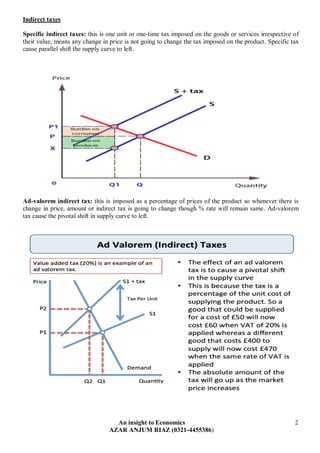
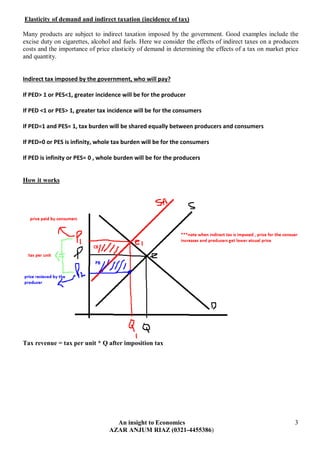
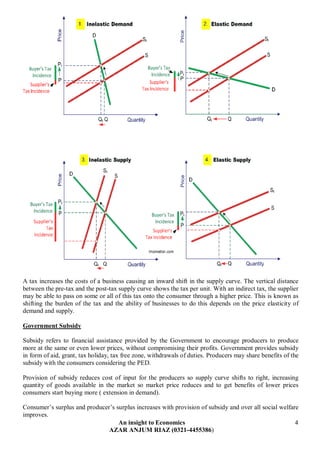
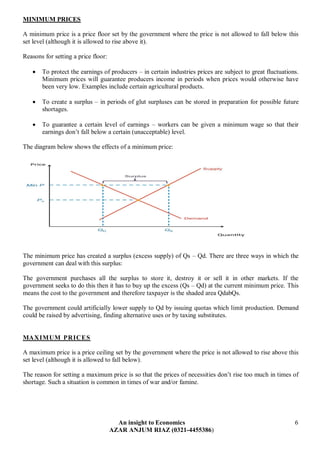
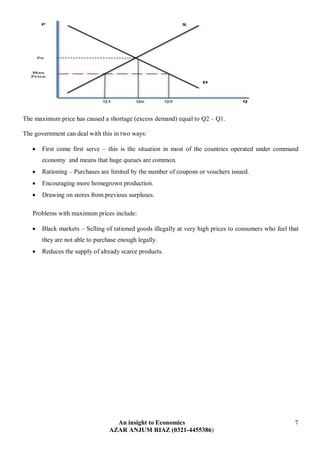
The document discusses various ways in which governments intervene in markets, including through taxation, subsidies, and setting minimum/maximum prices. It provides examples of direct and indirect taxes and how they impact supply and demand. Subsidies are described as shifting the supply curve right to lower prices and increase quantity. The impacts of minimum and maximum prices on surpluses and shortages are explained. Public goods that are non-excludable and non-rival in consumption require government provision. Merit goods with positive externalities and de-merit goods with negative externalities may also be addressed through government intervention.