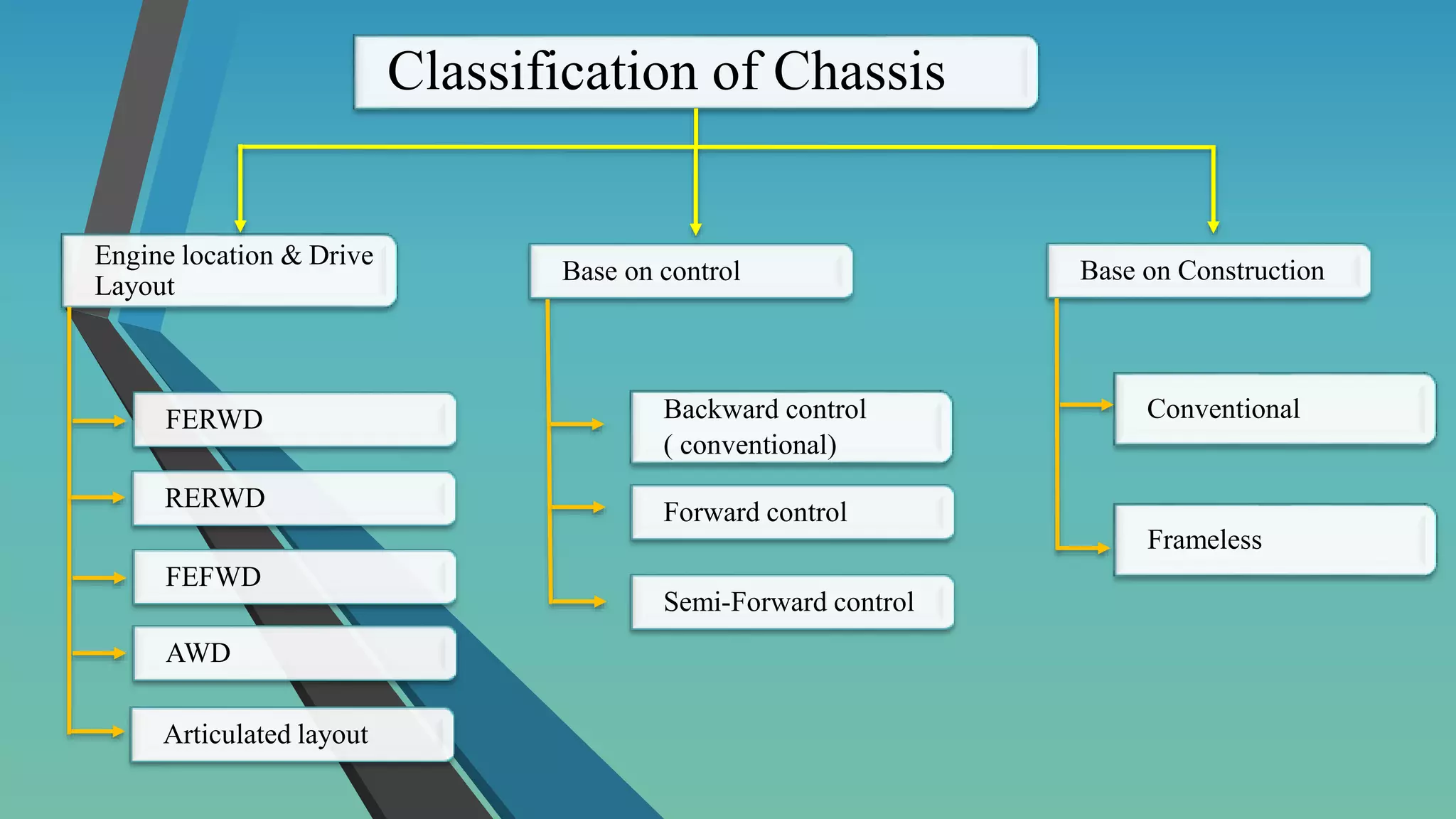
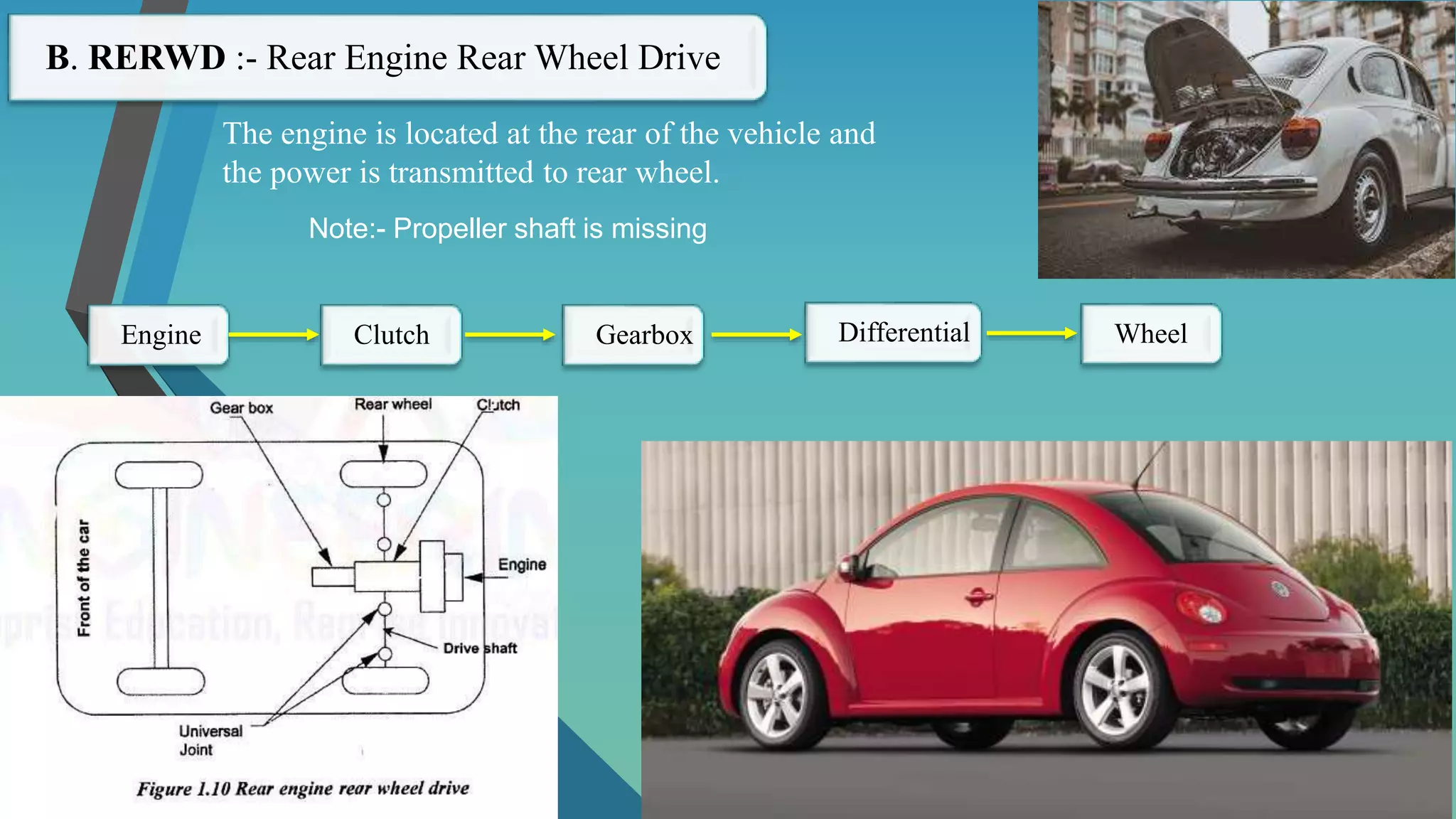
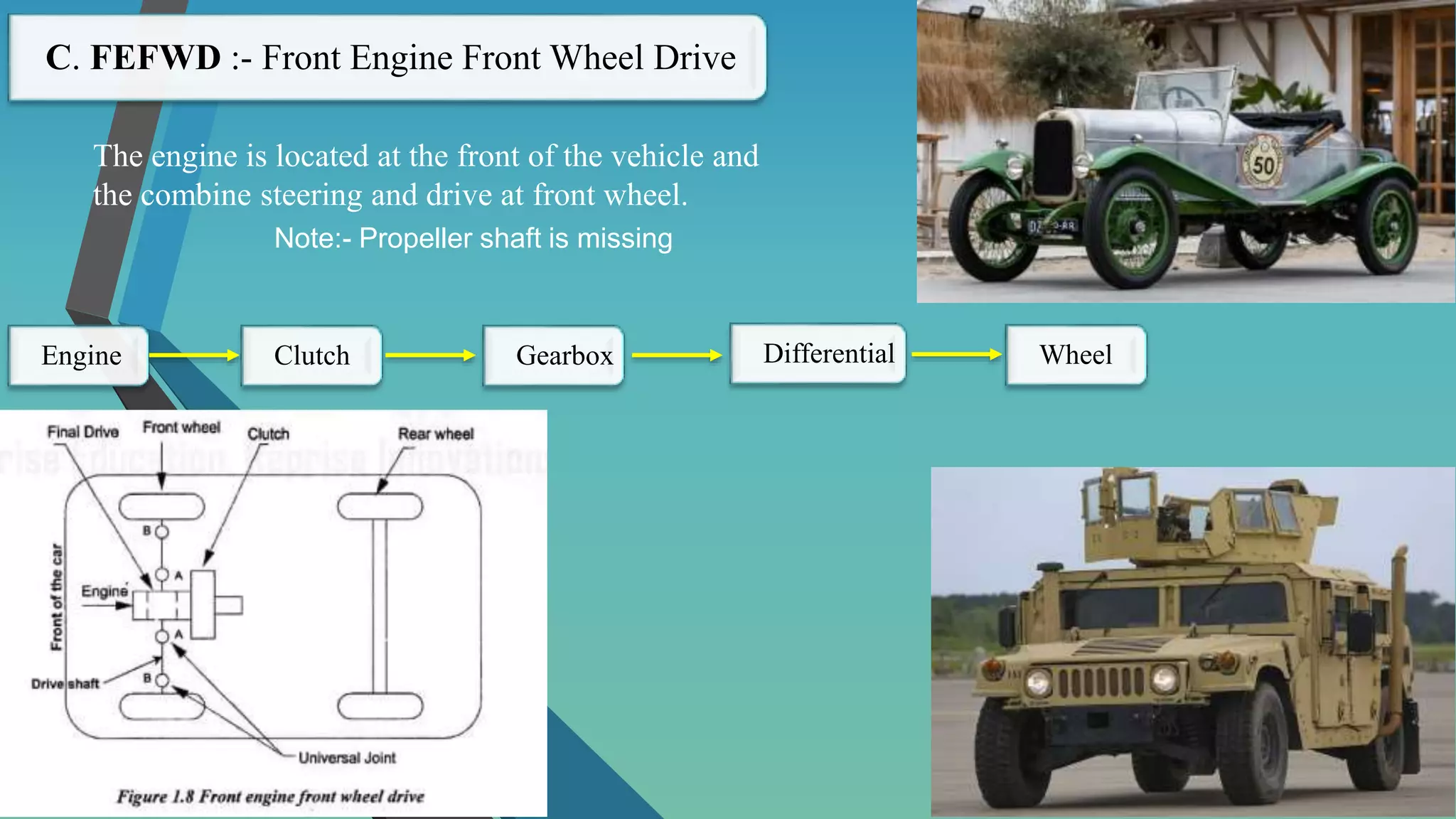
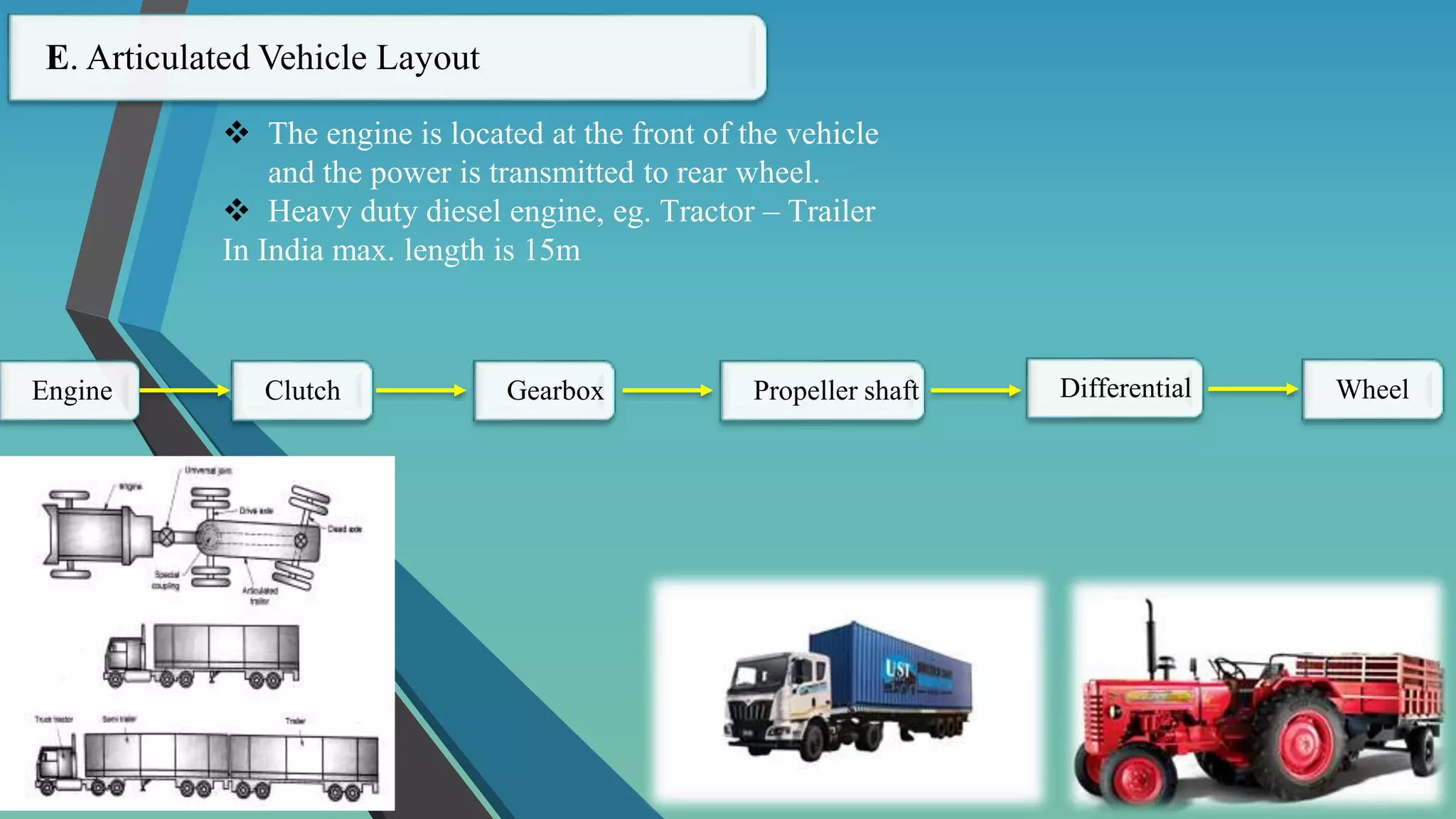
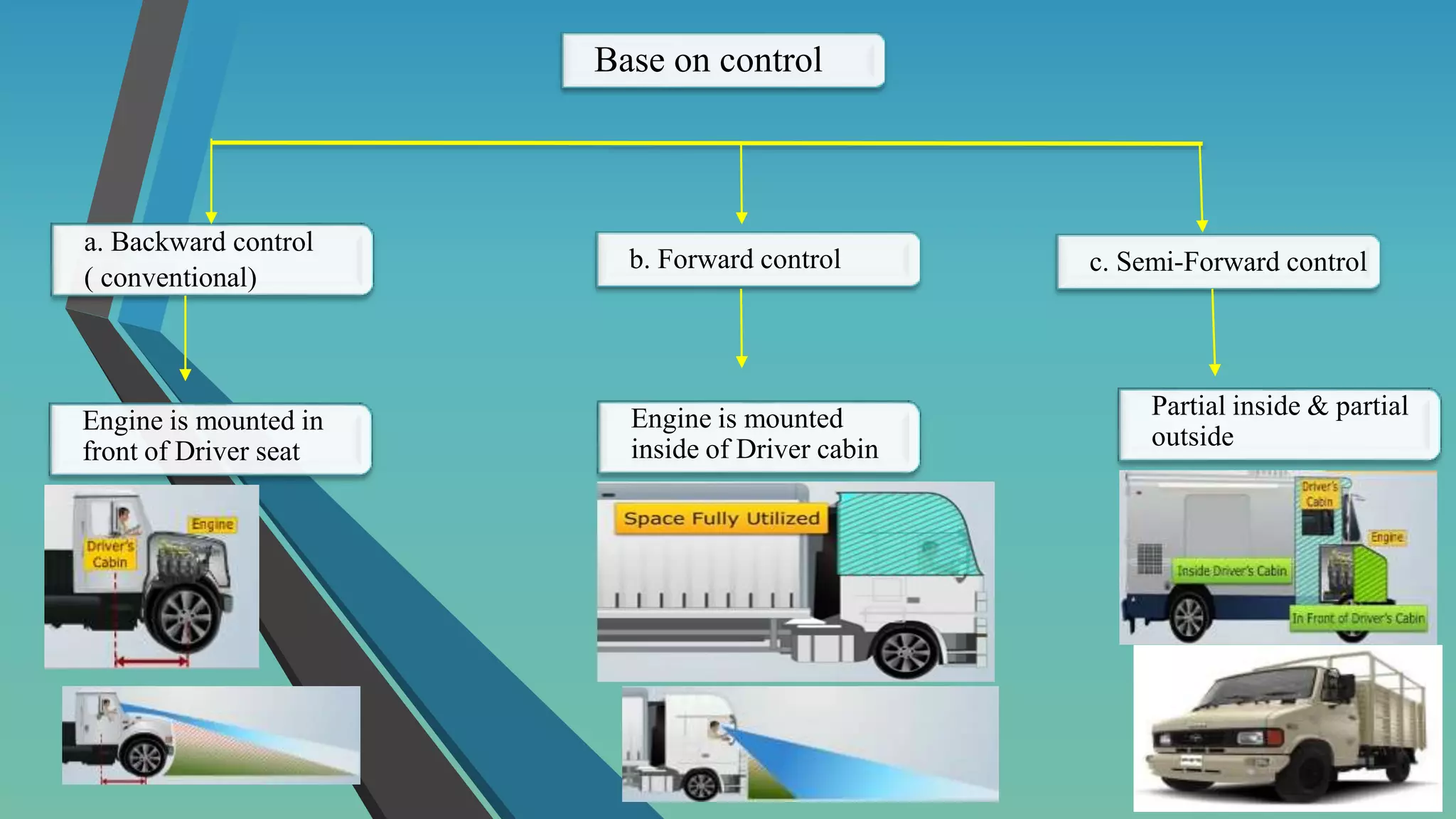
The document provides an overview of vehicle systems including chassis layouts, steering, suspension, braking, cooling, fuel, transmission, and safety systems. It discusses different chassis configurations based on engine location and drive layout. Key components of steering, cooling, fuel, and transmission systems are defined. Examples of gear ratios and calculations of input/output torque and speed for manual transmissions are provided. The summary covers the essential topics and concepts discussed in the document related to major vehicle subsystems in 3 sentences.