1. The document discusses reactions of alcohols including deprotonation, protonation, oxidation, and formation of esters and ethers.
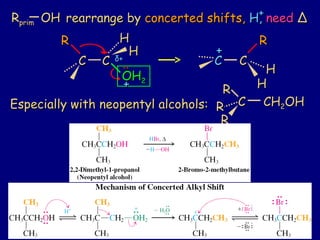
2. Specific reactions covered include deprotonation of primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols using various bases, carbocation rearrangements during SN1 reactions, and formation of ethers through SN2 and SN1 reactions of alcohols.
3. Ethers can be synthesized from alcohols through Williamson ether synthesis and cyclic ethers can be formed through an intramolecular version of this reaction.

![1. Deprotonation:1. Deprotonation:
ppKKaa (ROH) ~ 15-18.(ROH) ~ 15-18.
Need base stronger than RO :Need base stronger than RO :
a. RLi , e.g., CHa. RLi , e.g., CH33Li [pLi [pKKaa(CH(CH44) ~ 50];) ~ 50];
b. Na NHb. Na NH22 ( NH( NH33, 35); LDA (R, 35); LDA (R22NH, 40);NH, 40);
c.c. K H or Li H (HK H or Li H (H22, 38);, 38);
d. (CHd. (CH33))33CO [(CHCO [(CH33))33COH, 18]COH, 18]
--
::::
::
::
::
--++ ::
::
::
--
::
::
::
--++
::
--++](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter9-140330084459-phpapp02/85/Chapter9-2-320.jpg)










![Use of Inorganic EstersUse of Inorganic Esters
Mild way to convert ROH RXMild way to convert ROH RX withoutwithout HH++
Reagents:Reagents: PPBrBr33 for Rfor RBrBr;; PPClCl33 oror ClClSSClCl for Rfor RClCl..
OO
3R3ROOHH ++ PPBrBr33 3R3RBrBr ++ HH33PPOO33 [“[“PP((OOHH))33”]”]
Phosphorous acidPhosphorous acid
Mechanisms go through inorganic esters asMechanisms go through inorganic esters as
reactive intermediates (not isolated).reactive intermediates (not isolated).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter9-140330084459-phpapp02/85/Chapter9-14-320.jpg)



































