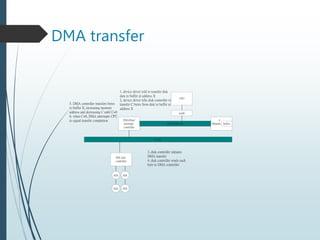
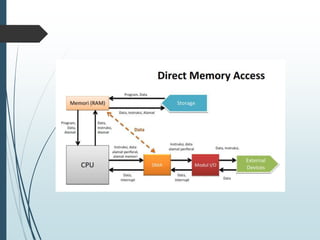
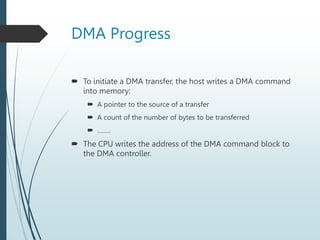
Direct Memory Access (DMA) allows data to be transferred directly between peripheral devices and memory without intervention from the central processing unit (CPU). This improves efficiency by avoiding the need to transfer data into CPU registers one byte at a time. To initiate a DMA transfer, the CPU writes a DMA command to memory specifying the source, number of bytes, and address. The DMA controller then operates the memory bus directly to transfer data while handshaking with the device controller. When complete, the DMA controller interrupts the CPU.