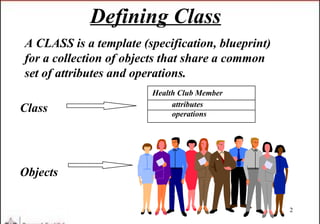
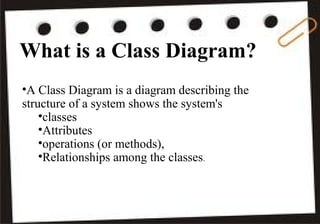
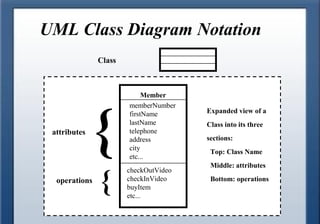
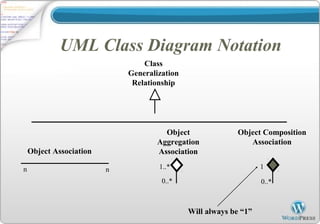
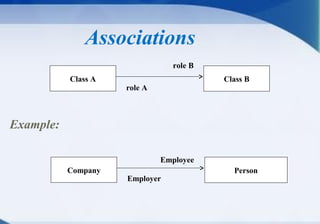
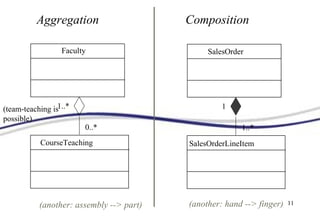
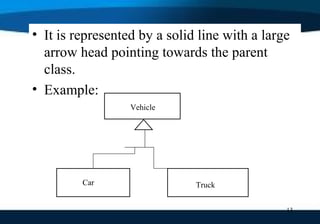
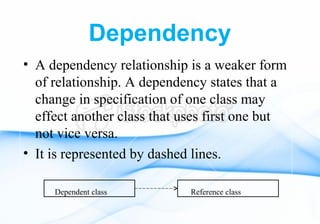
A class diagram shows the structure of a system through classes, attributes, operations, and relationships between classes. It includes classes and their properties like attributes and methods. It also shows relationships between classes like associations, aggregations, generalizations, and dependencies. The class diagram is a key tool in object-oriented analysis and design.