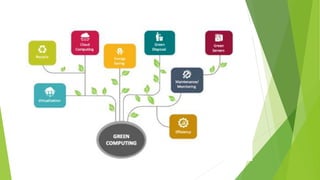
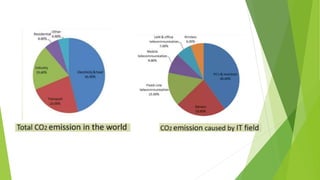
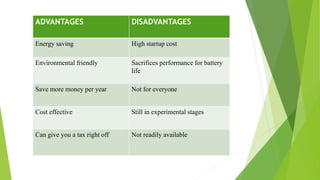
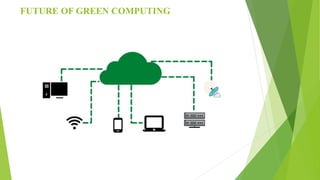
Green computing involves designing, manufacturing, and disposing of computers and servers with minimal environmental impact. It aims to reduce energy usage and hazardous materials. Approaches to green computing include virtualization and telecommuting to reduce resource usage and emissions. The goals are to mitigate climate change, save costs, ensure reliable power supplies, and properly dispose of electronics. Green computing is still developing but offers benefits like energy savings, environmental protection, and cost reductions over time.