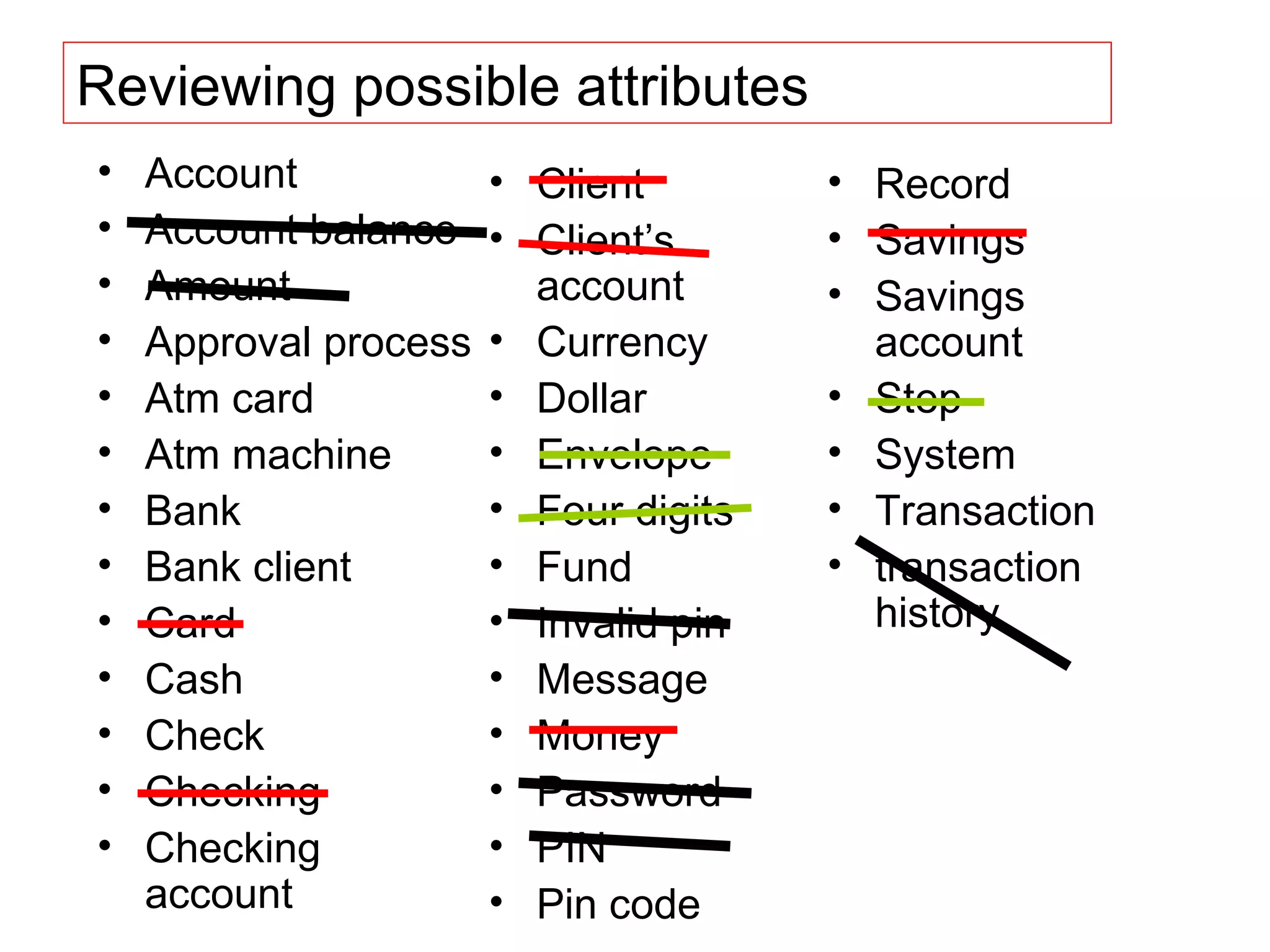
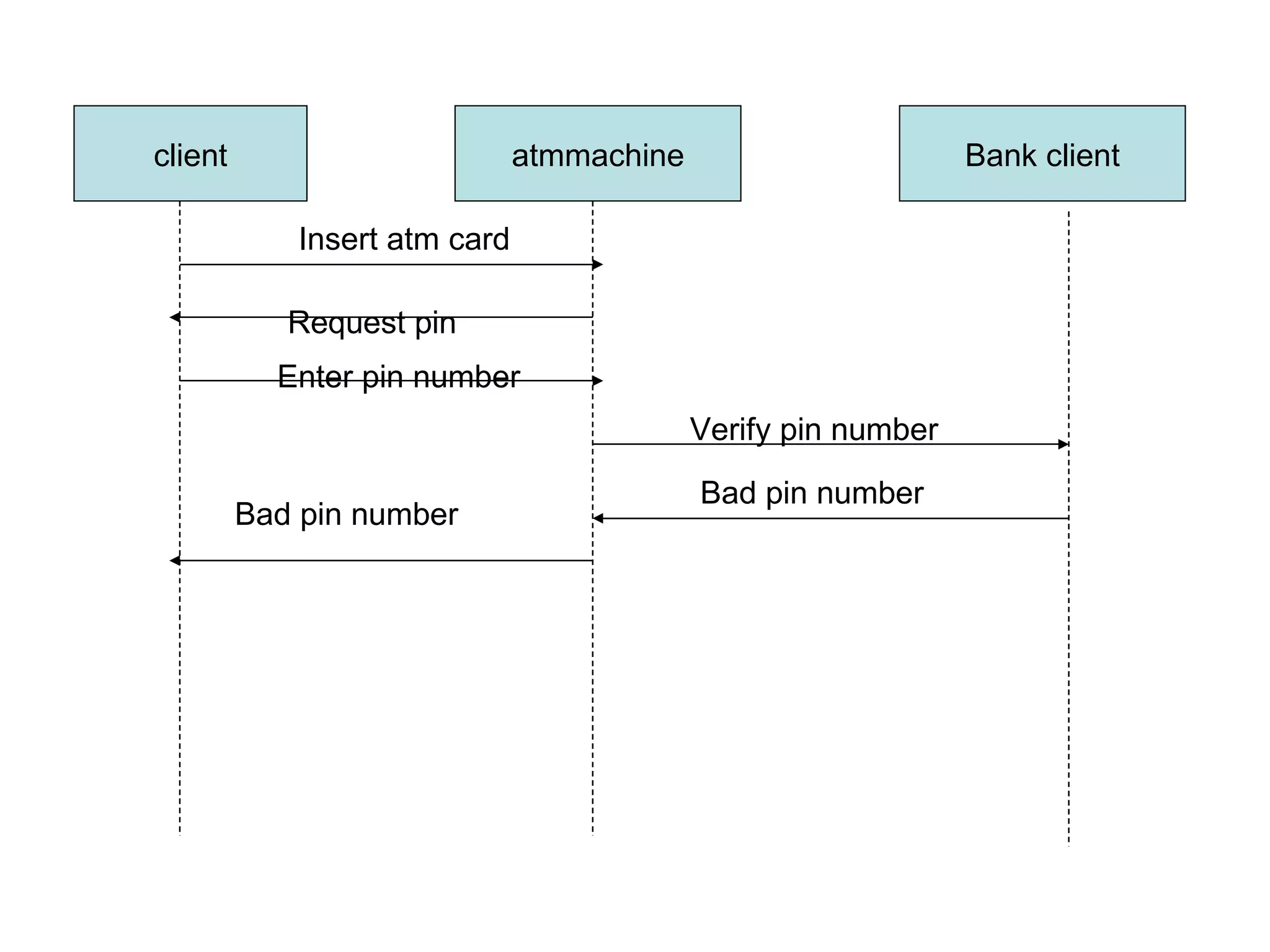
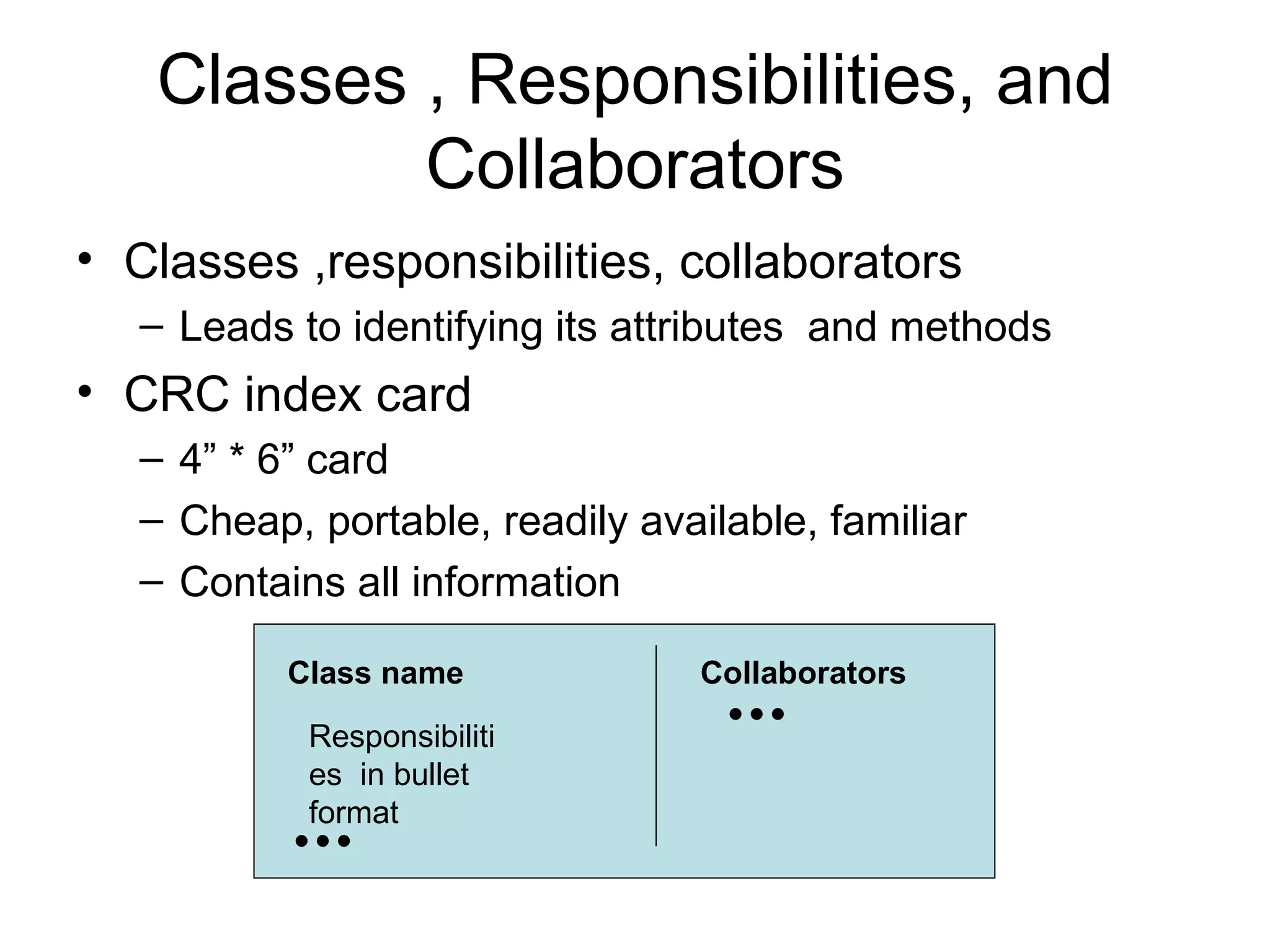
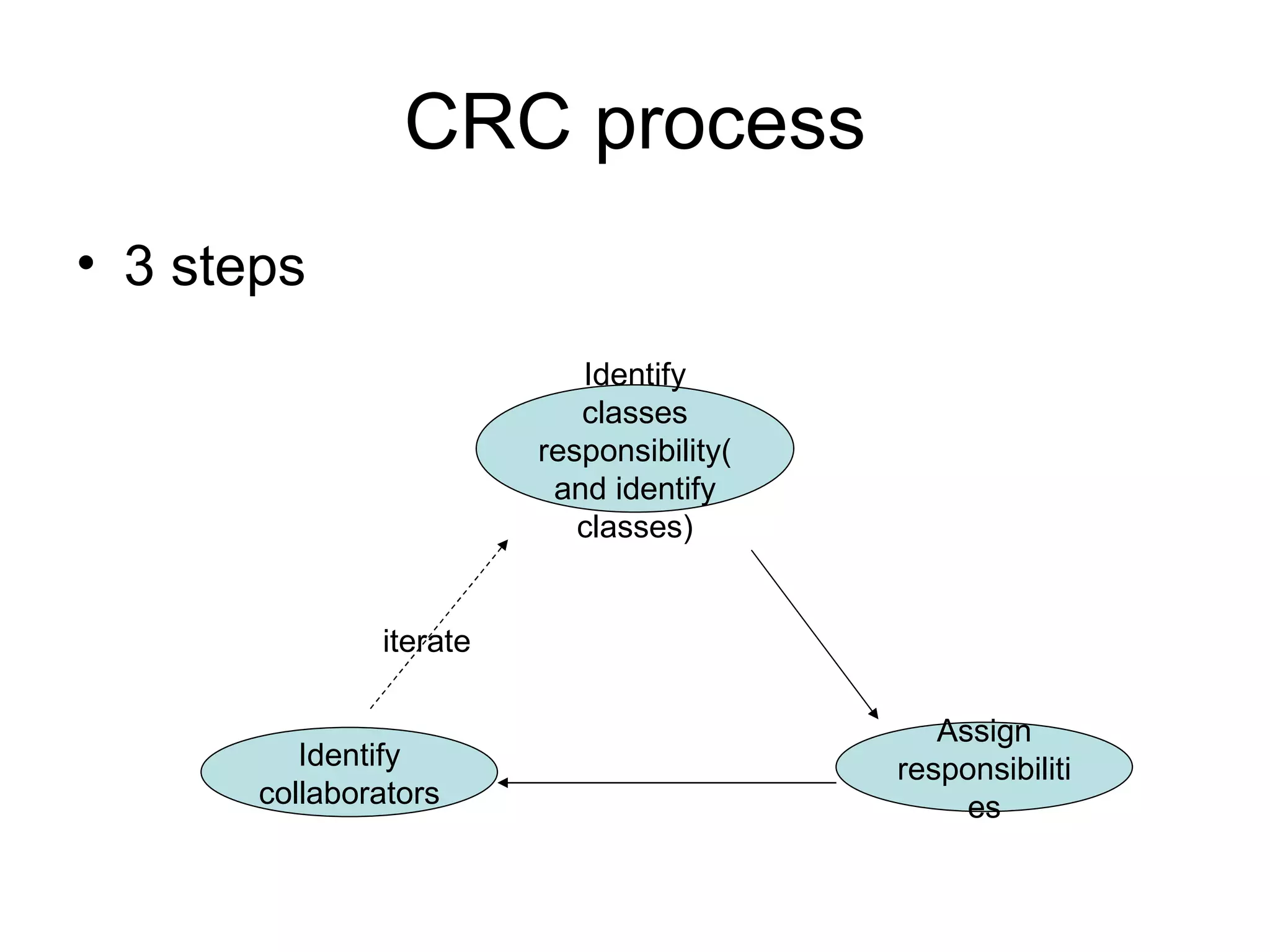
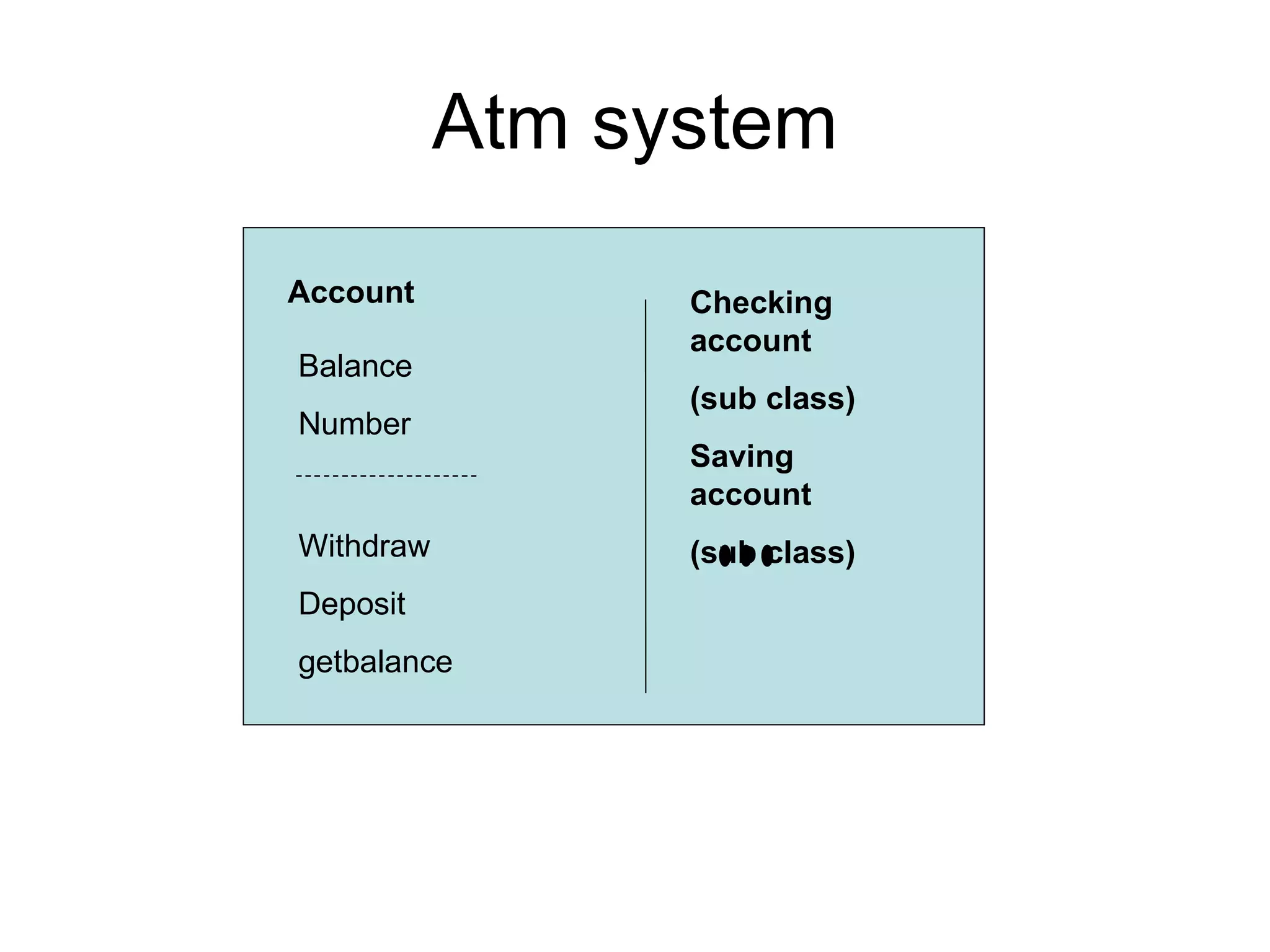
The document discusses different approaches for identifying classes during object analysis, including the noun phrase approach, common class patterns approach, use case driven approach, and Classes, Responsibilities, and Collaborators (CRC) approach. It provides guidelines for selecting classes, naming classes, identifying attributes versus classes, and an example of applying the noun phrase approach to identify initial classes for a bank ATM system.