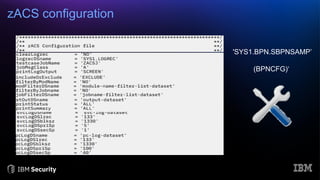
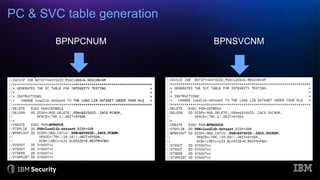
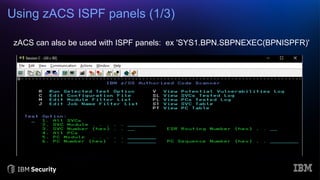
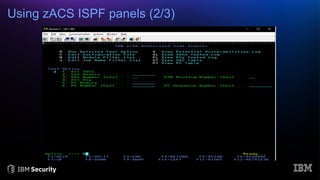
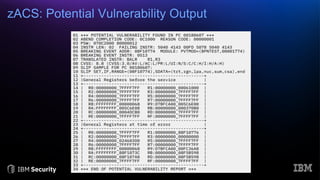
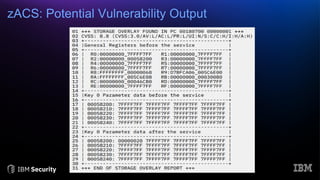
The document discusses system integrity on z/OS, emphasizing the importance of safeguarding against unauthorized access and exposure through various controls such as the authorized programming facility (APF) and resource access control facility (RACF). It introduces the IBM Z/OS Authorized Code Scanner (ZACS), a tool designed to help clients identify potential vulnerabilities in their authorized code and improve their security posture. The document also details the process for running ZACS and interpreting its outputs to address vulnerabilities.