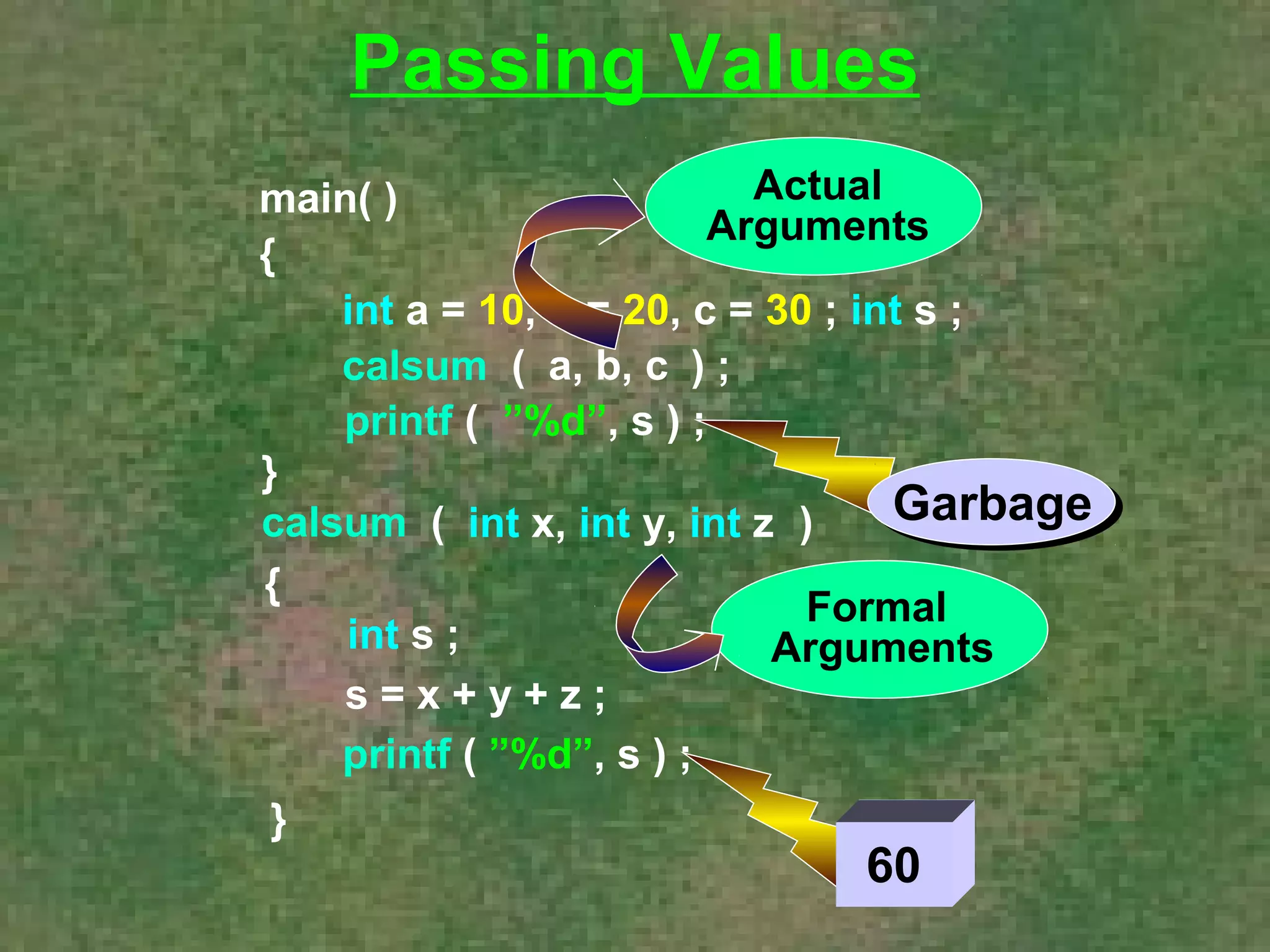
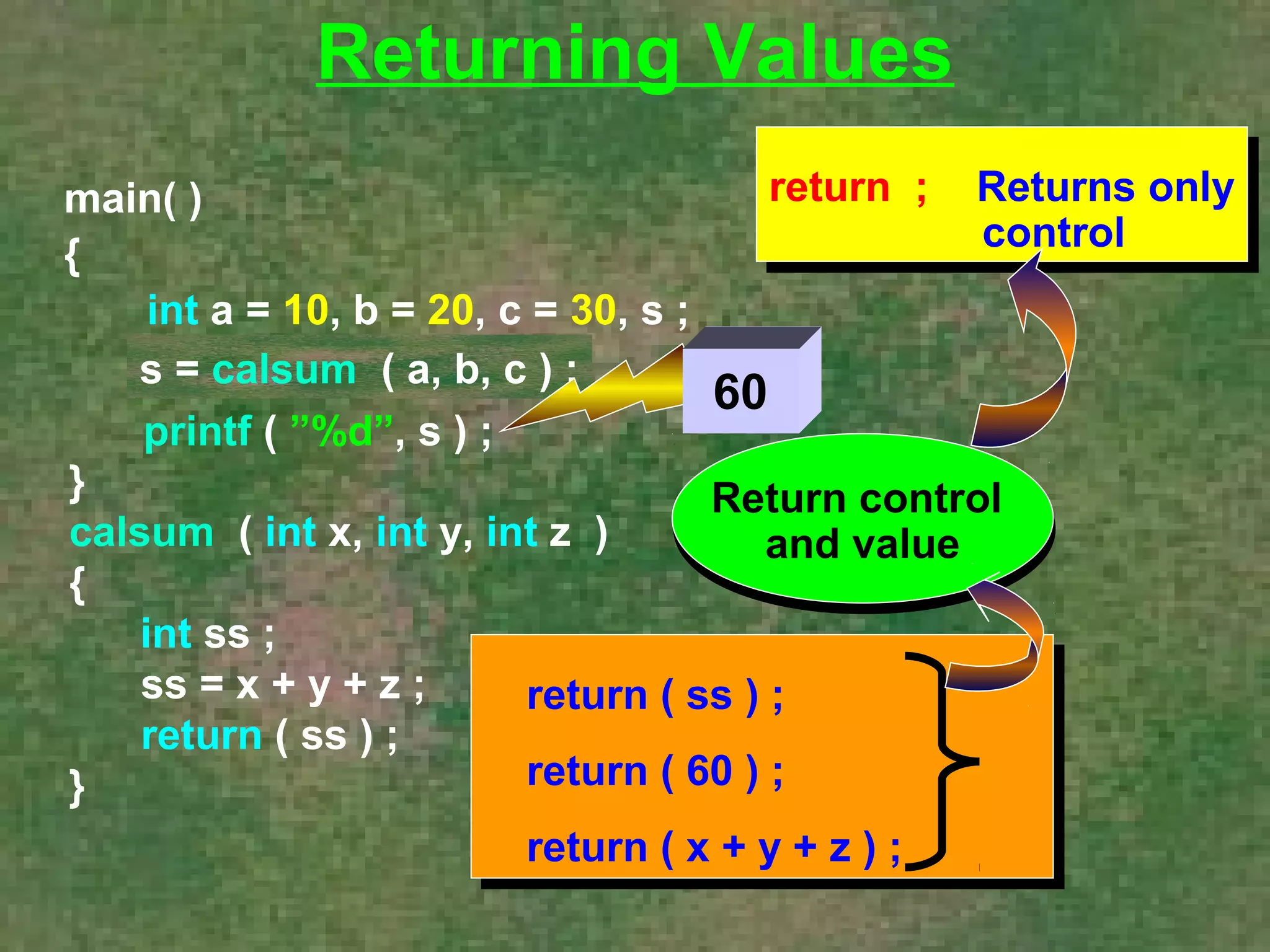
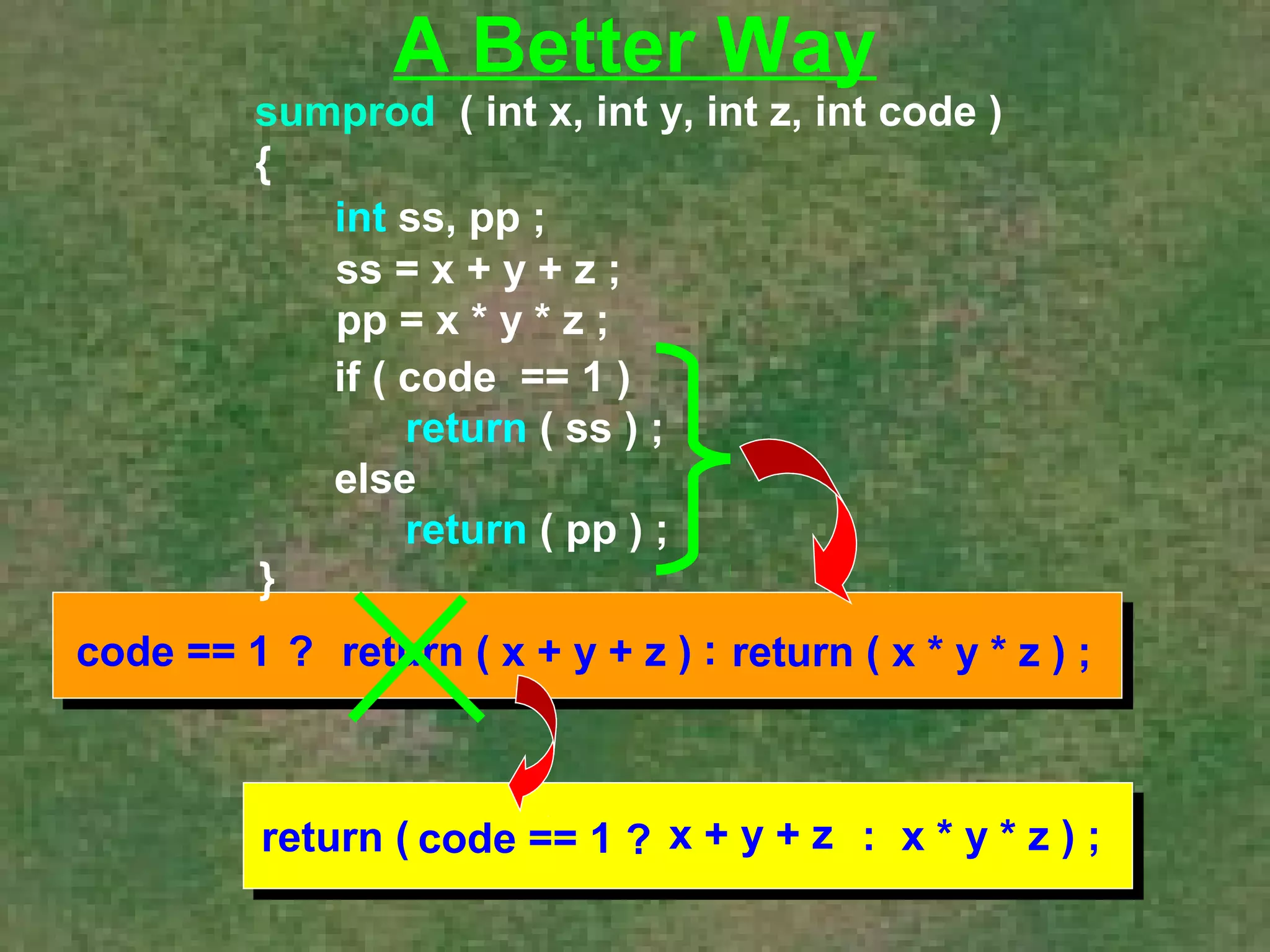
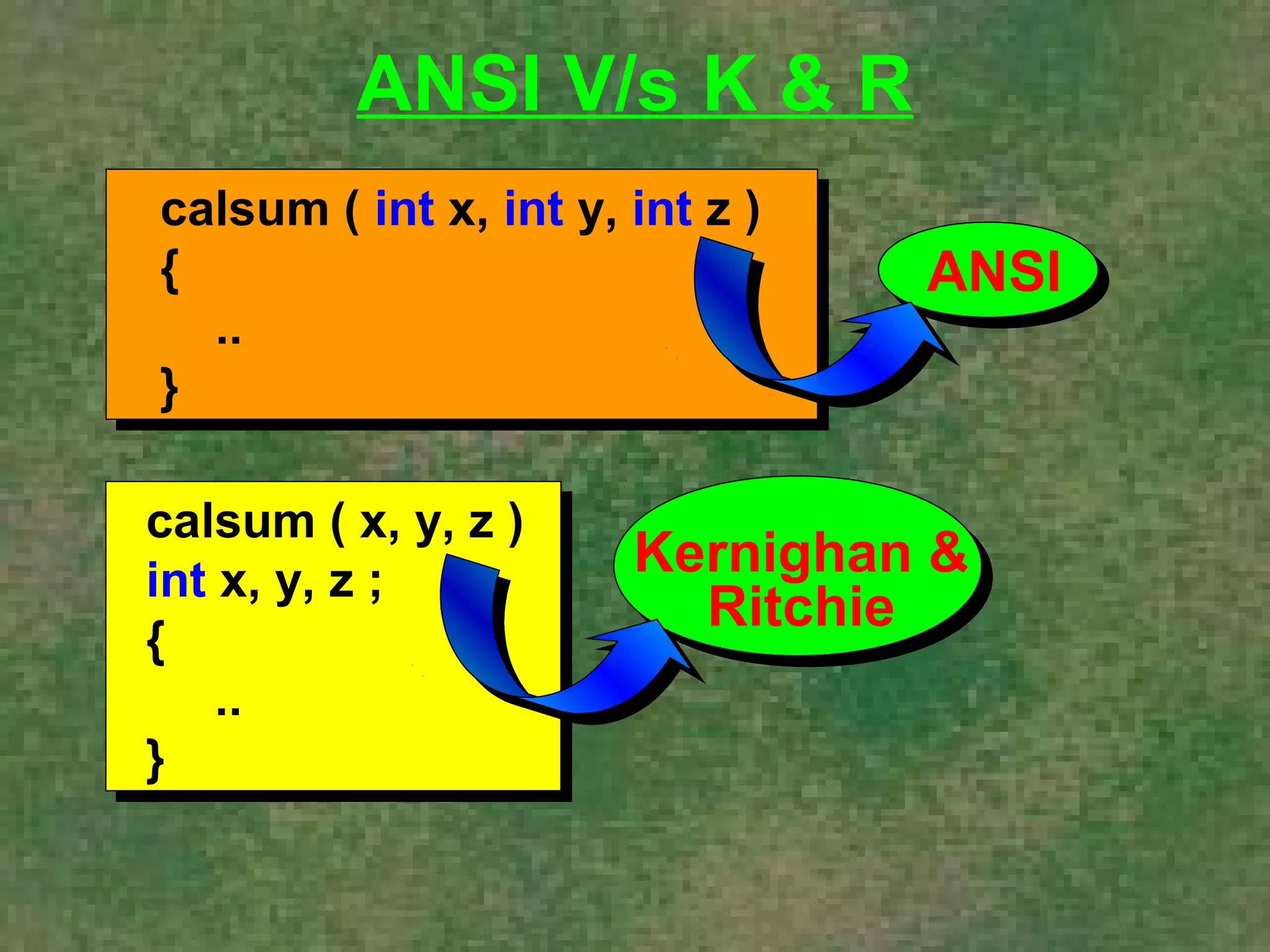
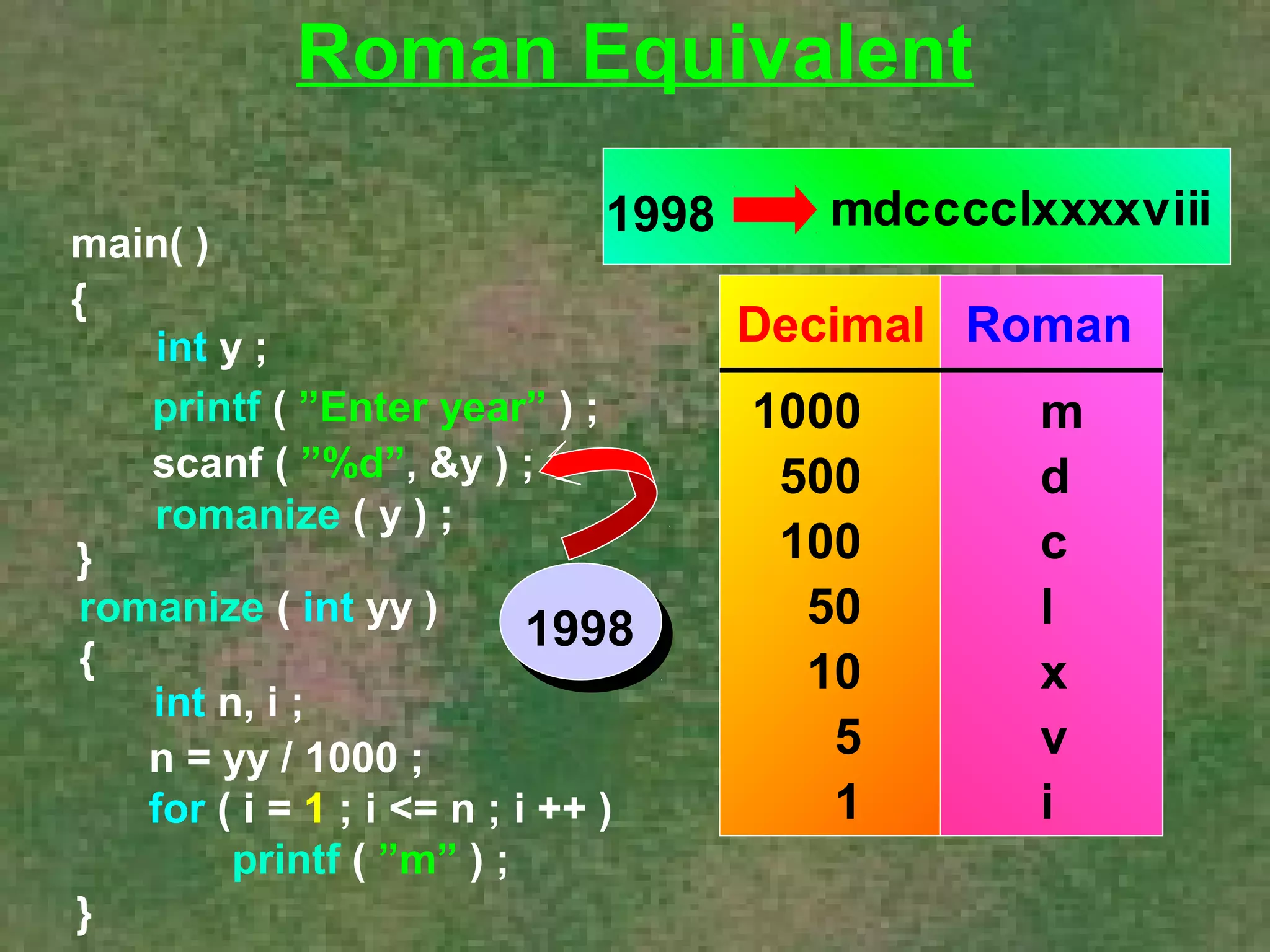
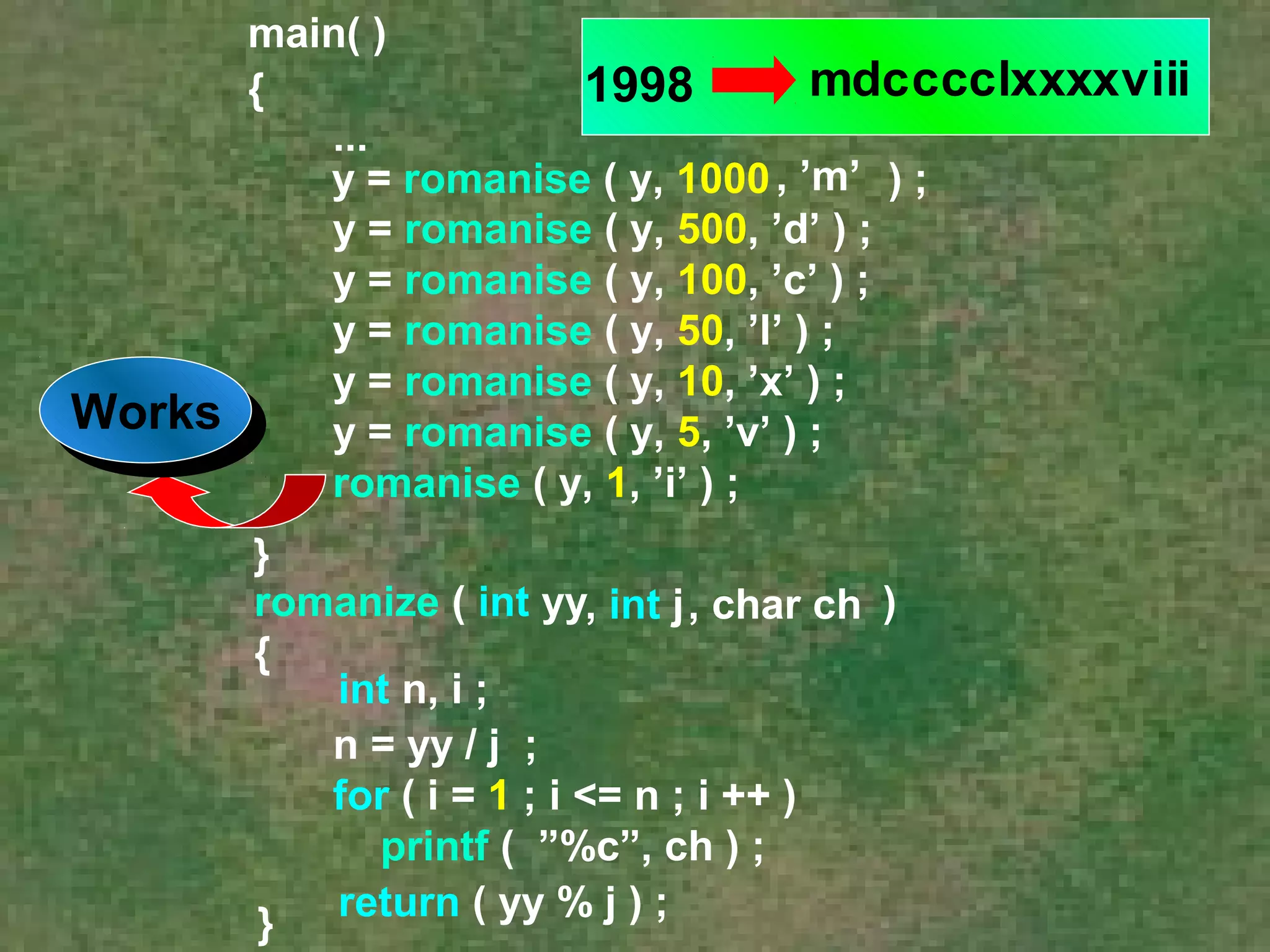
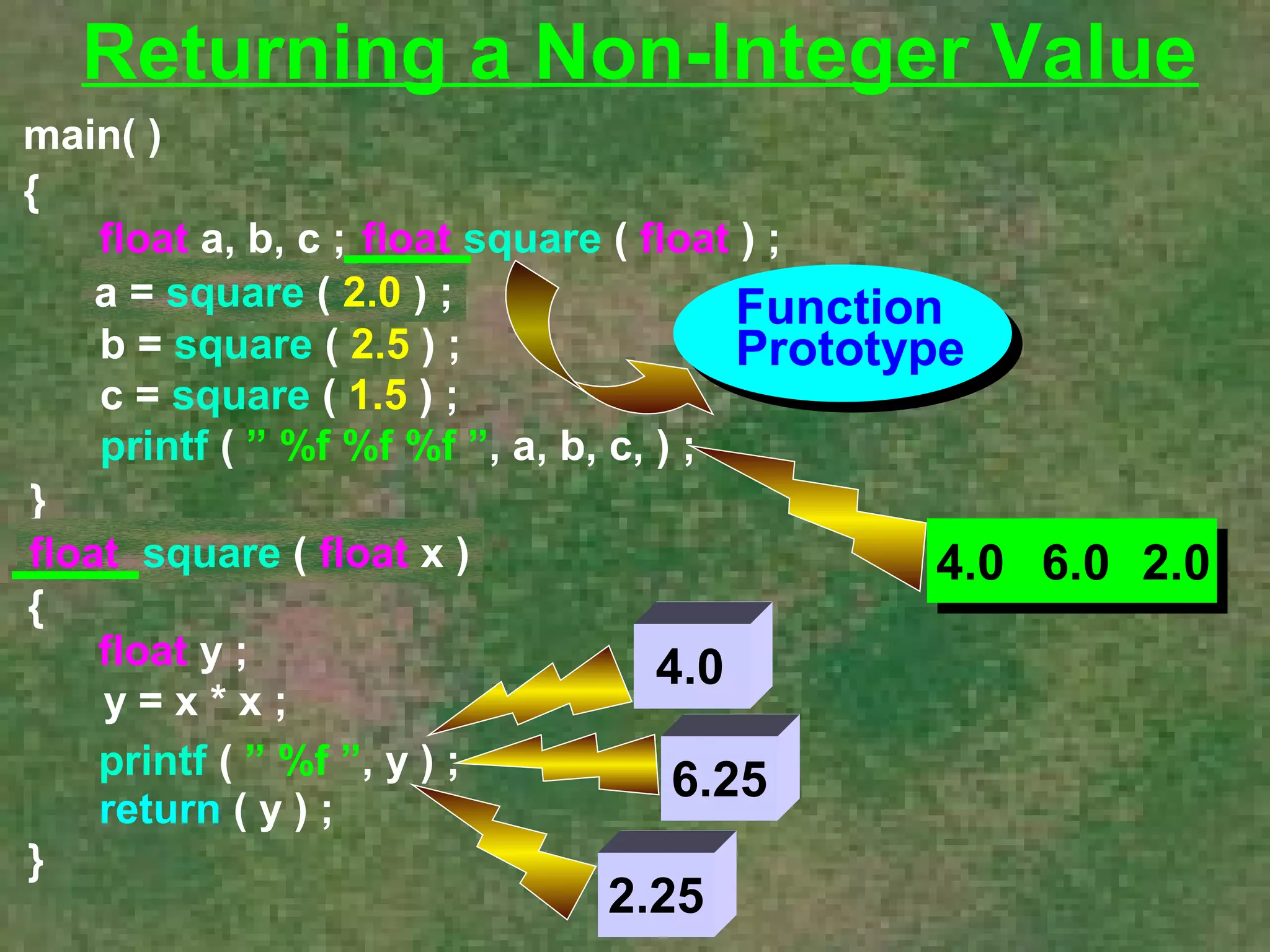
The document discusses various aspects of functions in C programming including passing values to functions, returning values from functions, and more advanced features like returning non-integer values, call by value/reference, and recursion. It provides examples of defining and calling functions, passing arguments, returning single and multiple values, and illustrates proper and improper usage of functions.