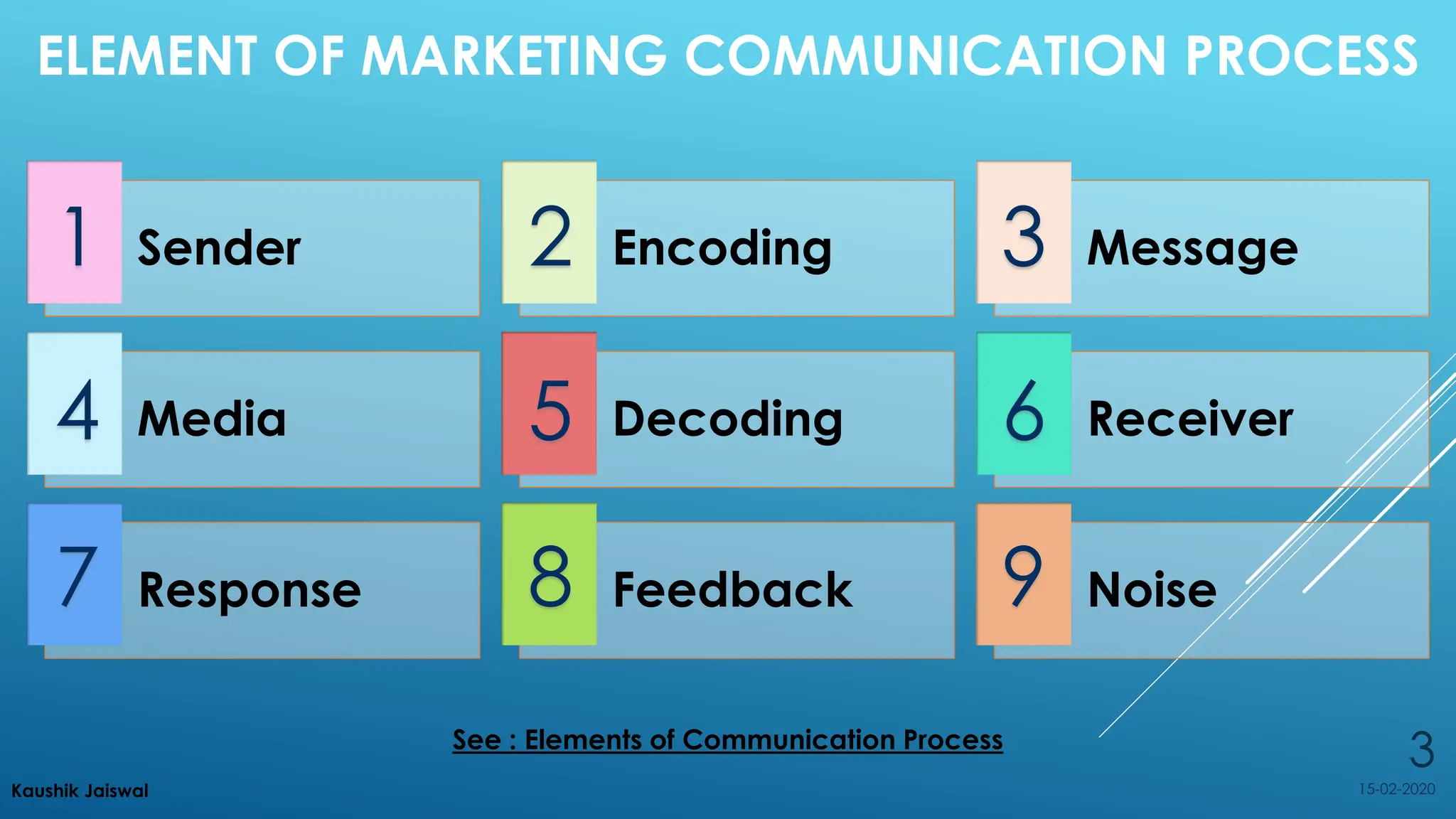
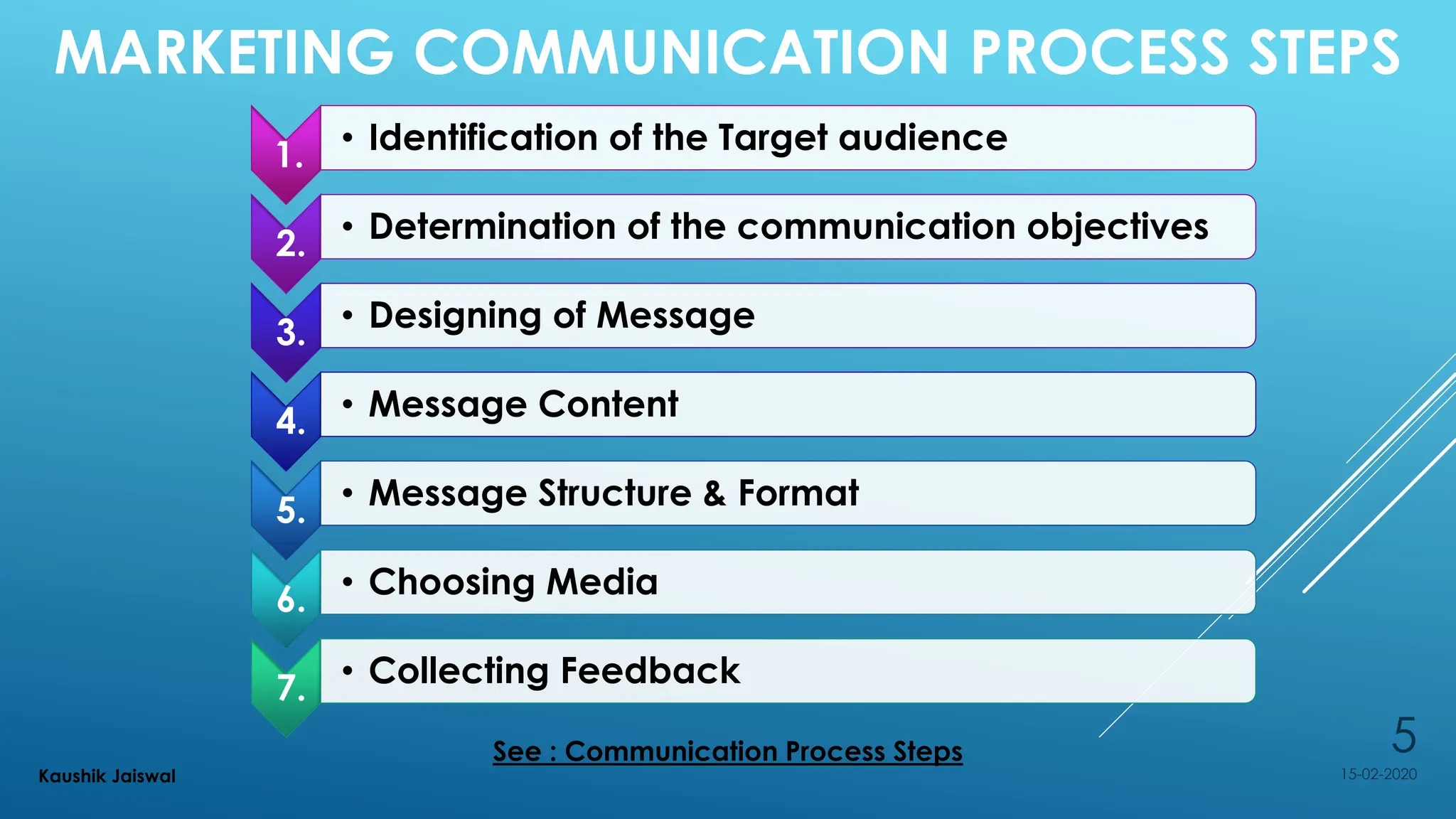
The document outlines marketing communication strategies, emphasizing the importance of understanding the target audience, designing effective messaging, and the various elements involved in the marketing communication process. It also details advertising copy essentials, types of advertisements, and various sales promotion tools aimed at boosting short-term sales. Specific tactics, such as discounts, gifting, sampling, and email marketing, are discussed as effective ways to engage customers and drive purchases.