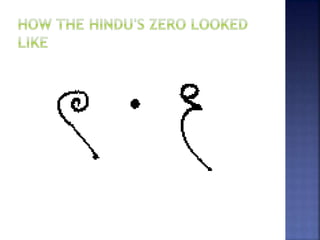
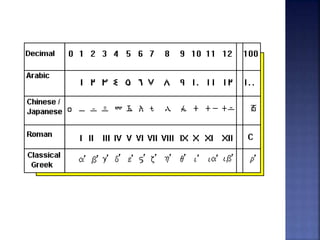
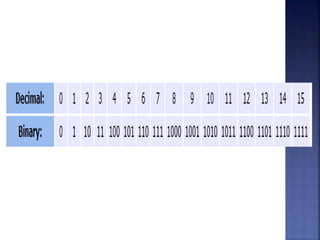
The document discusses the origins and importance of the number zero. It notes that zero was independently discovered by the Mayans and Indians, with the Indians representing it as a dot and the Mayans using a pair of wedges. The concept of zero spread to the Arabic world and was represented as a circle. It was introduced to Europe in the 9th century by an Italian mathematician. The document emphasizes that life would be much more complicated without zero, as it is a fundamental part of modern number systems like binary used in computers.