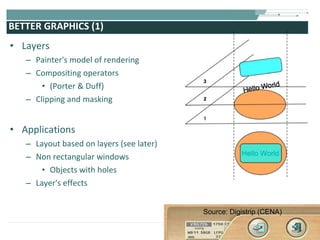
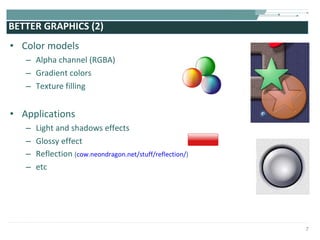
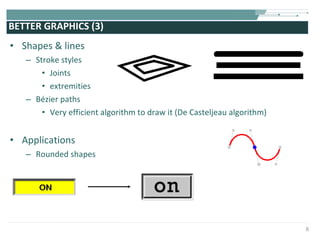
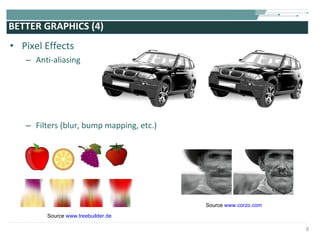
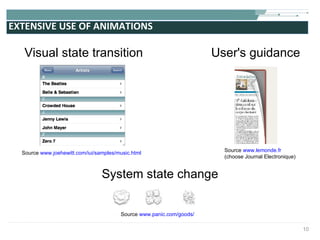
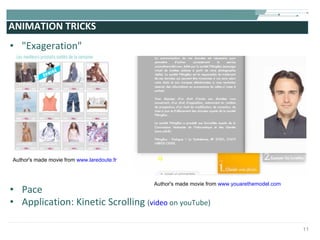
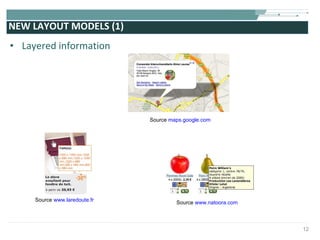
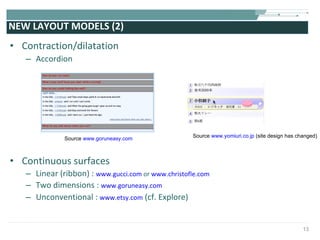
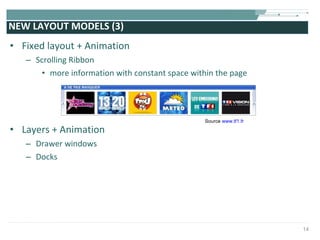
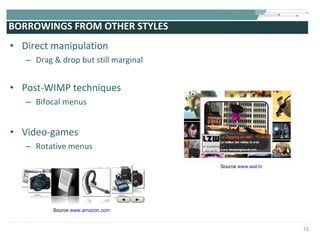
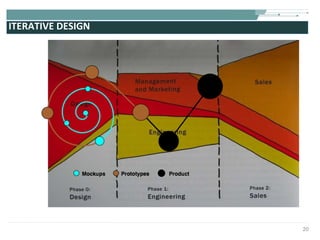
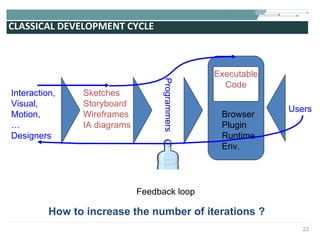
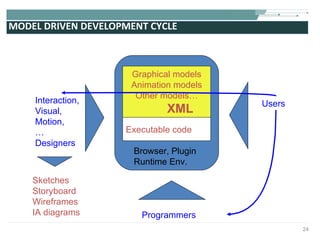
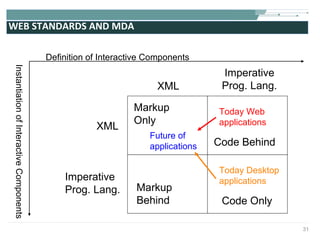
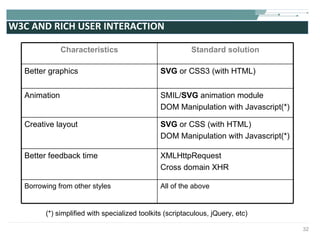
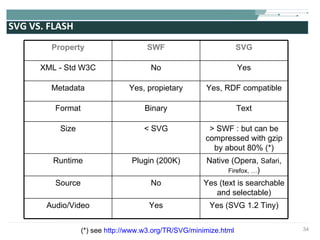
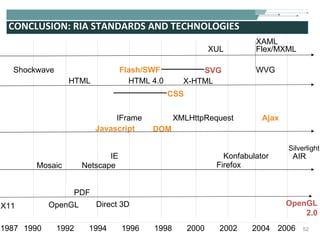
The document discusses the evolution of rich user interaction styles in graphical user interfaces (GUIs) utilizing SVG and multimedia elements, emphasizing iterative design and supportive technologies. It covers the characteristics of rich user interaction, such as improved graphics, animations, and user feedback, as well as web standards related to graphical design. The document further outlines the development of SVG, its advantages over other formats, and its application in creating interactive components.




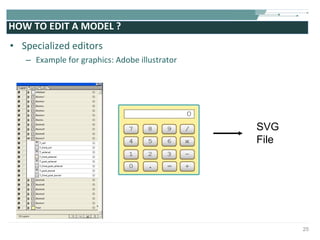
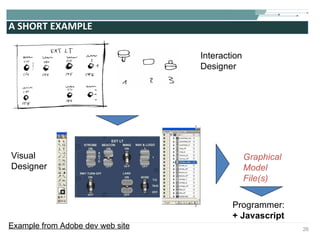
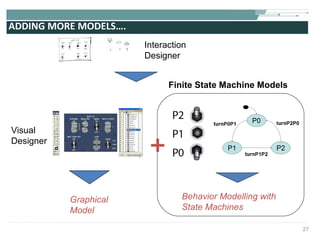








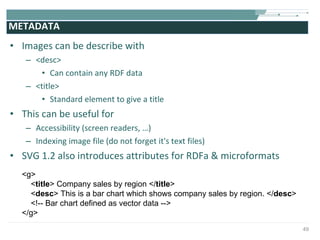
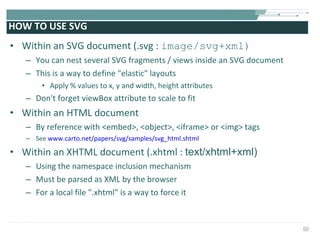

![COMPLETE SVG FILE EXAMPLE <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!DOCTYPE svg [ <!-- entities etc. here --> ]> <svg version="1.1" baseProfile="full" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink" width="8cm" height="6cm"> <defs> <!-- resources to be reused --> <linearGradient id="Gradient01"> <stop offset="20%" stop-color="#39F" /> <stop offset="90%" stop-color="#F3F" /> </linearGradient> <rect id="shape" width="1cm" height="1cm" stroke="blue" stroke-width="0.1cm"/> </defs> <!-- content --> <rect x=".1cm" y=".1cm" width="7.9cm" height="5.9cm" fill="none" stroke="black" stroke-width="1px" /> <use x="1cm" y="1cm" xlink:href="#shape" fill="#BBB"/> <use x="4cm" y="1cm" xlink:href="#shape" fill="url(#Gradient01)"/> <use x="1cm" y="4cm" xlink:href="#shape" fill="url(#Gradient01)"/> <use x="4cm" y="4cm" xlink:href="#shape" fill="blue"/> </svg>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/svgmd4slideshare2009-091002091454-phpapp01/85/Rich-User-Interaction-with-SVG-55-320.jpg)