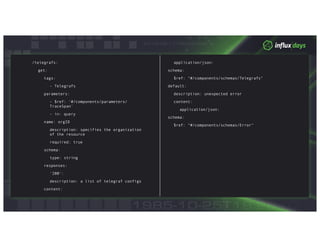
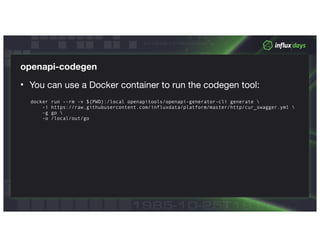
The document discusses InfluxDB 2.0's new approach to client libraries. It notes that in 1.x, client libraries were community-led with inconsistencies, but in 2.0 the client libraries will be developed as part of the platform and will have a consistent API. The document outlines how the InfluxDB API is defined using Swagger and how code generation and guidelines help develop consistent client libraries. It provides examples of critical path client libraries being built for various languages like Go, JavaScript, and Java.