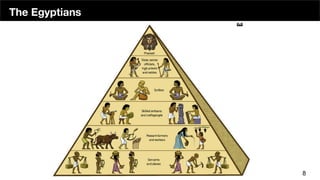
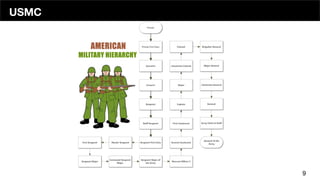
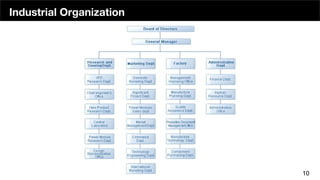
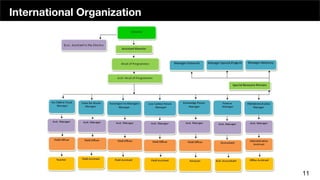
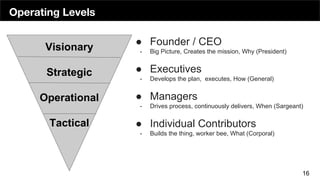
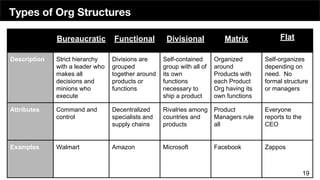
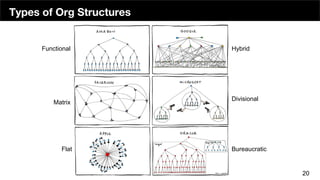
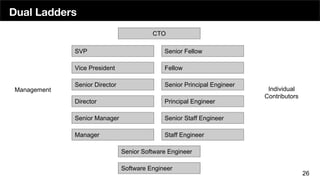
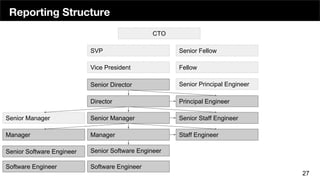
The document discusses the organizational structure of software companies, emphasizing the importance of understanding hierarchies, roles, and communication to navigate and advocate for oneself effectively. It outlines different types of organizational structures (bureaucratic, functional, divisional, matrix, flat) and operating levels (visionary, strategic, operational, tactical), as well as career paths for executives, managers, and individual contributors. The key takeaway is that one must learn the existing rules of an organization before attempting to implement change.