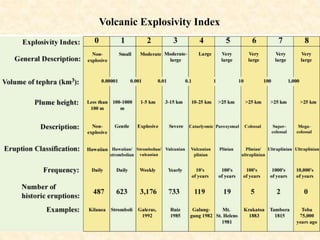
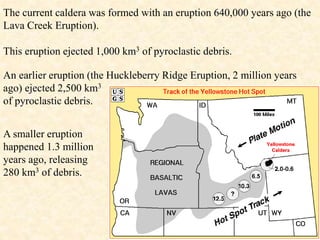
This document discusses the prediction and impacts of volcanic eruptions. It describes methods for long-term and short-term prediction of eruptions based on monitoring factors like gas emissions, surface tilting, and earthquake activity. The impacts discussed include hazards from lava flows, ash falls, pyroclastic flows, lahars, nuée ardentes, landslides, volcanic gases, tsunamis, and potential effects on global climate. Examples of historically deadly eruptions like Mount Pelée and Krakatoa are provided. The document also introduces the concept of supervolcanic eruptions ejecting over 1,000 cubic km of material.