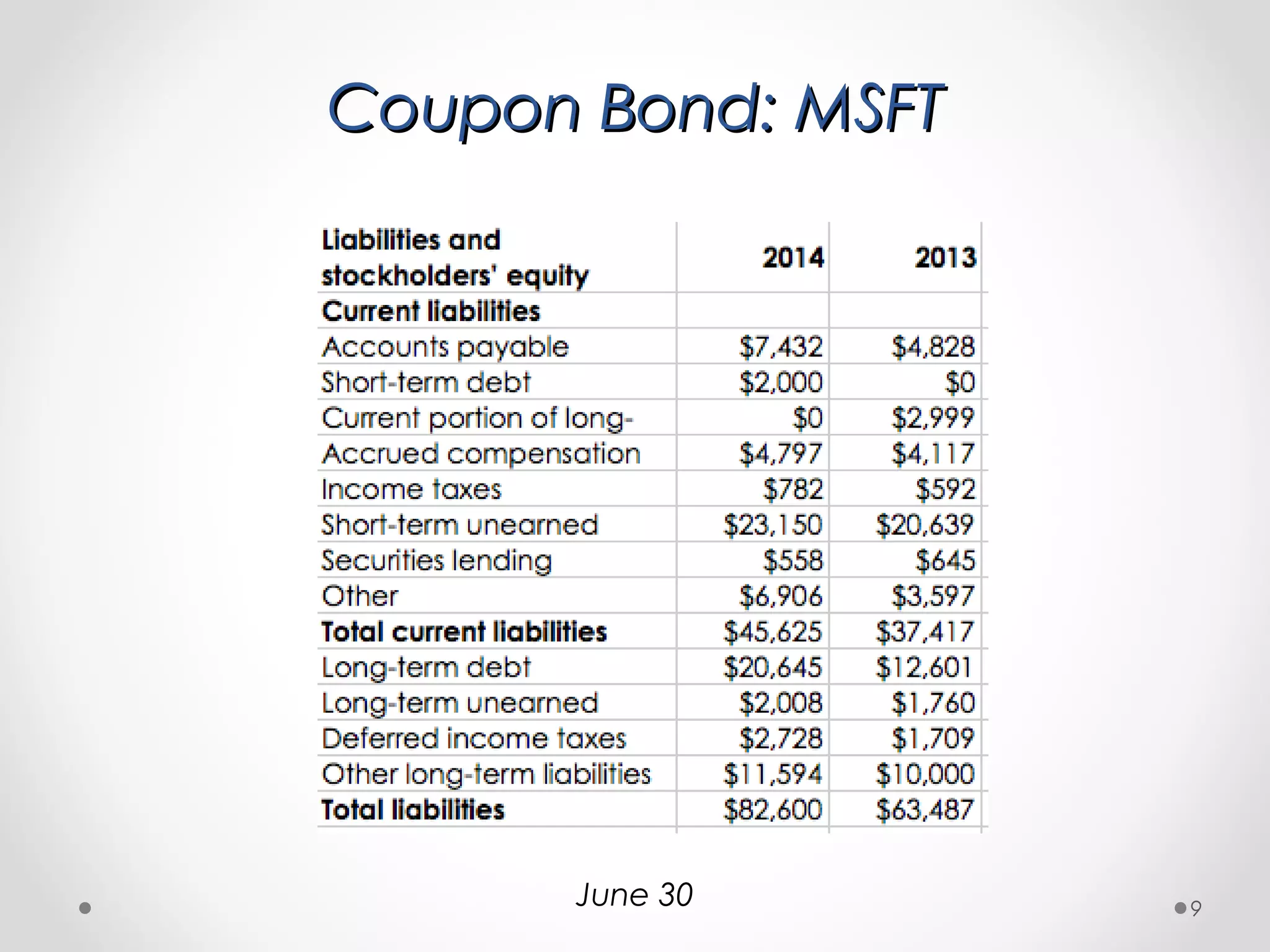
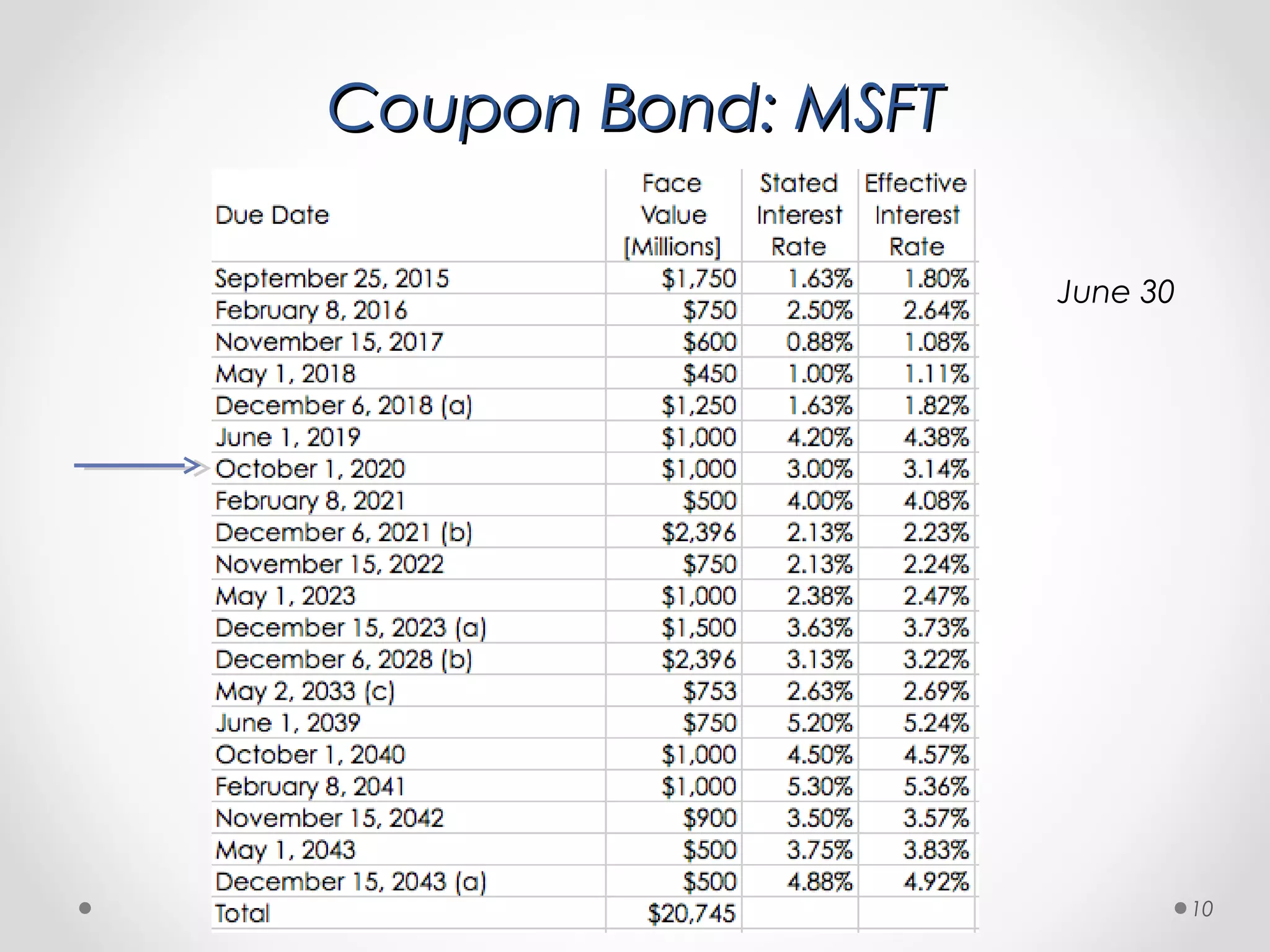
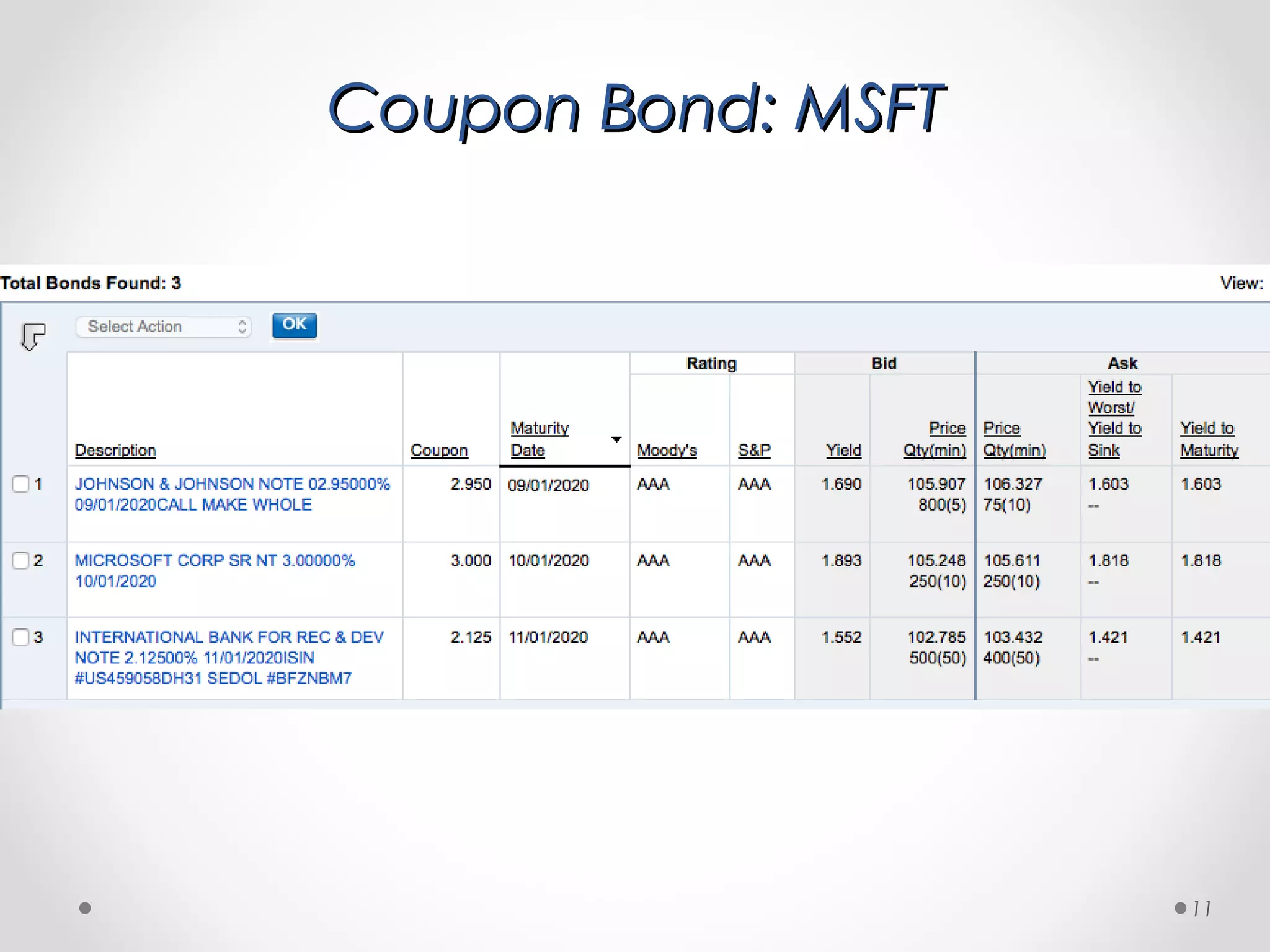
The document provides a comprehensive overview of bond pricing and yields, detailing key bond parameters such as principal, yield, maturity, and coupon rates. It explains calculations for bond prices and yields for both zero coupon and coupon bonds, alongside practical examples. Additionally, it addresses concepts like reinvestment risk and the impact of cash flow timing on bond pricing.