1) The document derives the formula for the volume of a square-based pyramid using integration.
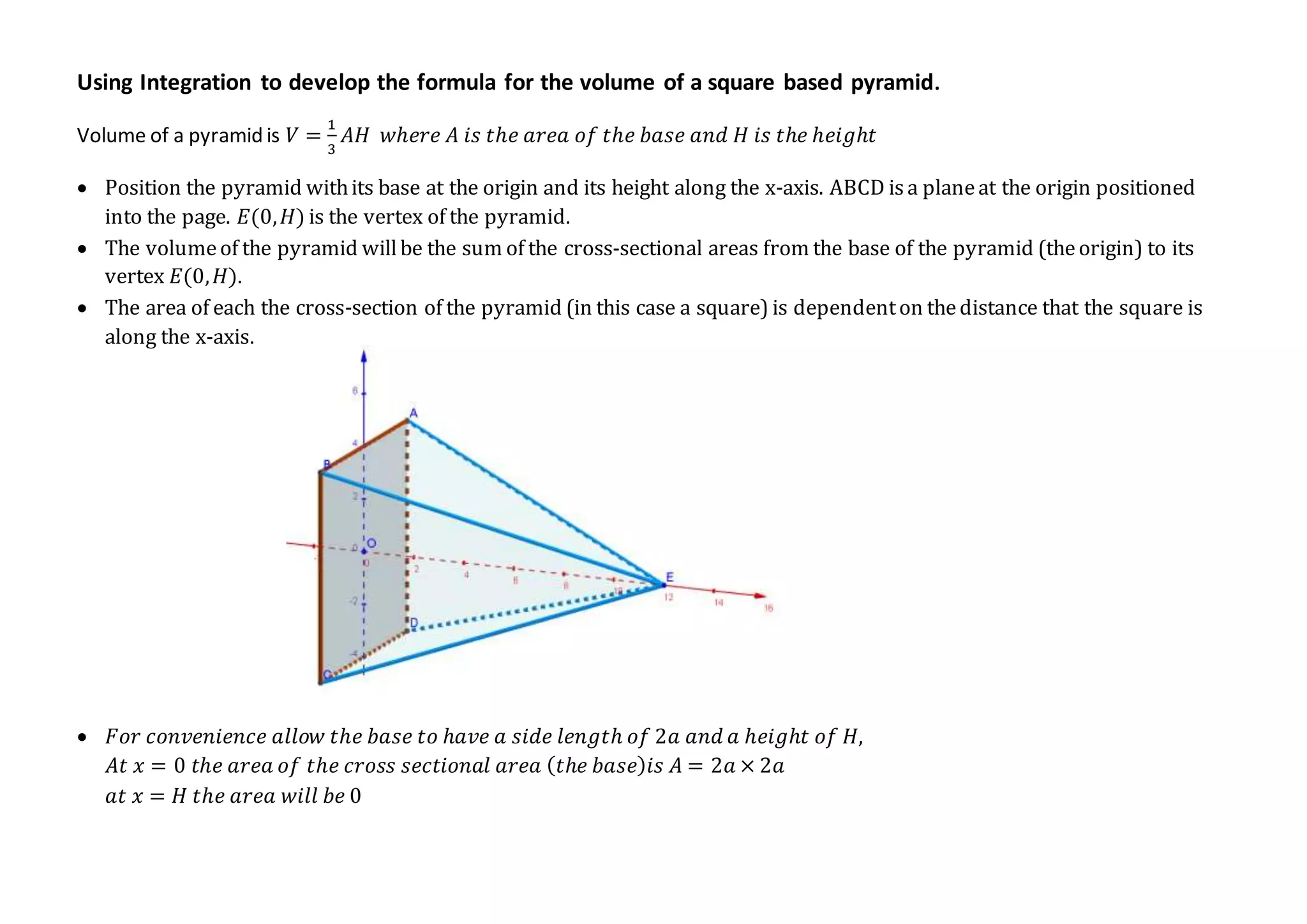
2) It models the pyramid with the base at the origin and height along the x-axis, and considers the volume as the sum of cross-sectional areas from the base to the vertex.
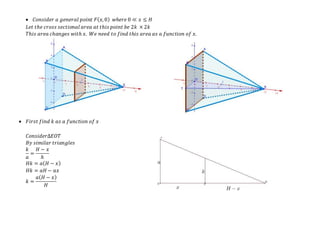
3) Through similar triangles and integrating the changing cross-sectional areas, it arrives at the formula Volume = (1/3) x Area of Base x Height.
![ 𝐹𝑖𝑛𝑑 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑎𝑟𝑒𝑎 𝑜𝑓 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑐𝑟𝑜𝑠𝑠 𝑠𝑒𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑜𝑓 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑝𝑦𝑟𝑎𝑚𝑖𝑑 𝑖𝑛 𝑡𝑒𝑟𝑚𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑥
𝐴𝑟𝑒𝑎 = 2𝑘 × 2𝑘
= 4𝑘2
= 4 [
𝑎( 𝐻 − 𝑥)
𝐻
]
2
=
4𝑎2( 𝐻 − 𝑥)2
𝐻2
=
4𝑎2
𝐻2
(𝐻2
− 2𝐻𝑥 + 𝑥2
)
𝐹𝑖𝑛𝑑 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑣𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑚𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑝𝑦𝑟𝑎𝑚𝑖𝑑 𝑏𝑦 𝑠𝑢𝑚𝑚𝑖𝑛𝑔 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑎𝑟𝑒𝑎𝑠 𝑜𝑓 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑐𝑟𝑜𝑠𝑠 𝑠𝑒𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑓𝑟𝑜𝑚 𝑥 = 0 𝑡𝑜 𝑥 = 𝐻
= ∫
4𝑎2
𝐻2
( 𝐻2
− 2𝐻𝑥 + 𝑥2) 𝑑𝑥
𝐻
0
=
4𝑎2
𝐻2
∫ 𝐻2
− 2𝐻𝑥 + 𝑥2
𝑑𝑥
𝐻
0
=
4𝑎2
𝐻2
[ 𝐻2
𝑘 − 𝐻𝑘2
+
𝑥3
3
]
=
4𝑎2
𝐻2
[(𝐻3
− 𝐻3
+
𝐻3
3
) − (0)]
=
4𝑎2
𝐻2
×
𝐻3
3
=
4𝑎2
𝐻
3
𝑔𝑖𝑣𝑒𝑛 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑎𝑟𝑒𝑎 𝑜𝑓 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑏𝑎𝑠𝑒 𝐴 = 2𝑎 × 2𝑎 = 4𝑎2
𝑉𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑚𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑝𝑦𝑟𝑎𝑚𝑖𝑑 =
1
3
𝐴𝐻 𝑎𝑠 𝑟𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑖𝑟𝑒𝑑](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/usingintegrationtodeveloptheformulaforthevolumeofasquarebasedpyramid-151013073845-lva1-app6892/85/Volume-of-a-square-based-pyramid-by-Integration-3-320.jpg)