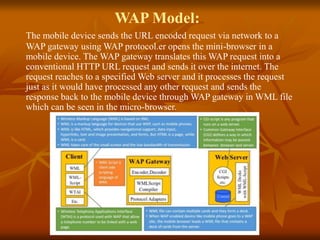
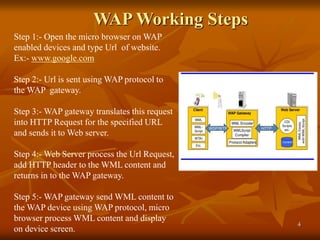
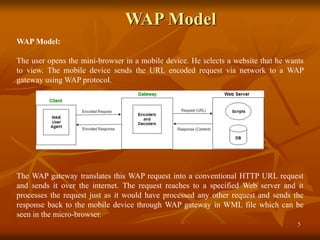
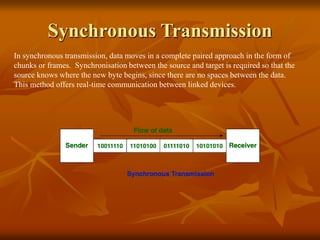
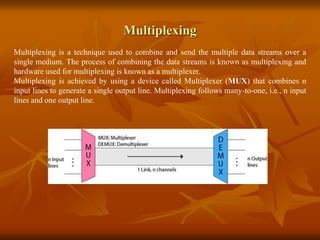
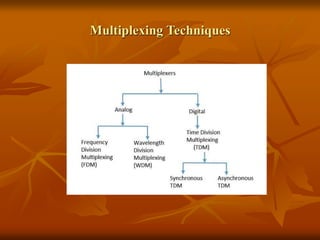
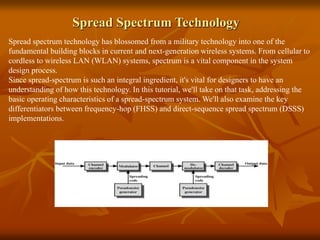
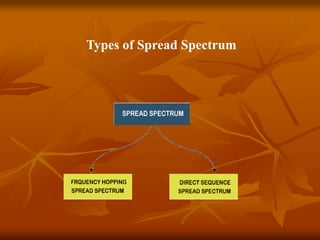
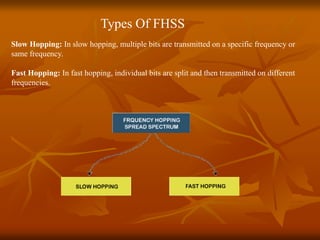
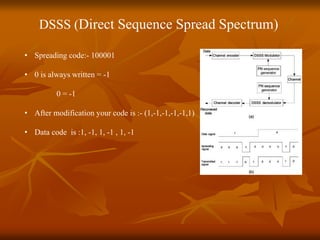
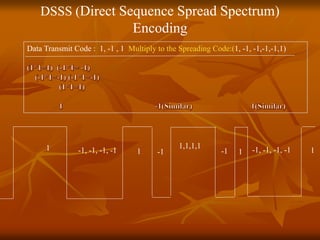
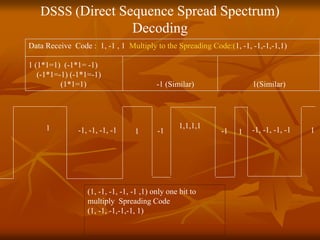
The document provides an overview of Wireless Application Protocol (WAP), detailing its function as a protocol for enabling internet access on mobile devices using Wireless Markup Language (WML). It explains the WAP model, working steps, and the protocol stack that includes various layers for application, session, transaction, security, and transport. Additionally, the document discusses data transmission methods, multiplexing techniques, and spread spectrum technology, covering both frequency-hopping and direct-sequence methods.