This document provides tips for writing a high-quality scientific paper, including outlines for each section and brevity in writing. The key points are:
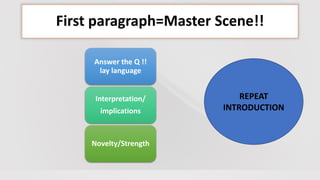
1) Each section of the paper (introduction, methods, results, discussion) should have a clear structure and logical flow of ideas. The introduction should establish the research question and lay background for future sections.
2) It is important to be concise in writing to keep the reader focused on the main points. Less is more.
3) The discussion section should focus on interpreting the main findings in the context of previous literature and addressing limitations, rather than simply reviewing past studies.
4) Writing tools like paraphrasing software, reference managers, and