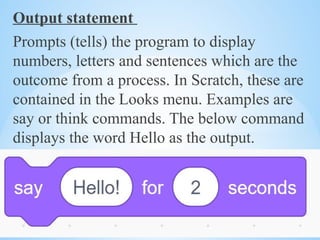
Visual programming allows users to create programs using graphics such as blocks and icons, making coding more accessible. Key features include control blocks, sprites, and a block palette for organizing programs visually. Examples of visual programming platforms include Scratch and Blockly, which utilize reserved words, syntax rules, and control structures to execute instructions.