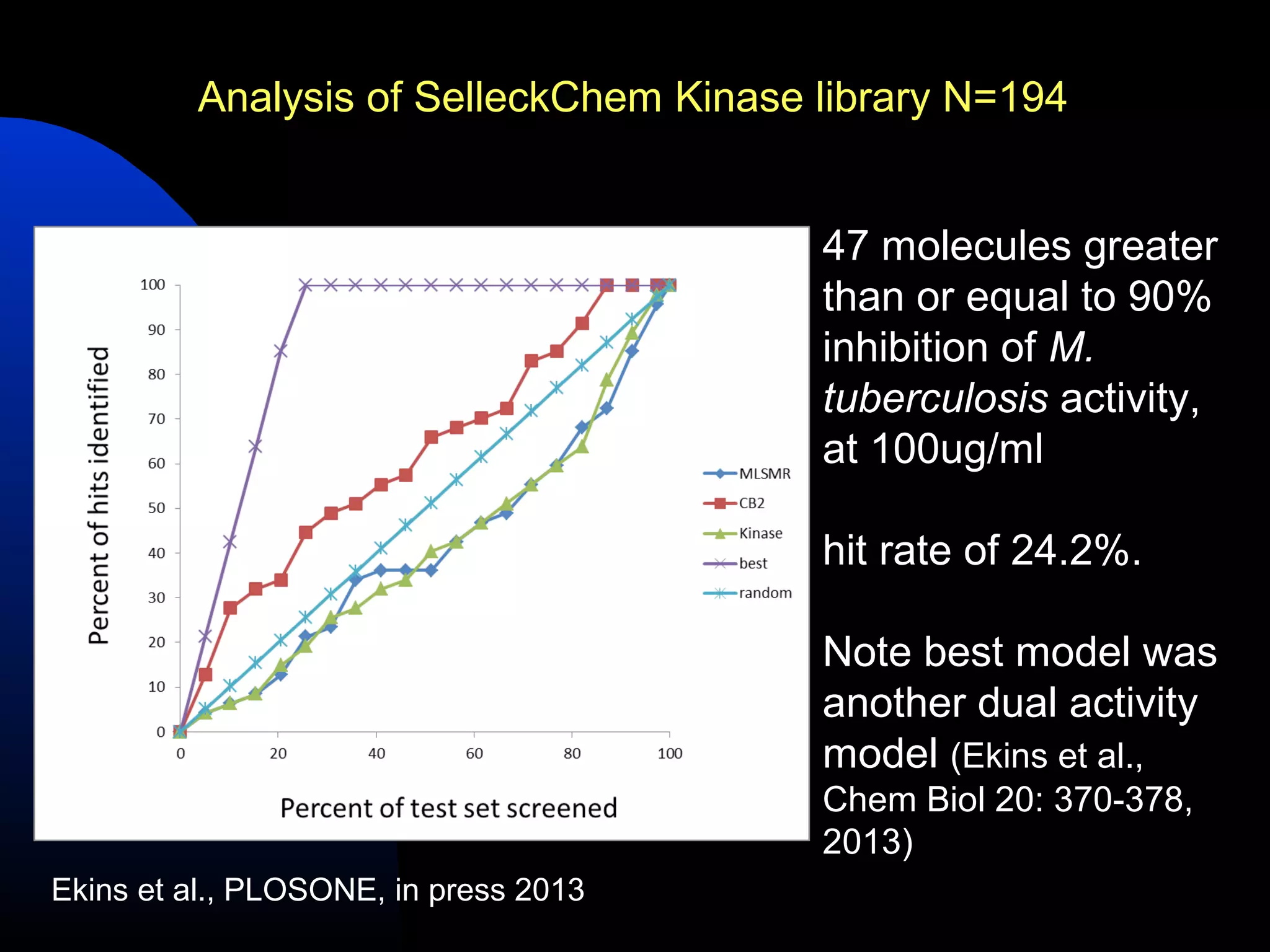
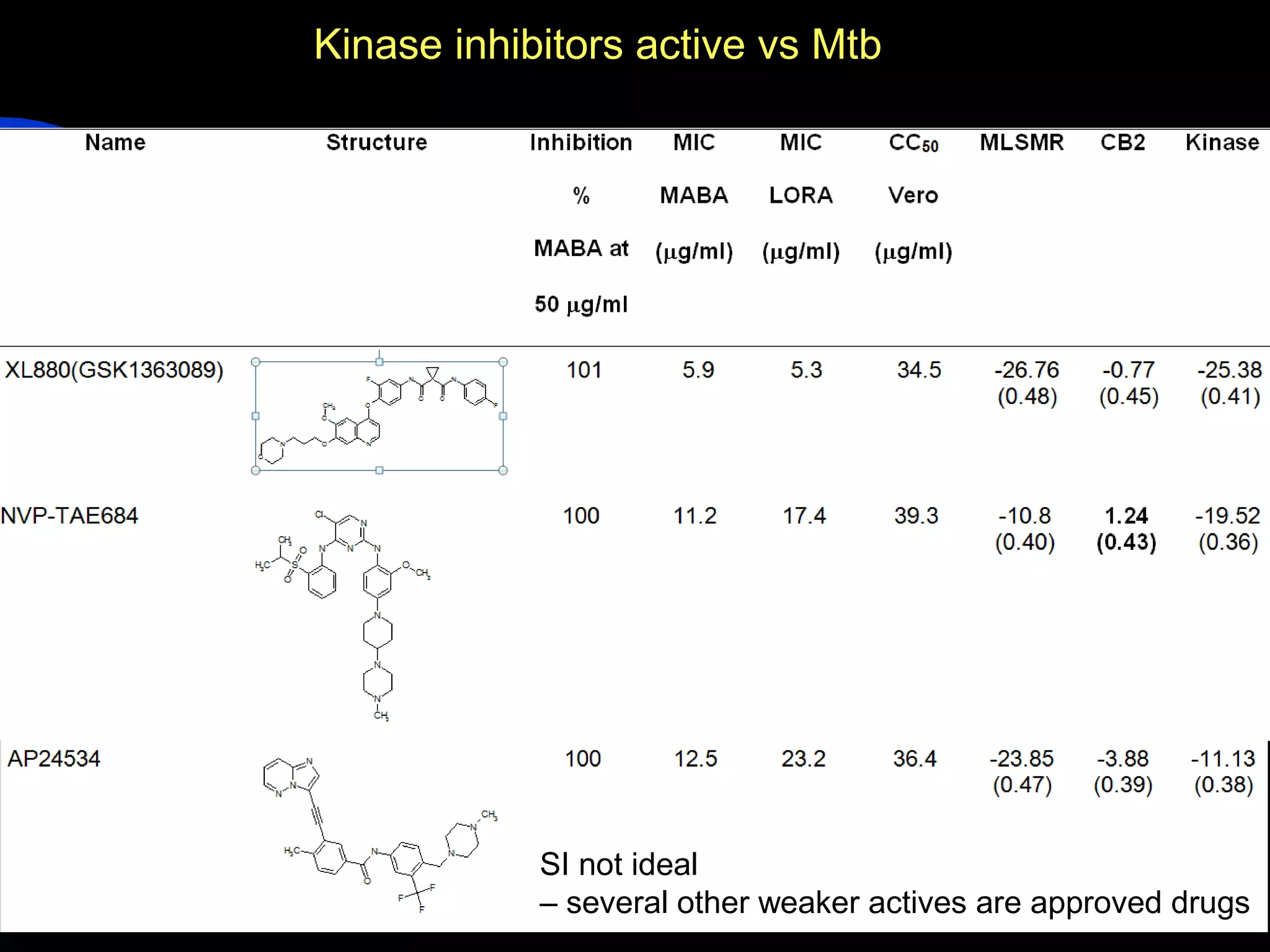
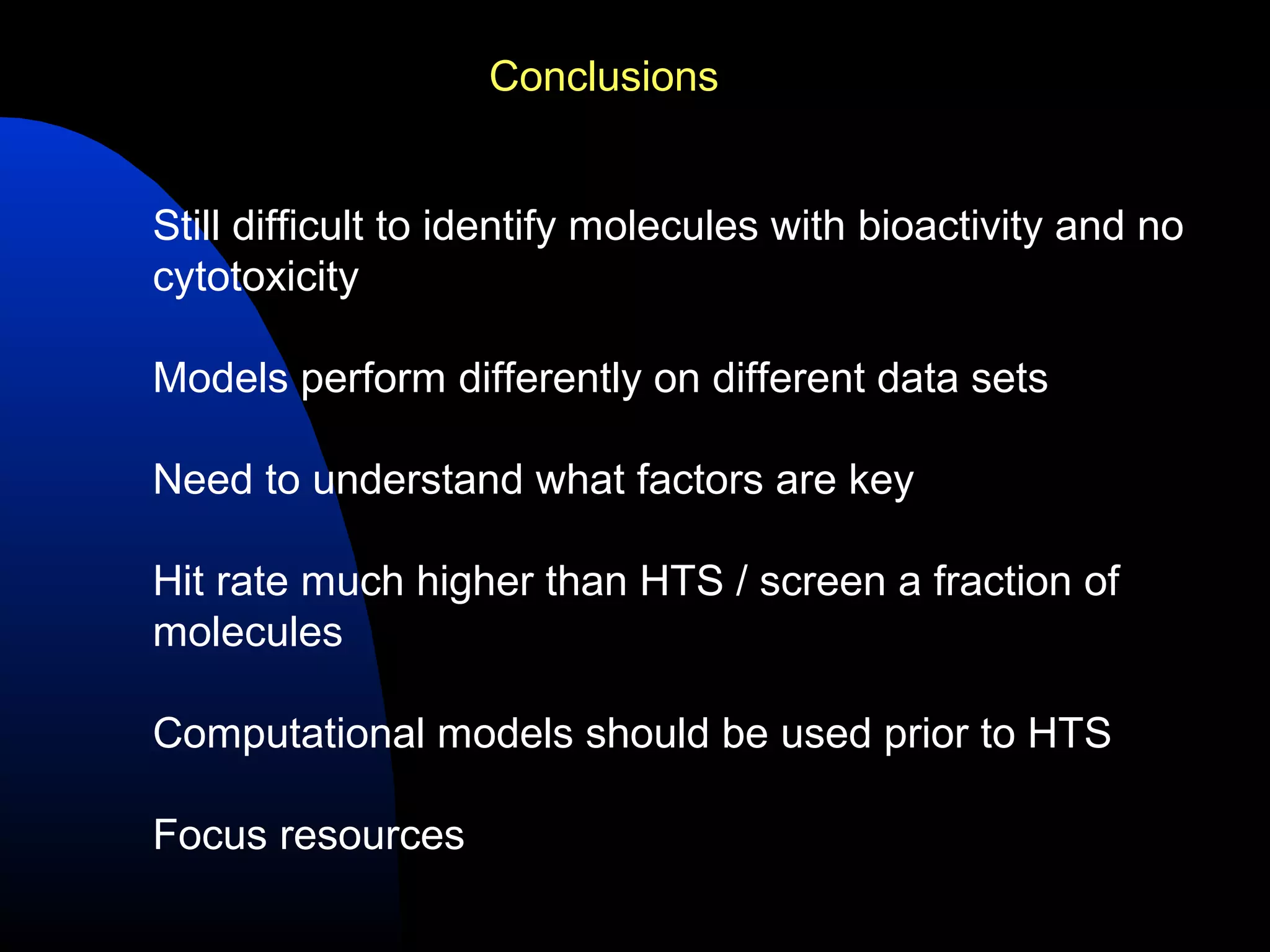
This document summarizes research applying Bayesian machine learning models to enhance high-throughput screening for drug discovery against Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb). The researchers built Bayesian classification models using over 200,000 compounds and their bioactivity data against Mtb. They tested the models on new screening data, achieving hit rates 4-10 times higher than random. The models were also used to prospectively select compounds for screening from large libraries, identifying several novel potent lead series. This work demonstrates that computational models can efficiently prioritize compounds for screening to increase hit discovery for Mtb drug development.