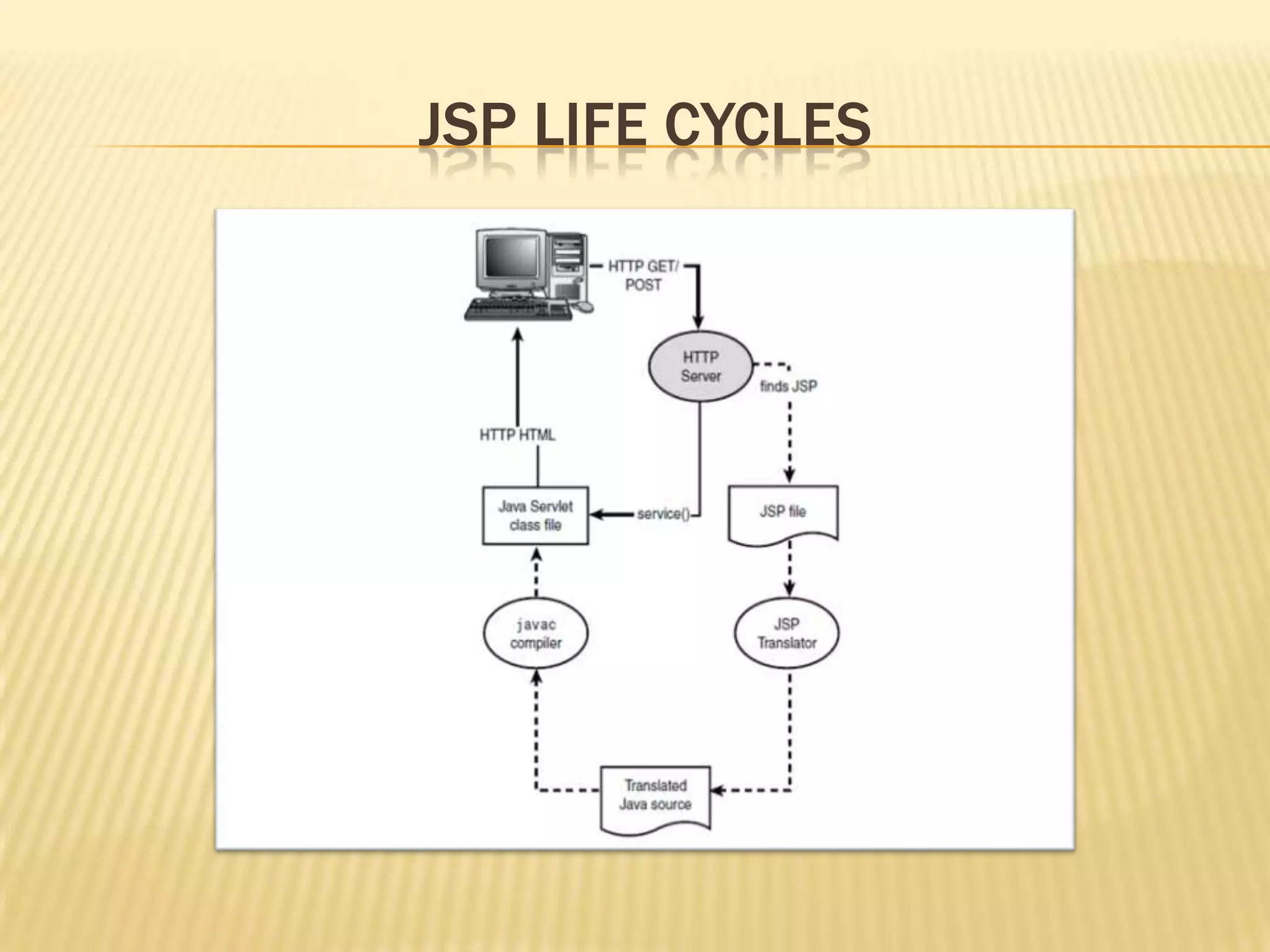
JSP is a technology based on Java that produces dynamic web pages. JSP files contain HTML tags as well as special JSP tags where Java code is embedded. There are three main types of JSP elements - directives, scripting elements, and action elements. Directives provide information to the JSP engine, scripting elements contain Java code, and action elements perform tasks like accessing Java beans. Common implicit objects in JSP include application, page, session, and request objects. Java beans can be used with JSP through action tags like useBean, setProperty, and getProperty.