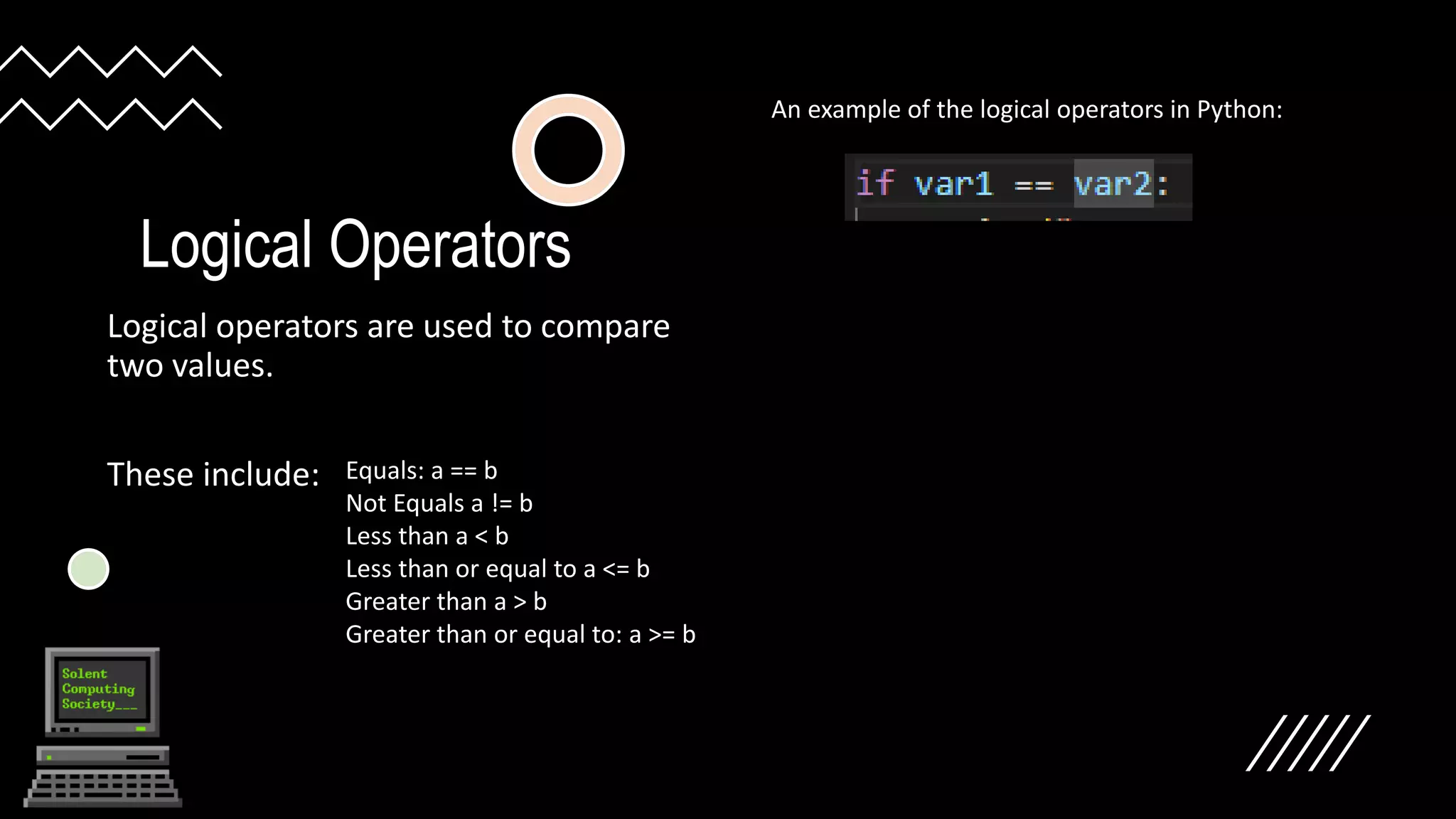
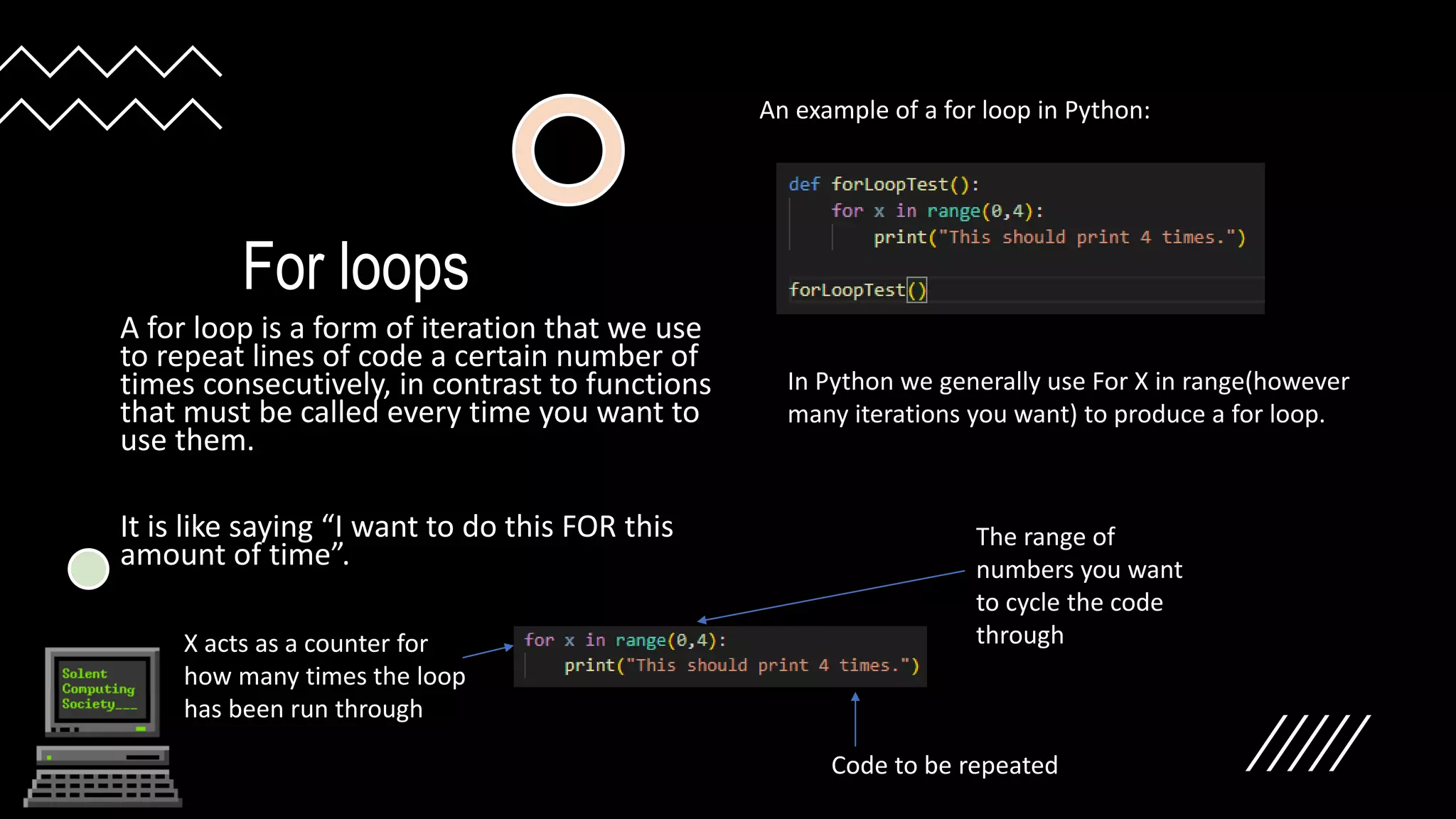
Logical operators like ==, !=, <, <=, >, >= are used to compare two values in Python. If statements allow running code conditionally based on these comparisons. Else statements provide alternative code if the if condition is not met. Functions define reusable blocks of code that can be called anywhere. For loops repeat code a specified number of times using range(), while while loops repeat until a condition is no longer met. Both loops can be placed in functions.