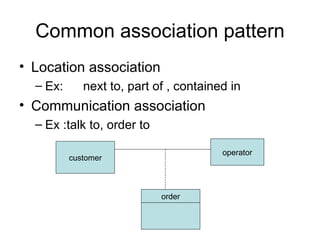
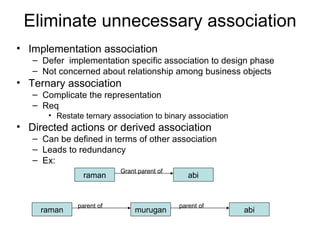
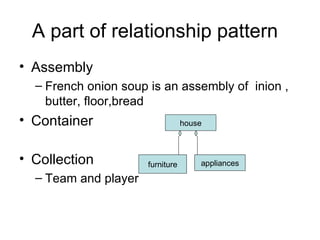
This document discusses different types of relationships in object-oriented modeling: association, generalization (super-substructure), and aggregation. Association represents a connection between objects and can be binary, ternary, or higher-order. Generalization shows inheritance relationships in a hierarchy. Aggregation represents a "part-of" relationship where a class contains other component classes.