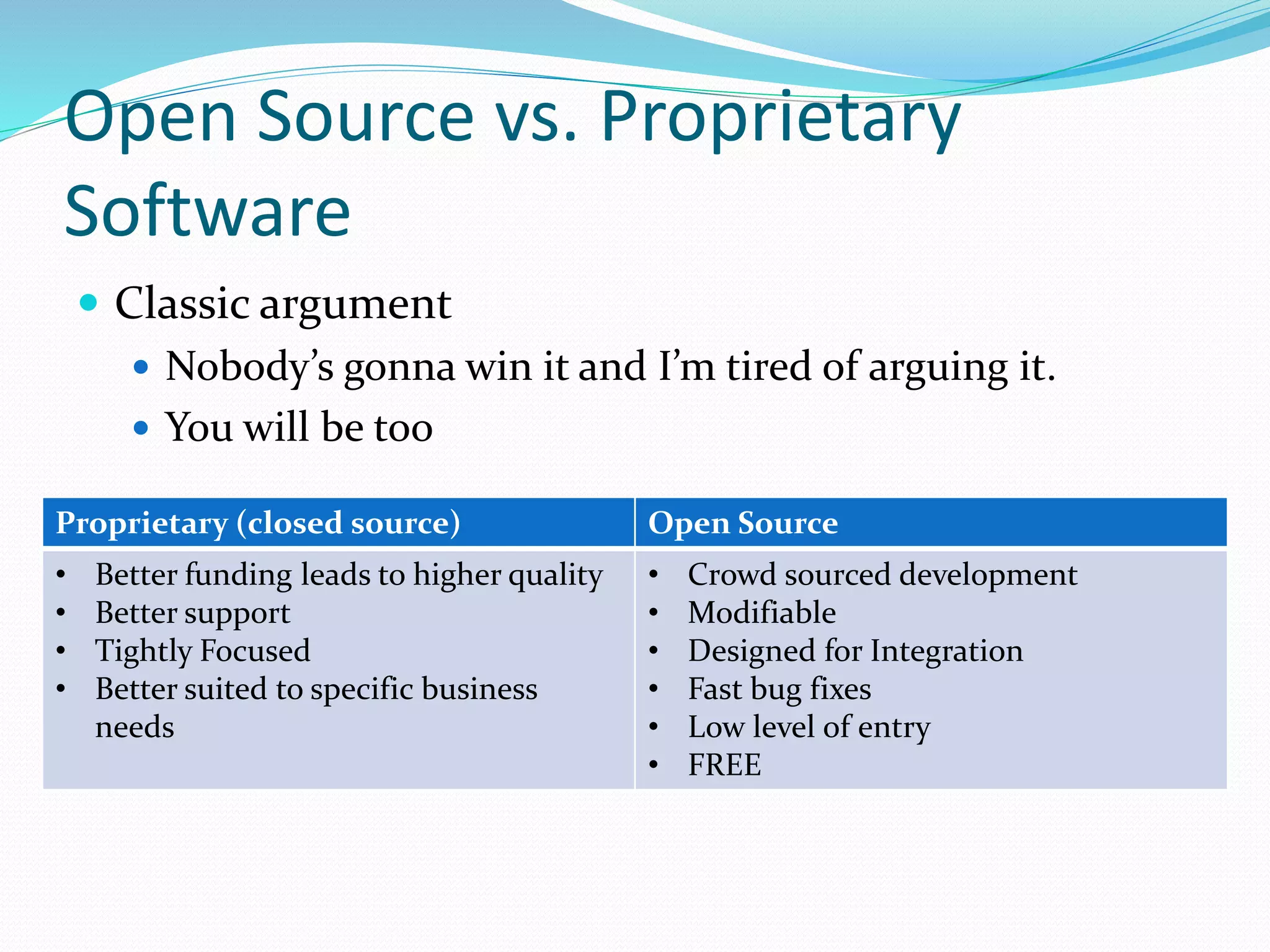
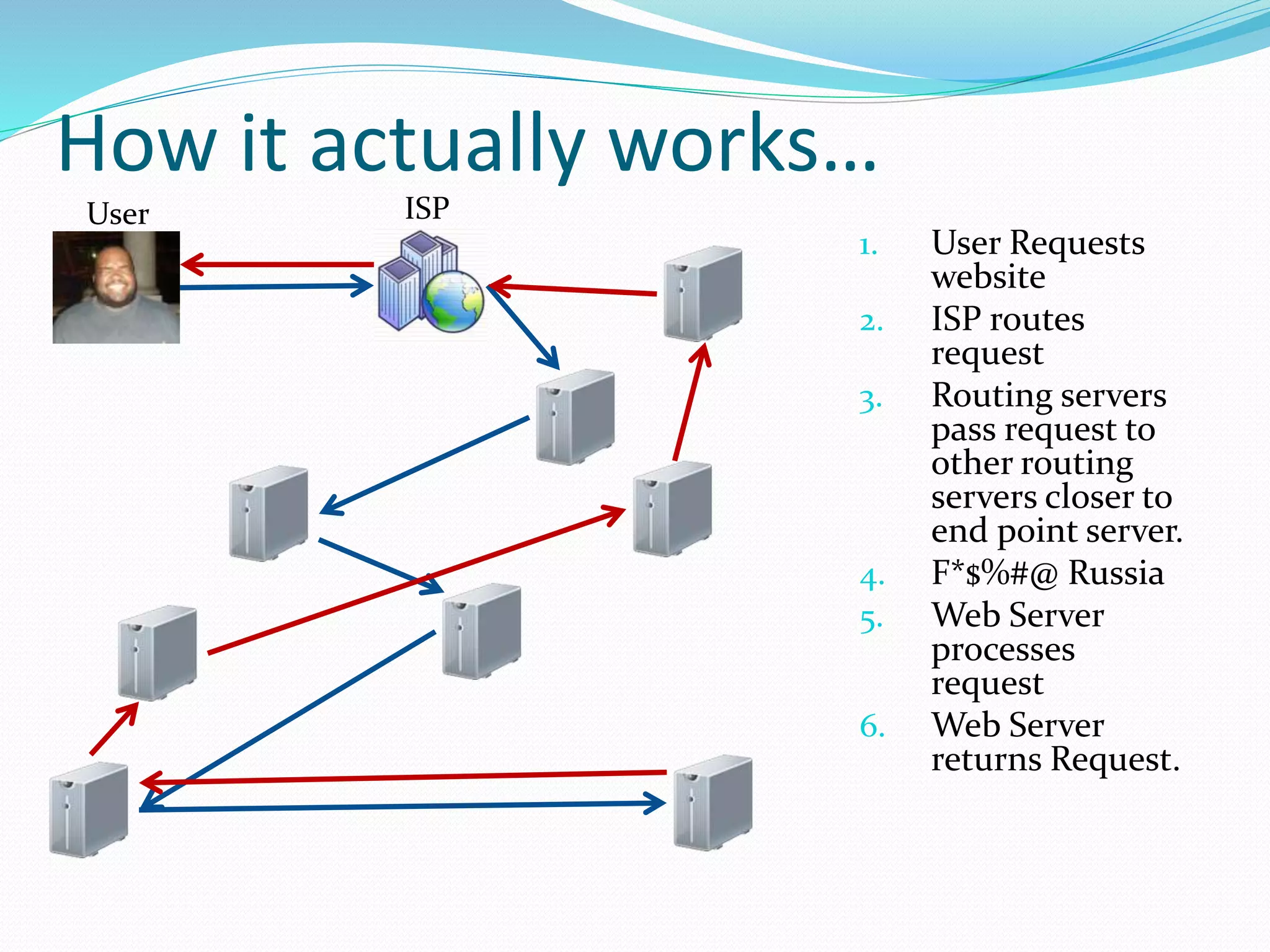
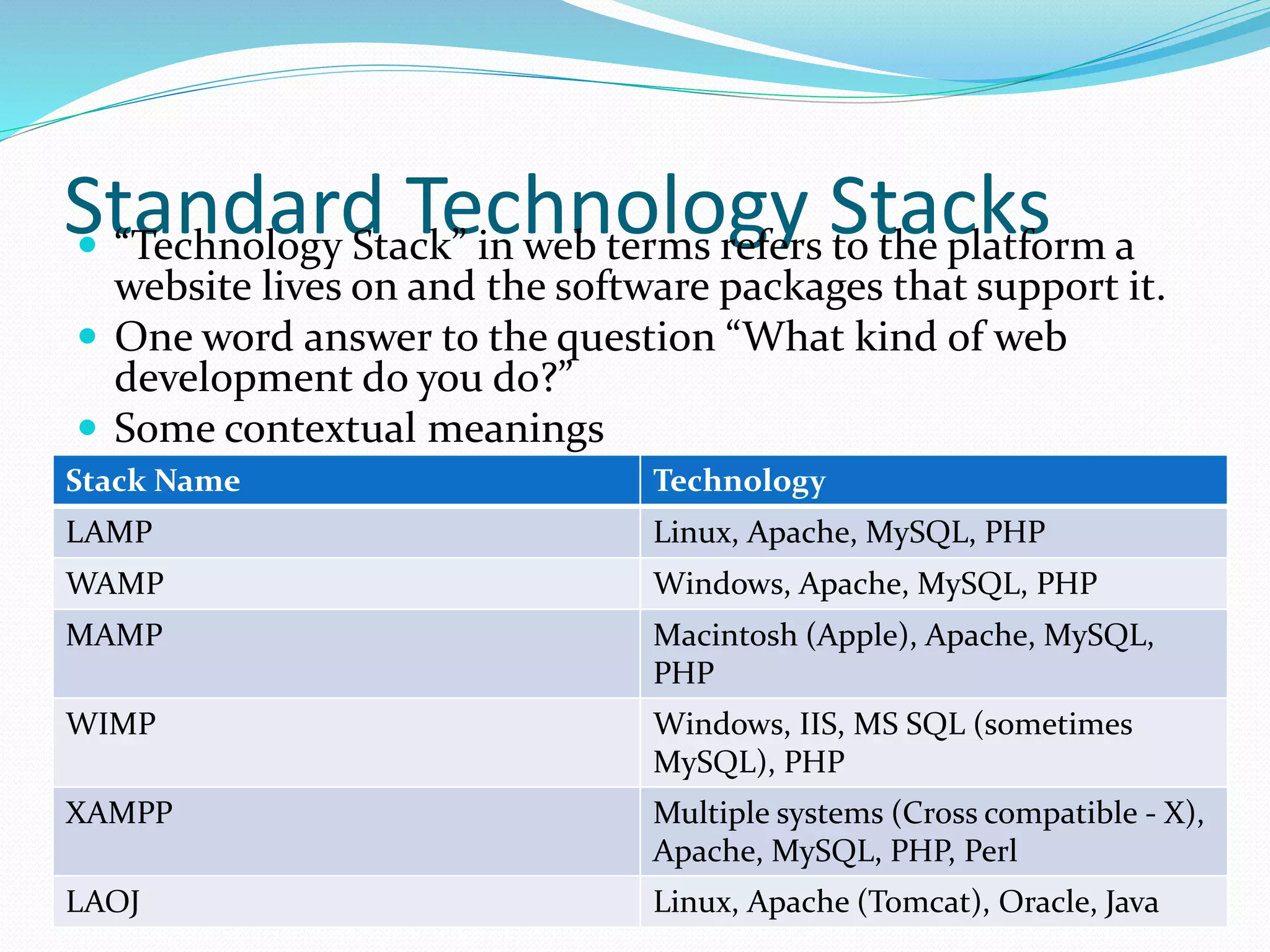
The document outlines a web development course taught by Nick Hepner, emphasizing the fundamentals of web technologies including HTML, PHP, and relational databases. It discusses the characteristics of open source versus proprietary software, the roles of browsers and servers, and the structure of the web, while also touching on different technology stacks. Additionally, it introduces various programming languages and tools essential for web development, highlighting important concepts like markup, caching strategies, and data management.