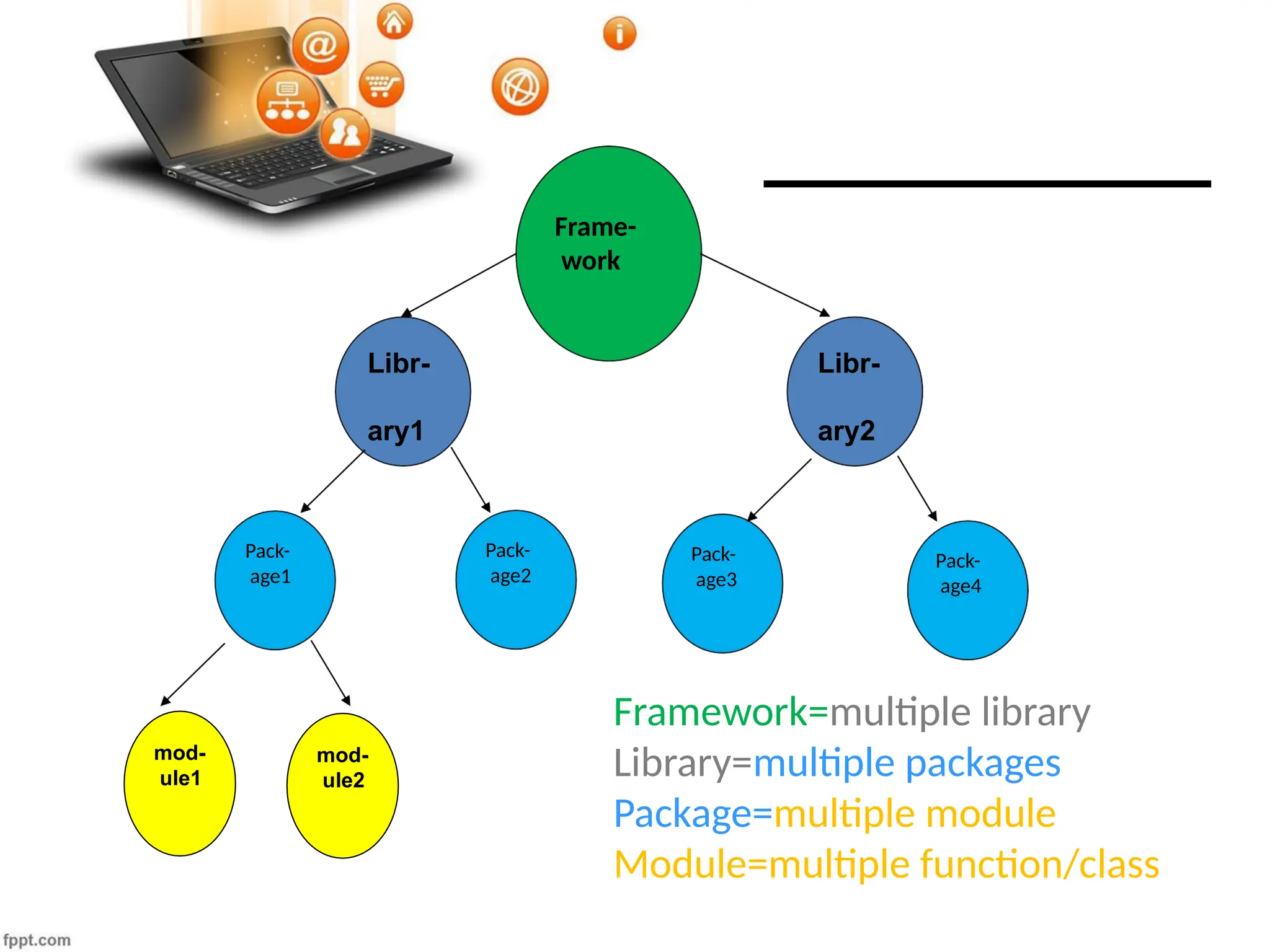
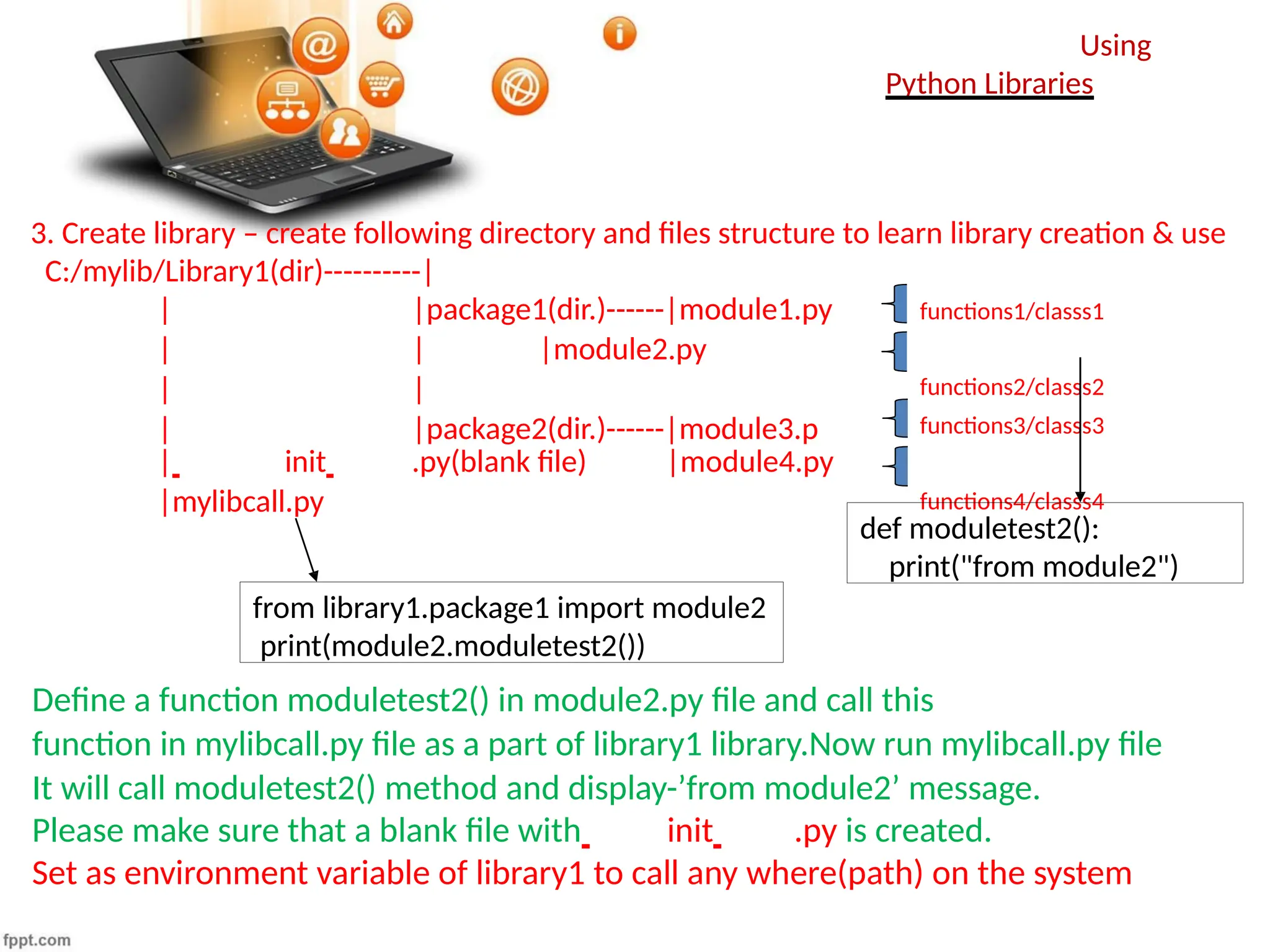
The document provides an overview of Python programming concepts including modules, packages, libraries, and frameworks. It explains how to create and use modules and packages, the distinction between libraries and standard libraries, and introduces recursive functions with examples. Key elements include importing modules, creating libraries, and utilizing frameworks like Django.