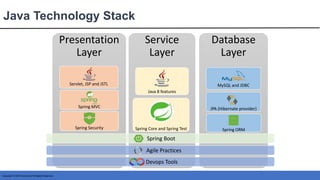
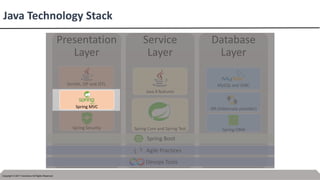
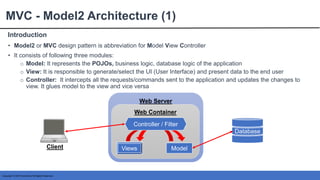
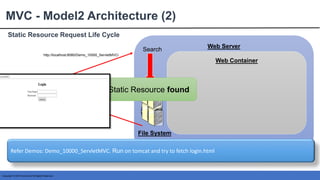
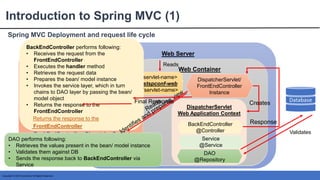
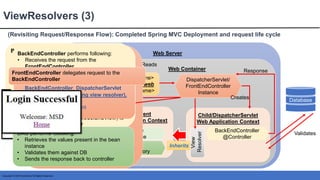
This document provides an introduction to Spring MVC and its core concepts. It discusses the Model-View-Controller (MVC) architecture that Spring MVC is based on, including the model, view and controller components. It also describes the request processing lifecycle in Spring MVC, from the client request to the controller processing to view resolution. Additionally, it covers important Spring MVC concepts like context configuration, context hierarchy, and view resolvers.