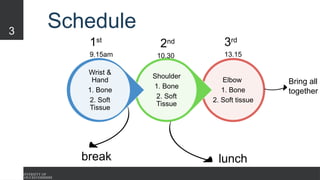
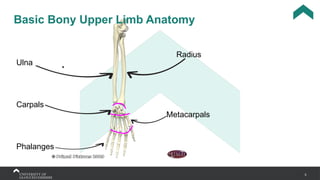
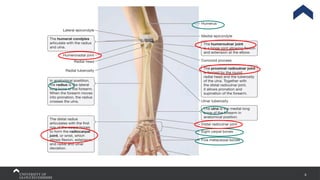
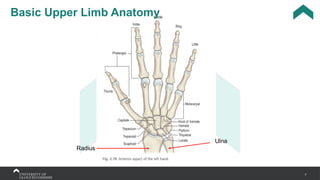
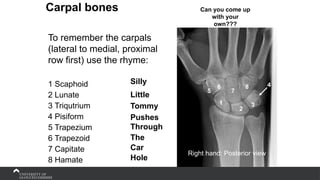
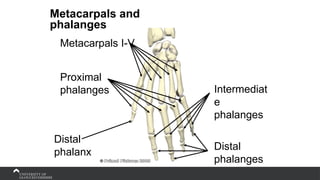
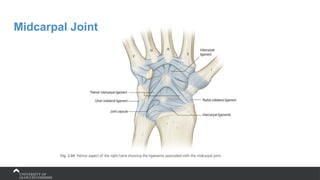
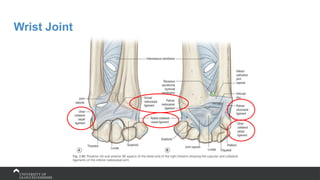
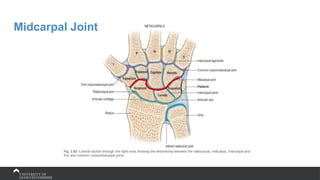
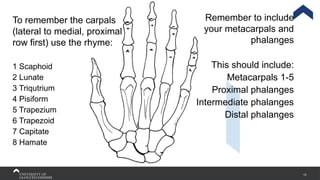
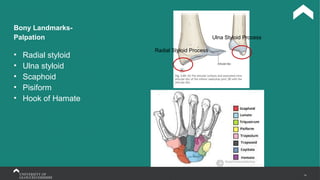
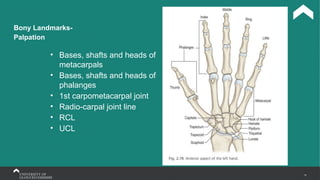
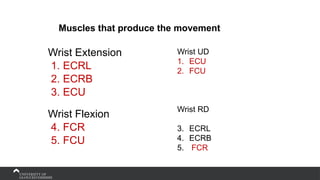
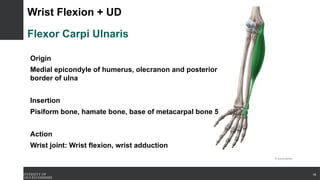
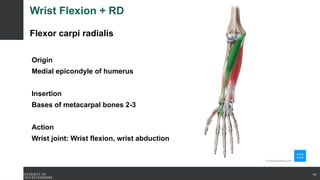
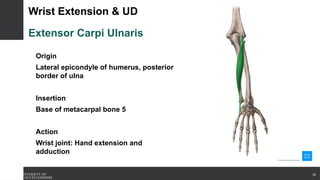
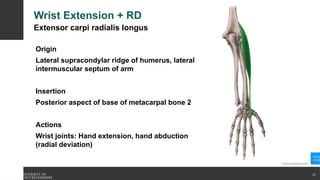
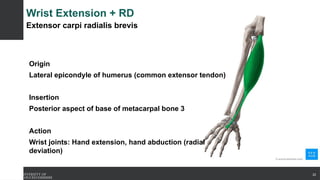
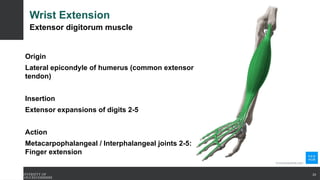
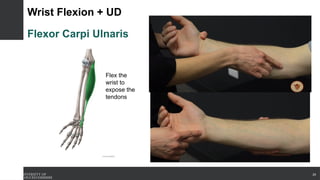
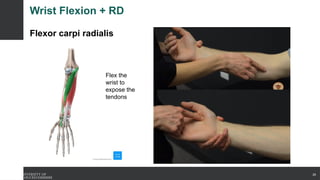
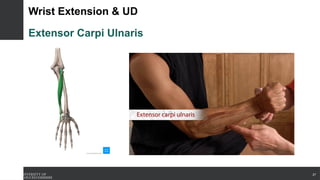
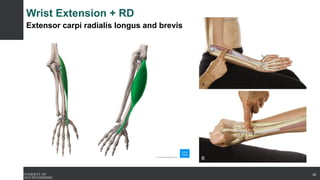
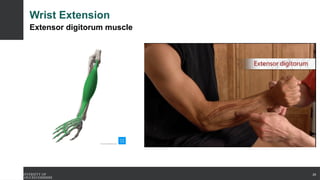
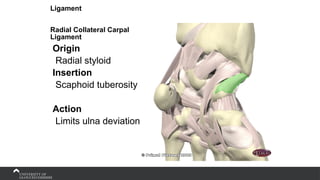
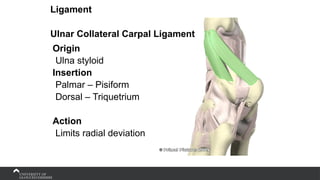
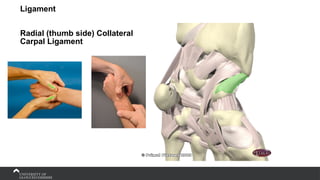
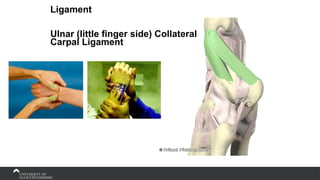
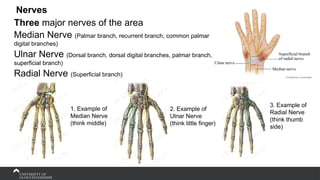
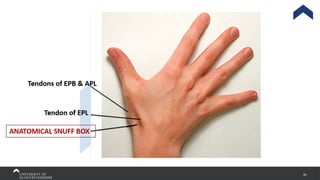
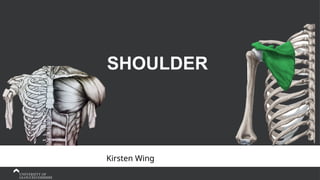
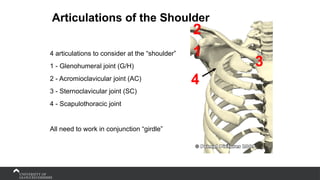
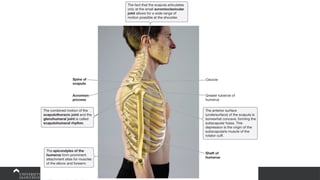
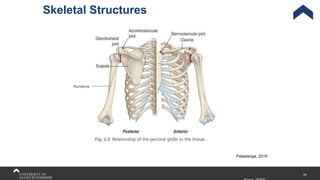
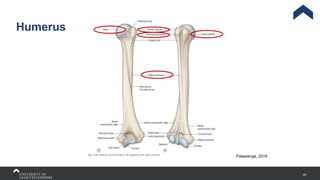
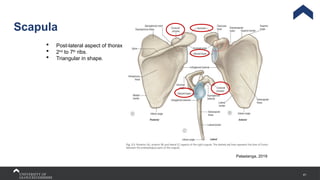
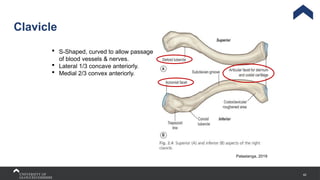
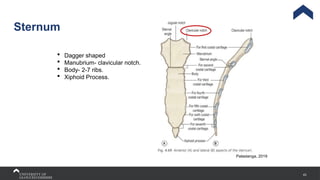
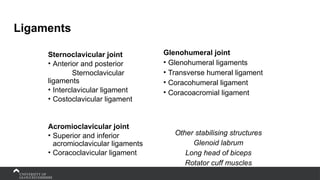
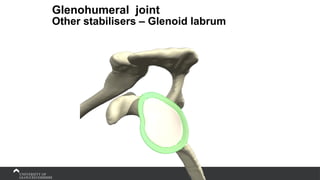
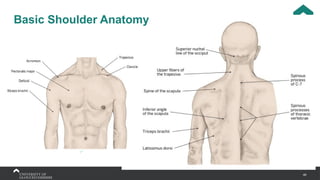
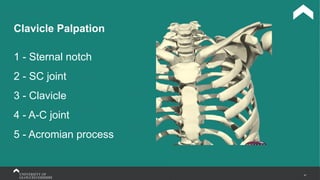
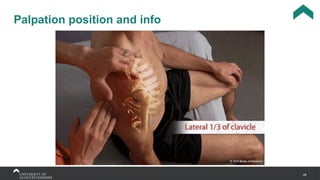
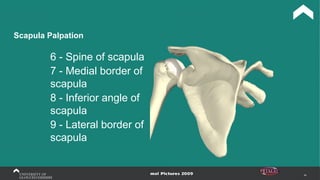
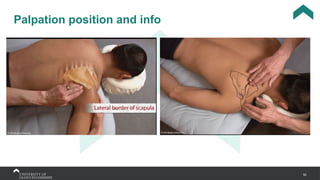
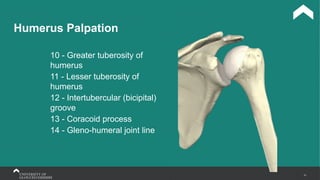
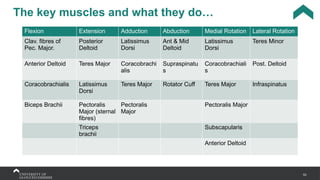
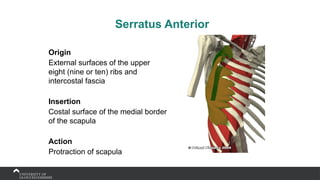
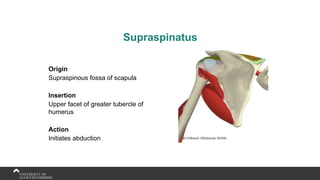
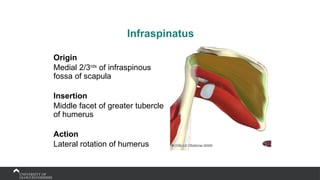
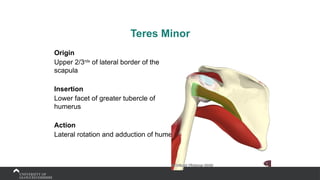
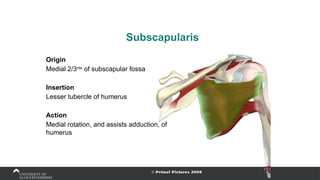
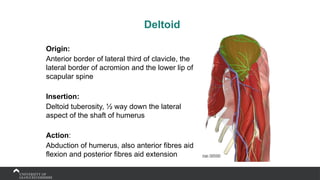
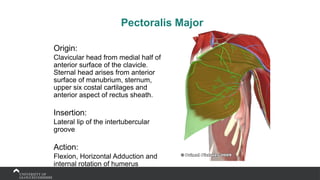
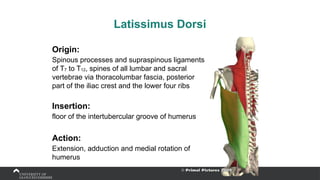
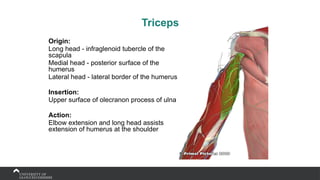
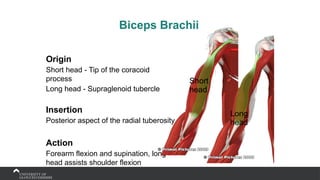
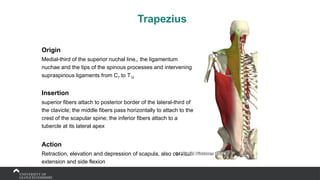
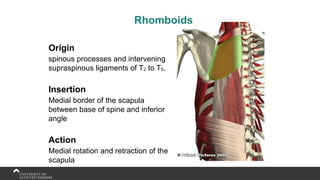
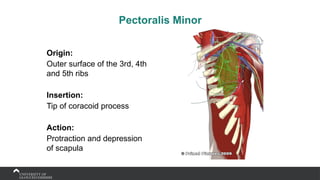
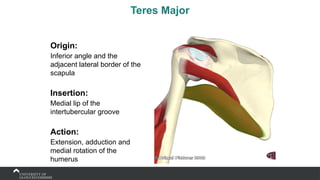
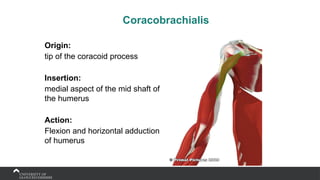
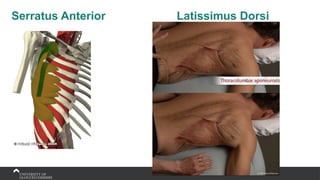
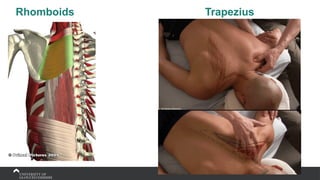
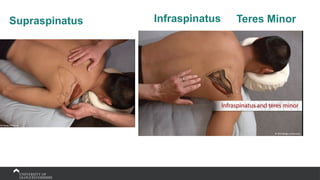
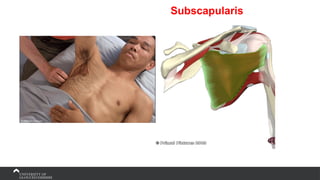
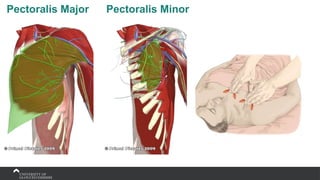
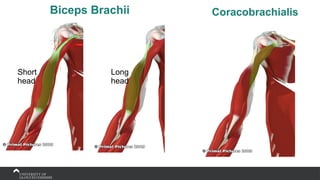
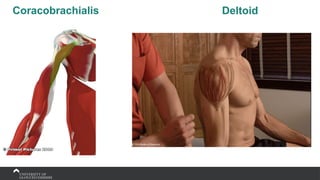
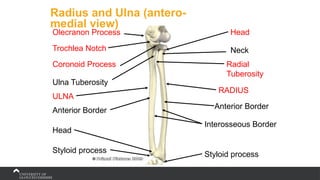
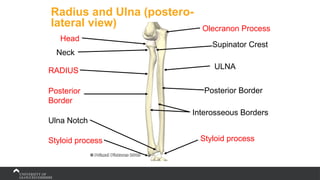
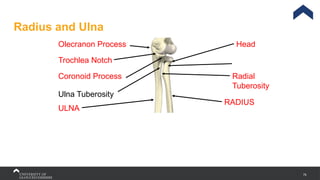
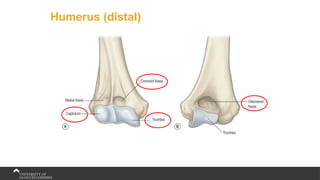
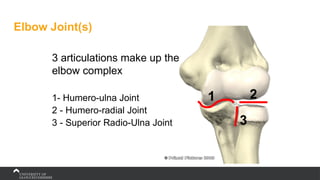
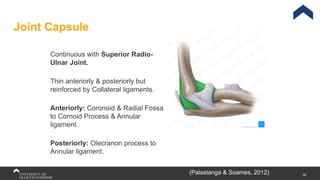
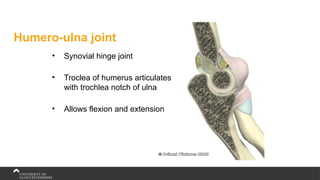
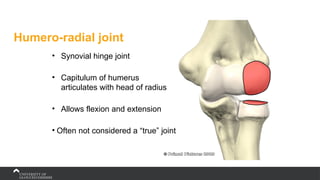
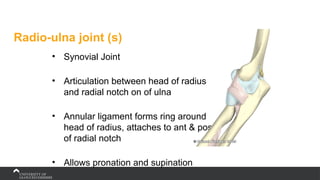
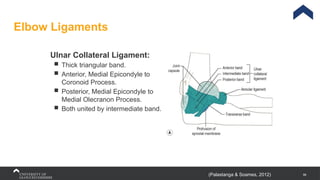
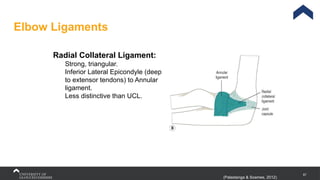
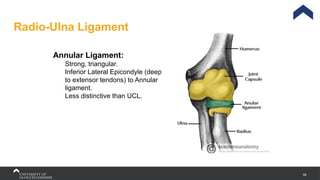
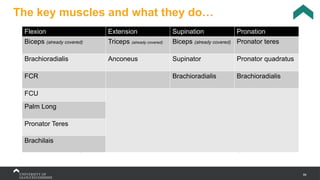
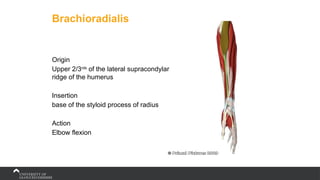
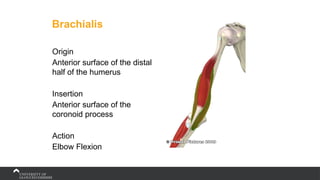
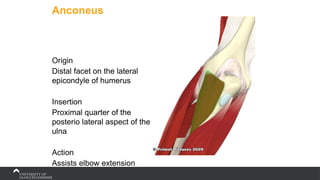
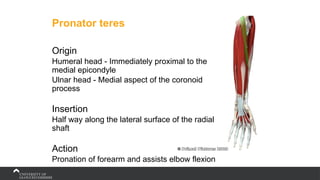
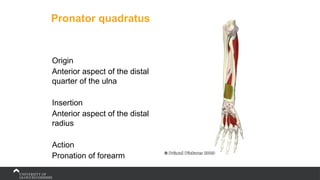
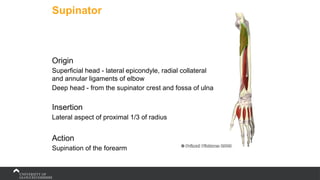
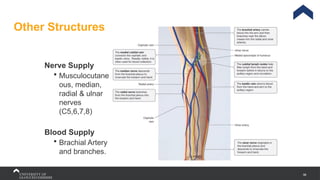
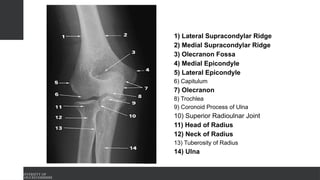
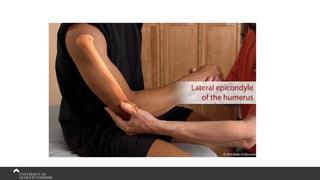
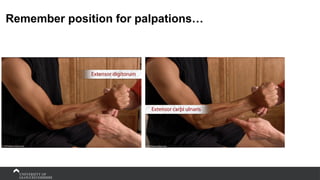
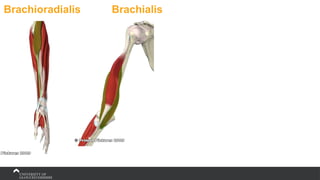
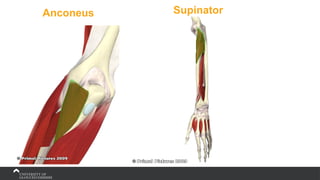
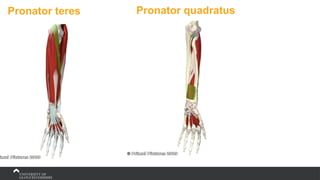
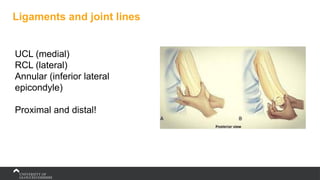
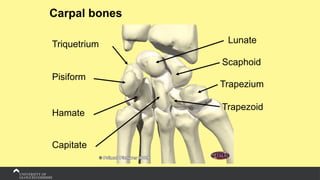
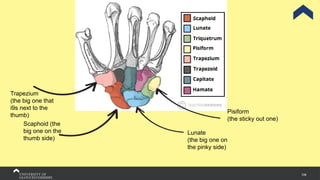
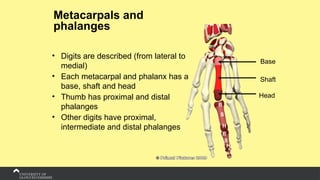
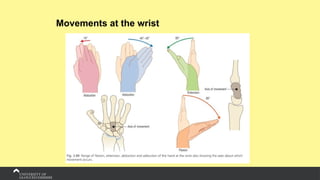
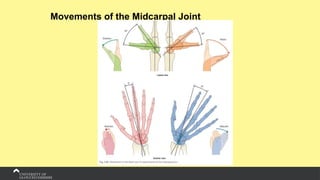
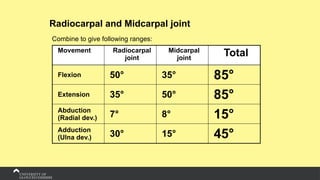
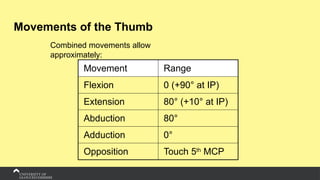
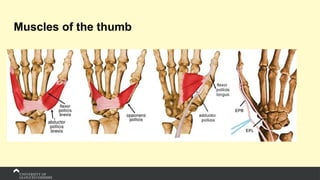
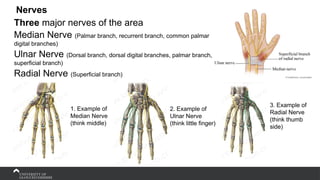
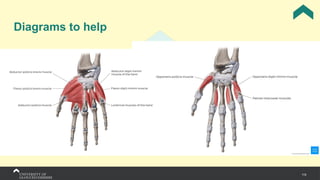
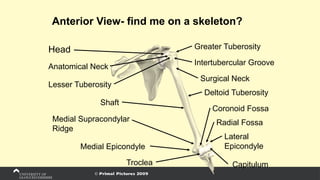
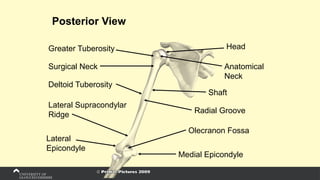
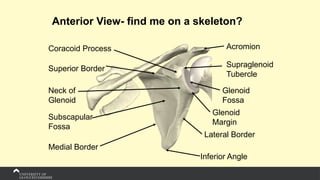
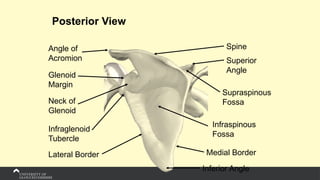
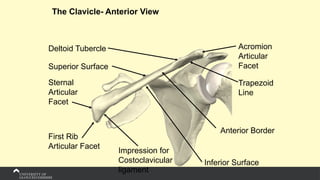
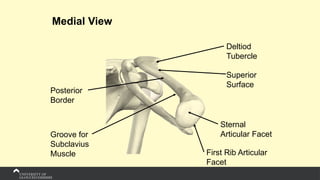
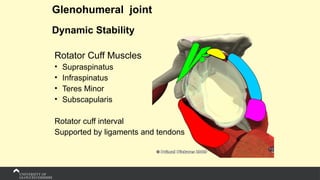
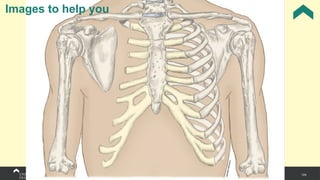
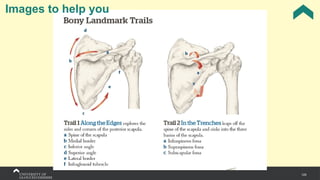
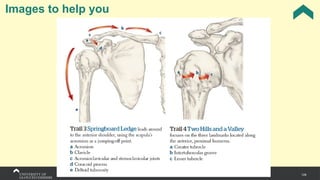
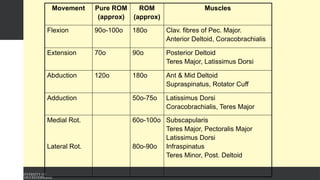
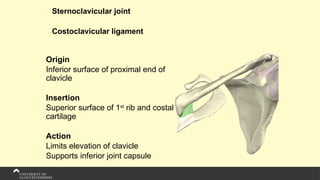
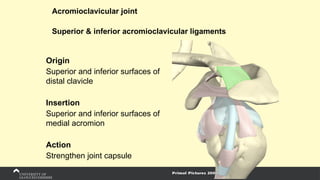
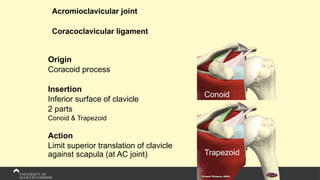
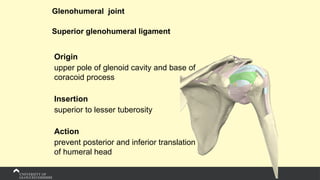
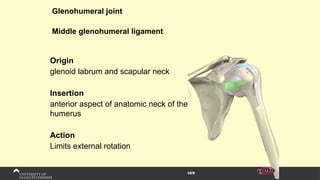
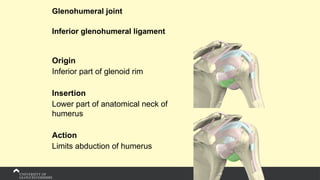
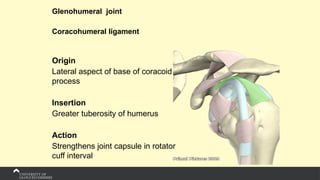
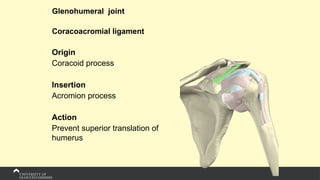
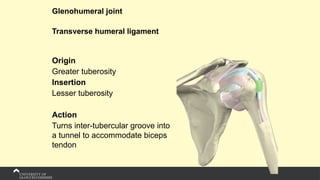
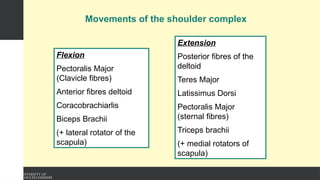
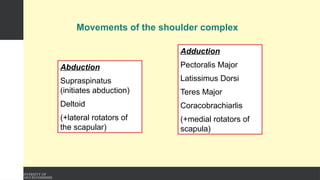
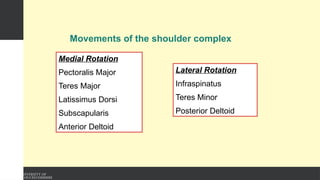
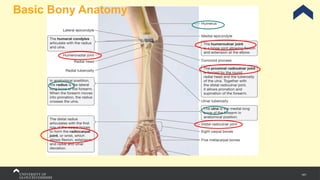
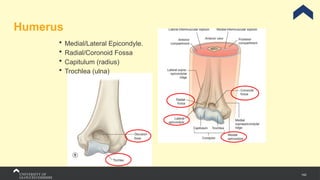
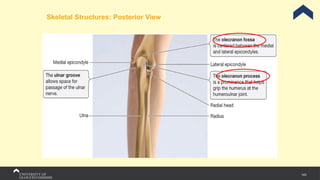
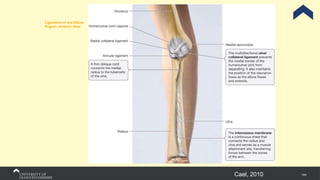
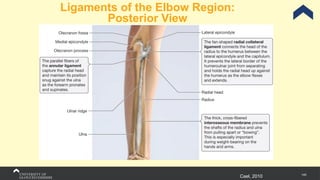
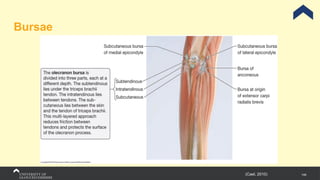
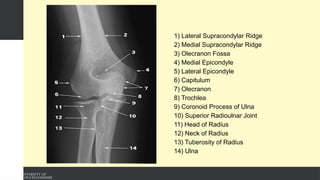
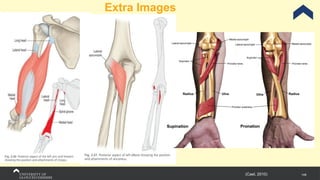
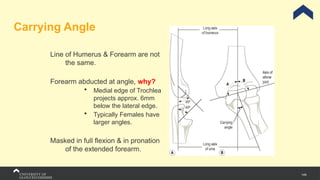
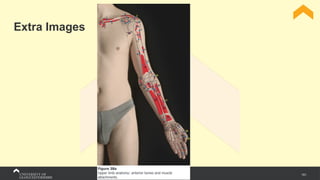
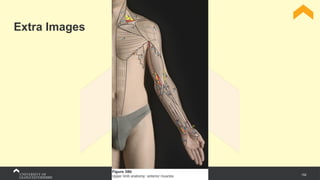
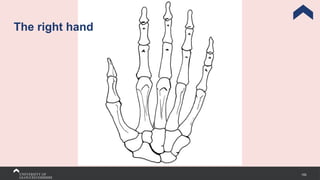
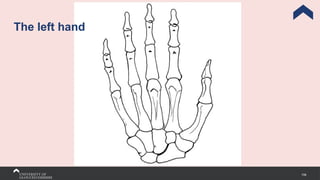
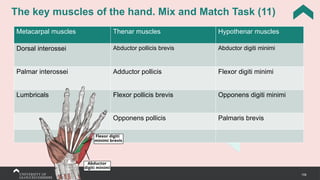
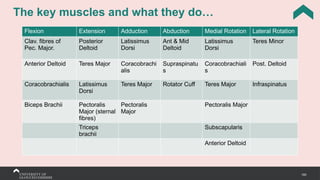
The document covers the anatomy of the upper limb, focusing on the wrist, hand, elbow, and shoulder complex. It outlines essential bony structures, muscles, ligaments, and their functions necessary for understanding upper limb movement and palpation techniques. Additionally, it provides guidelines for participation and interaction during sessions led by instructor Kirsten Wing.