Embed presentation
Download to read offline
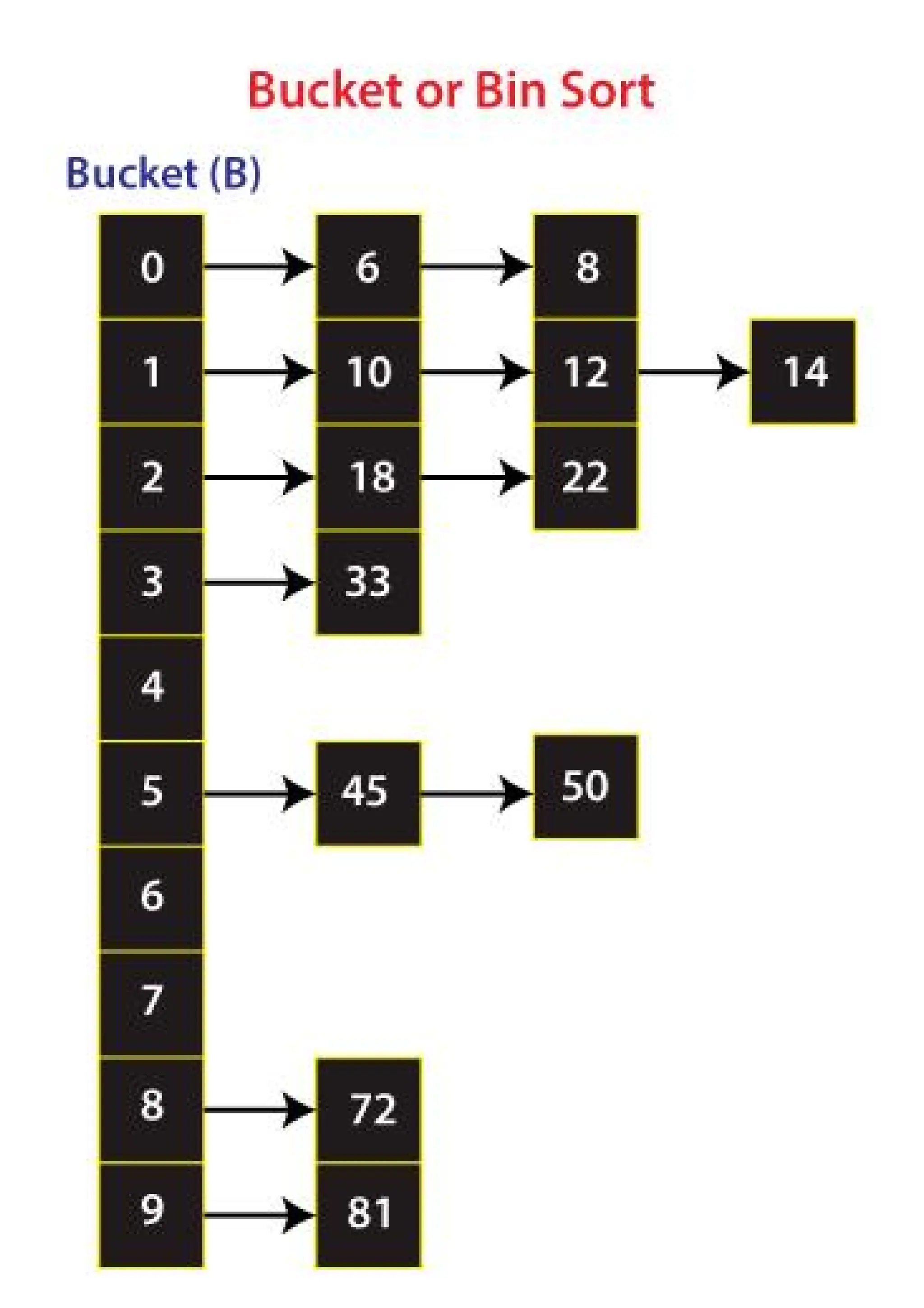
Bucket sort is a sorting algorithm that distributes the elements of an array into several buckets. Each bucket is then sorted individually, either using a different sorting algorithm or recursively applying the bucket sort algorithm. The final sorted array is obtained by concatenating the sorted buckets. How Bucket Sort Works: Create Buckets: Divide the range of input values into n equally spaced intervals (buckets). Distribute Elements: Iterate through the array and place each element into its corresponding bucket based on its value. Sort Buckets: Sort each non-empty bucket. This can be done using another sorting algorithm (like insertion sort) or recursively applying bucket sort. Concatenate Buckets: Finally, concatenate the sorted buckets to get the sorted array. Characteristics: Time Complexity: The average case time complexity is (O(n + k)), where (n) is the number of elements and (k) is the number of buckets. The worst-case time complexity can be (O(n^2)) if all elements fall into a single bucket. Space Complexity: (O(n + k)) due to the storage of buckets. Stability: The bucket sort is stable if the sorting algorithm used for sorting the buckets is stable. Conclusion Bucket sorting is a powerful sorting technique for certain types of data, particularly when the data is uniformly distributed. Its efficiency and potential for parallelization make it a valuable tool in a programmer's toolkit, especially for sorting floating-point numbers or integers within a known range.
