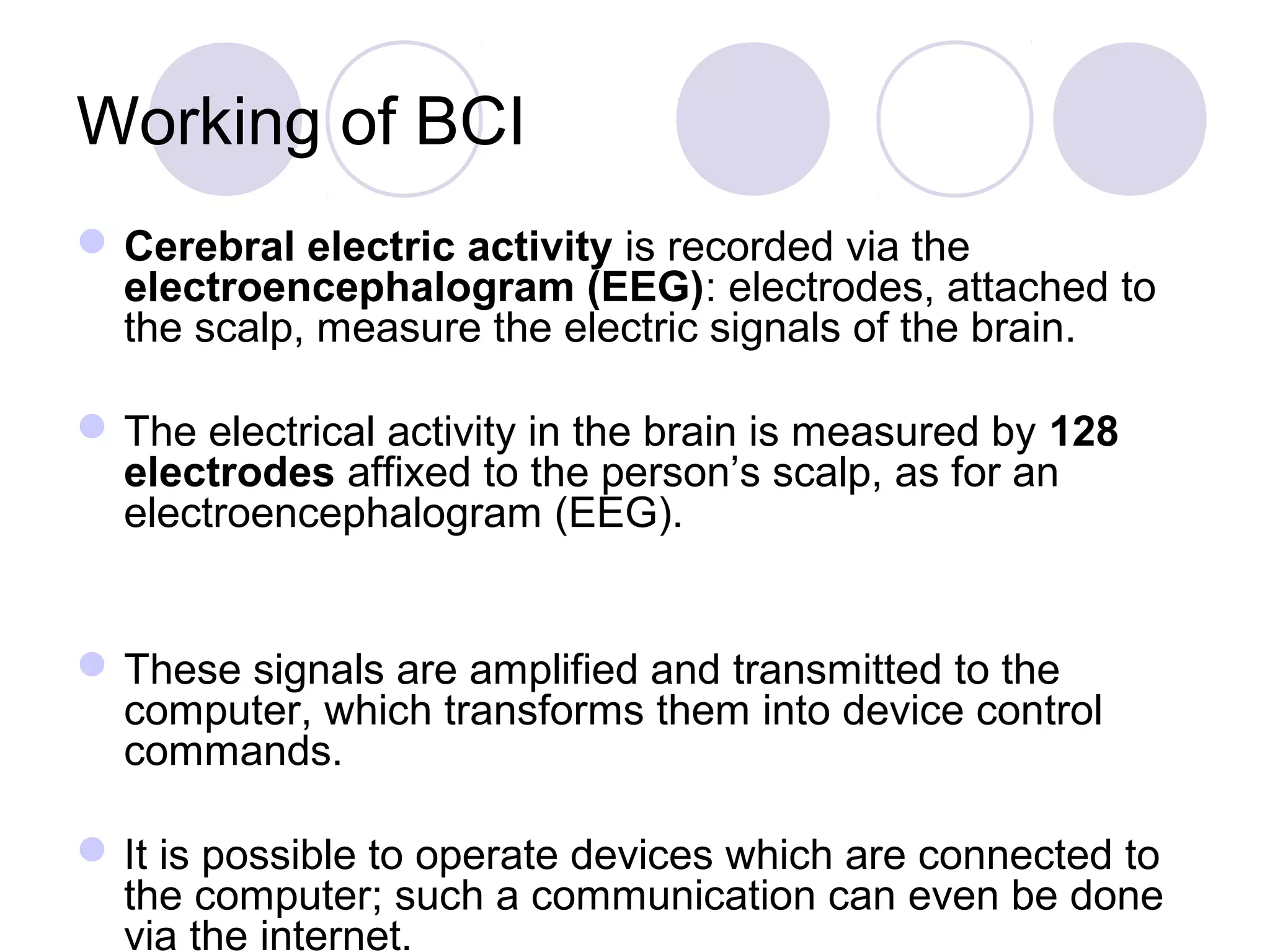
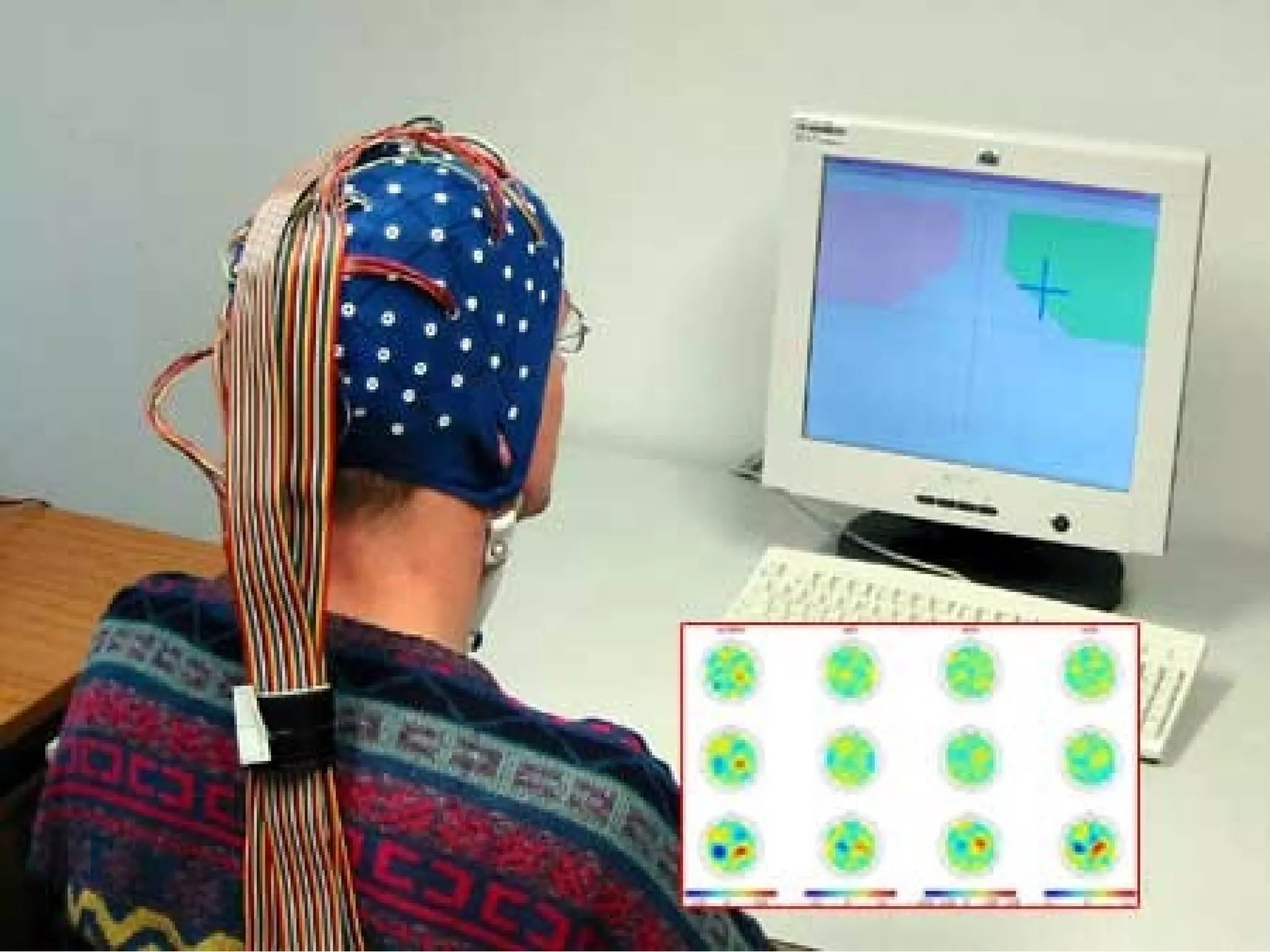
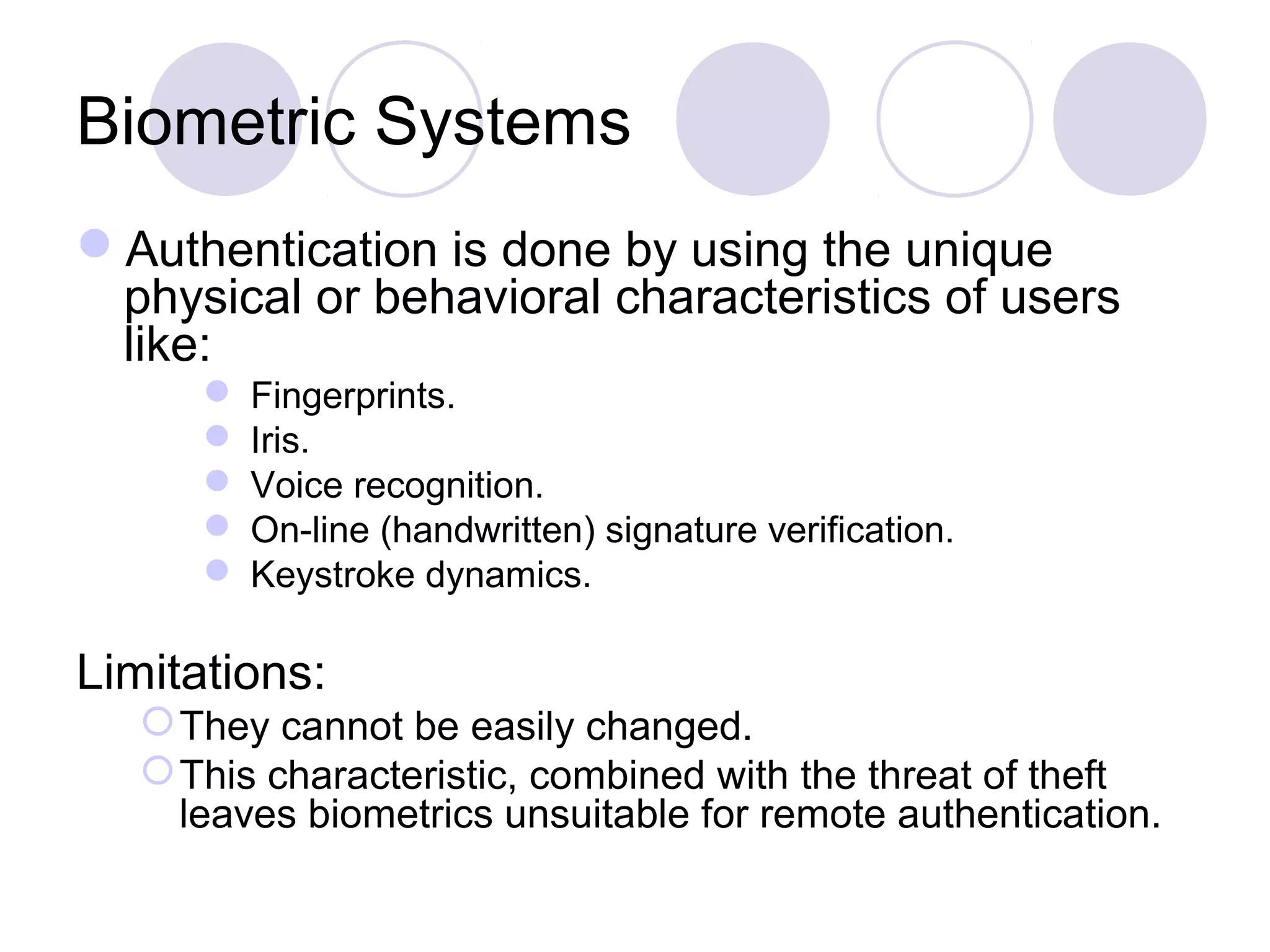
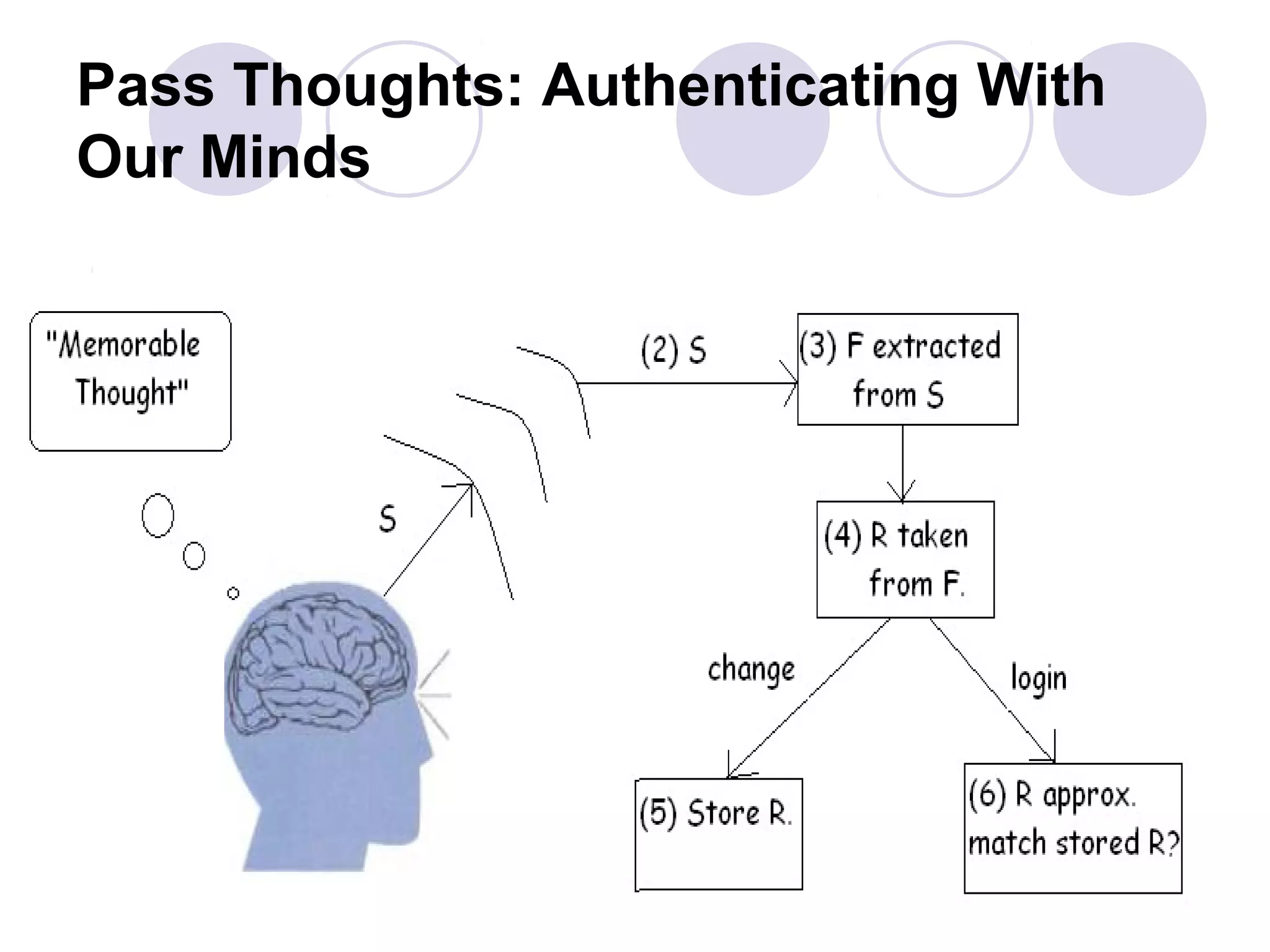
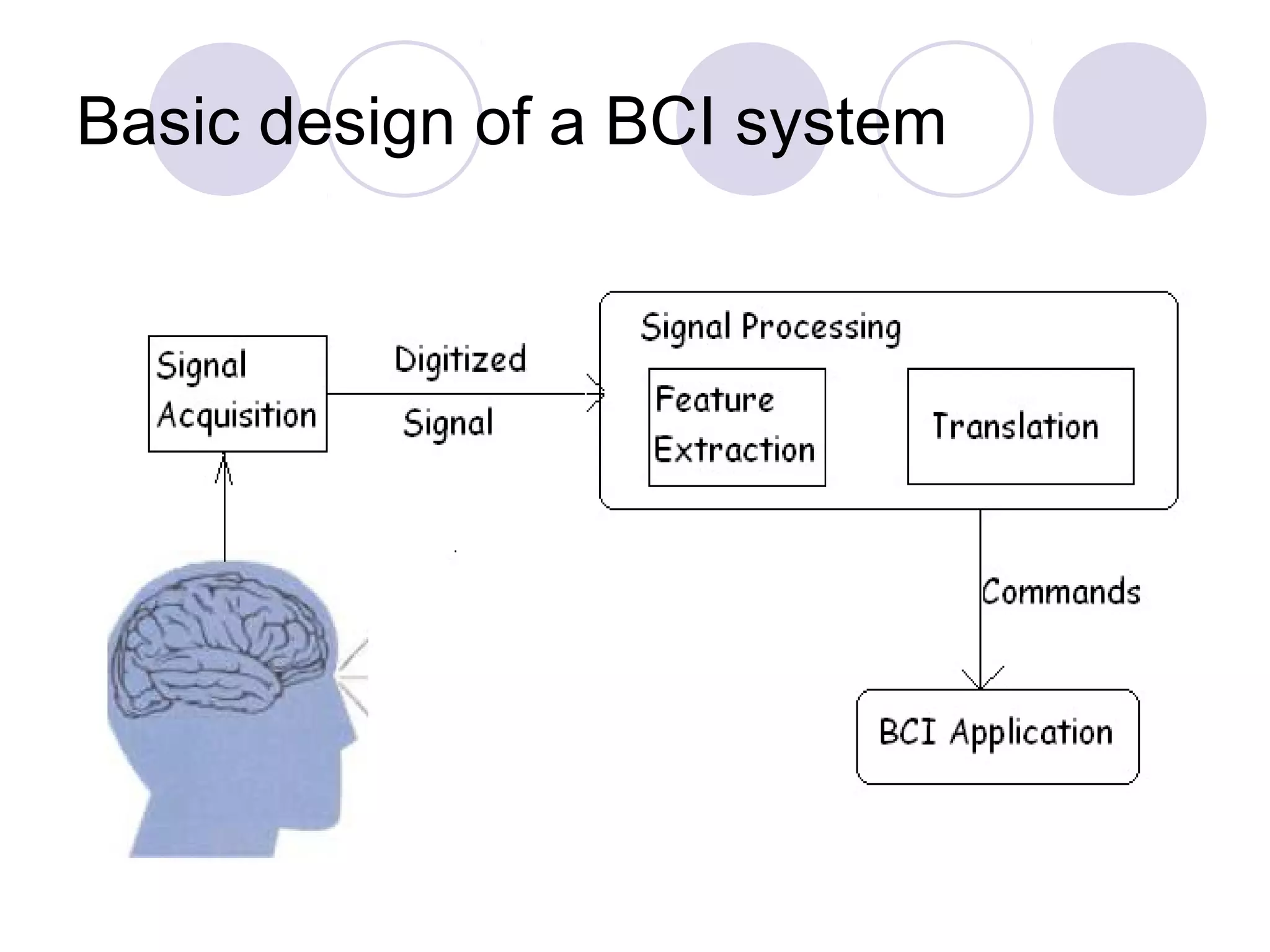
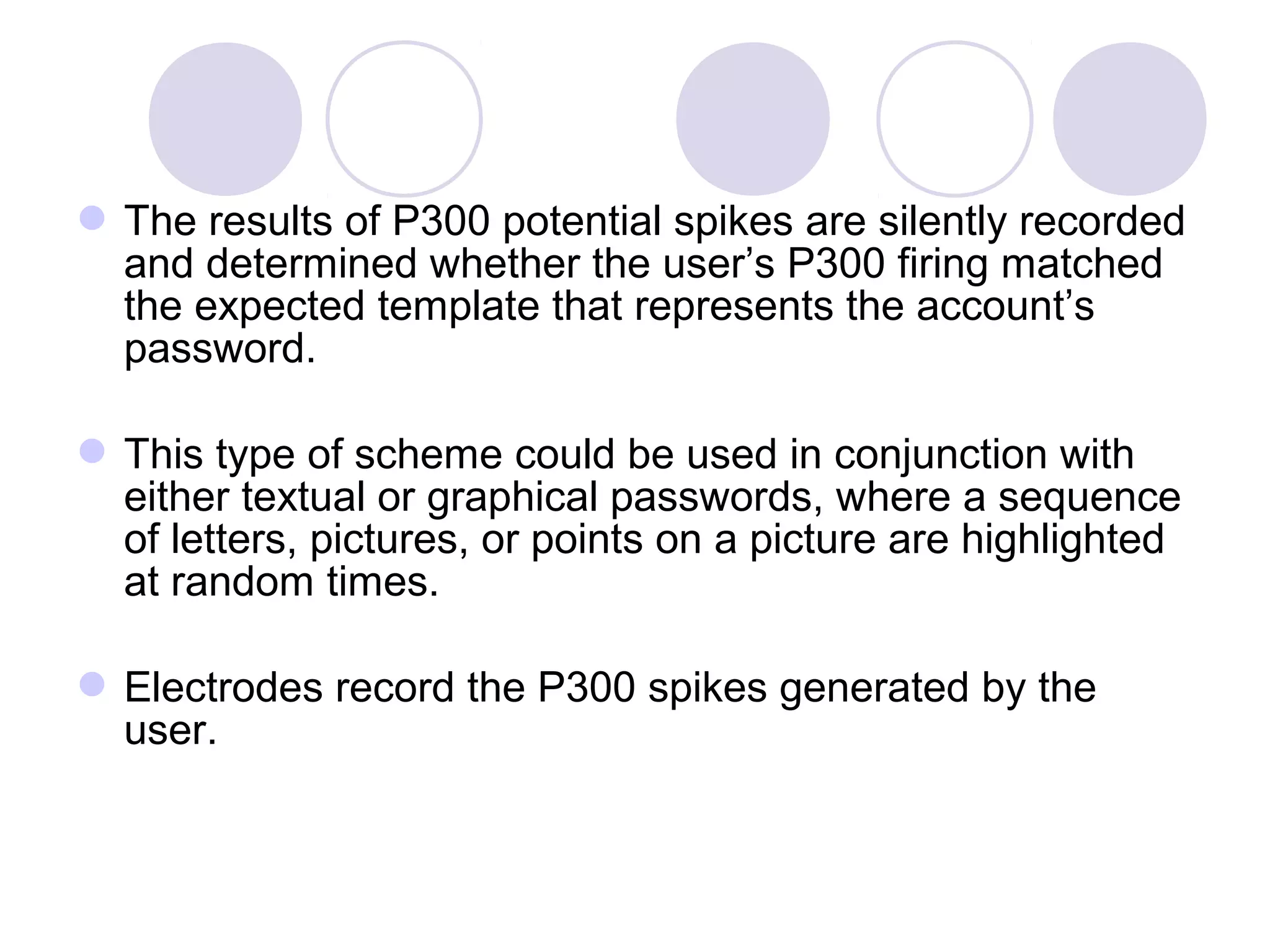
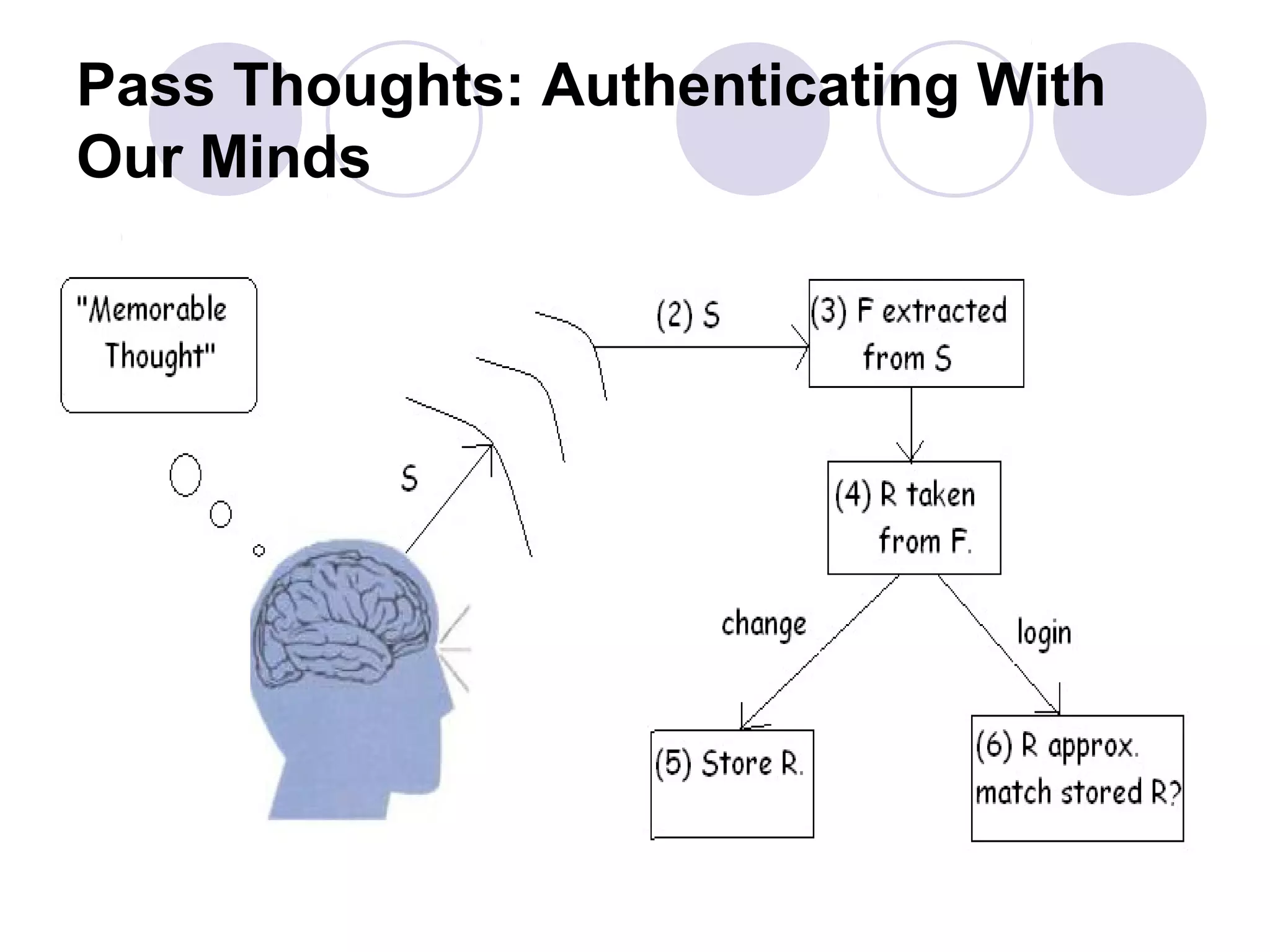
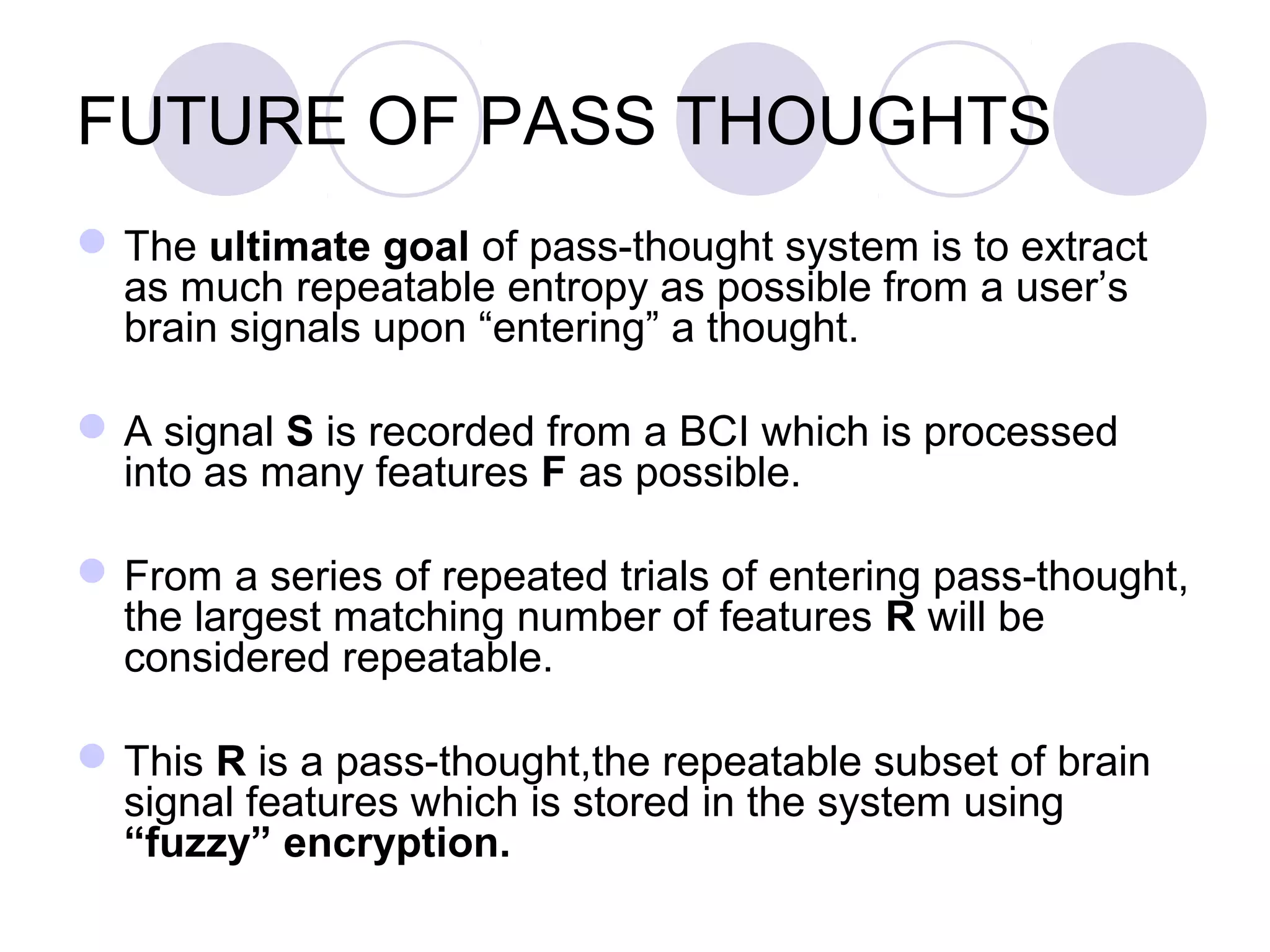
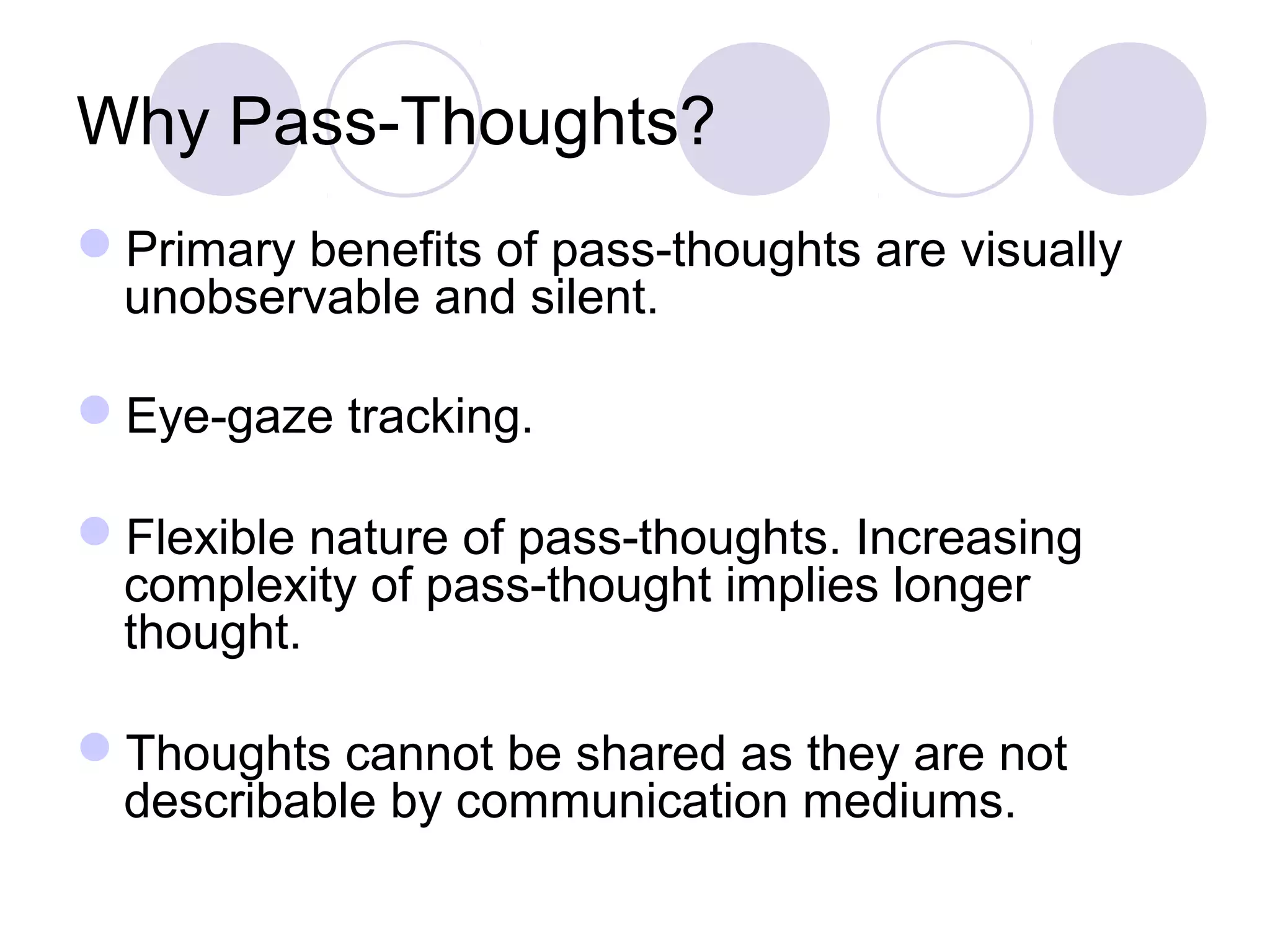
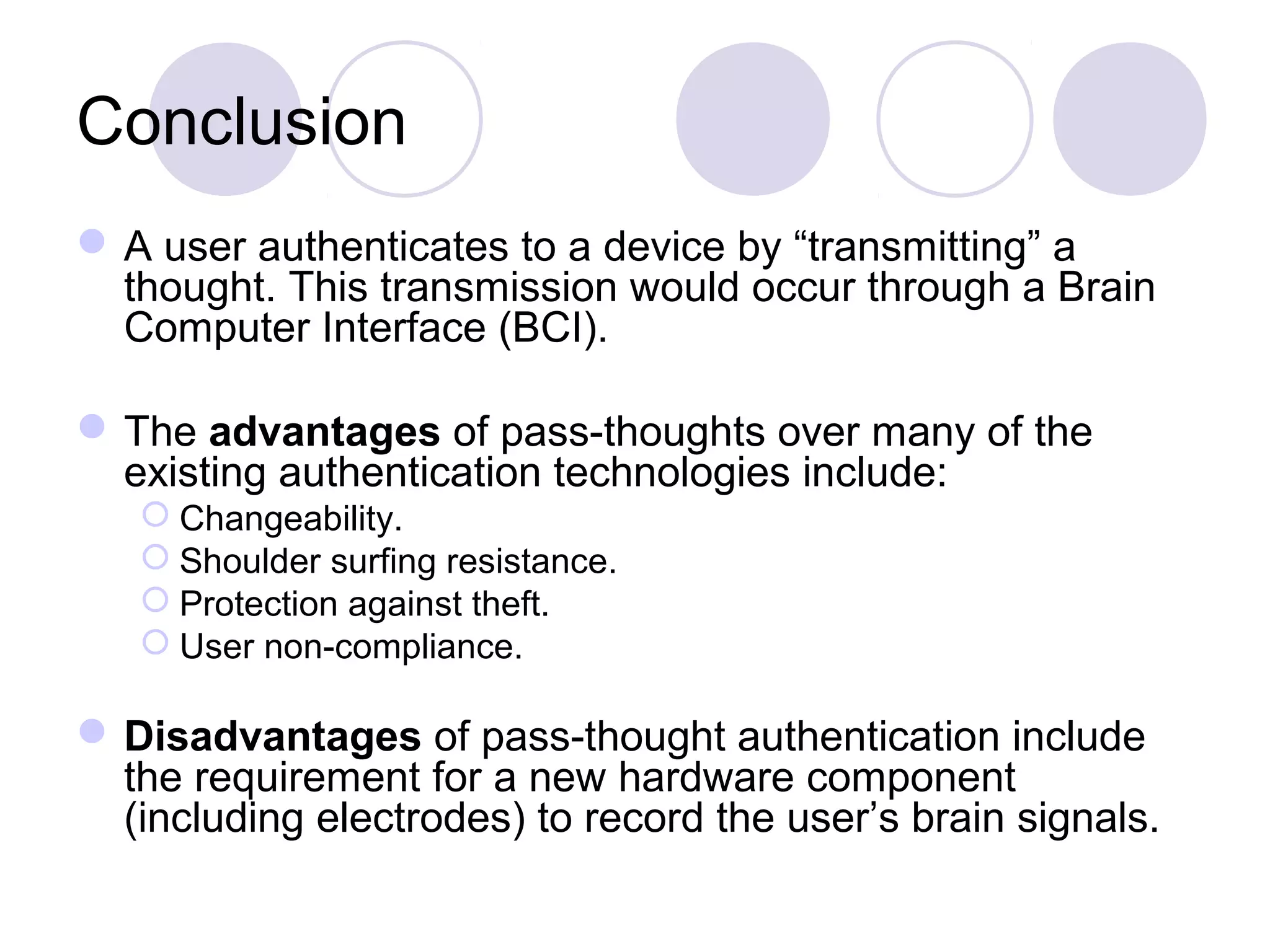
The document presents a novel user authentication method called pass-thoughts, which utilizes brain-computer interface (BCI) technology to transmit thoughts directly to a computer. It outlines the workings of BCIs, their applications, and compares them to existing authentication methods, highlighting both their advantages, such as shoulder surfing resistance, and disadvantages like the need for specialized hardware. The ultimate goal is to utilize unique brain signals for secure authentication, providing a more flexible and changeable alternative to traditional systems.