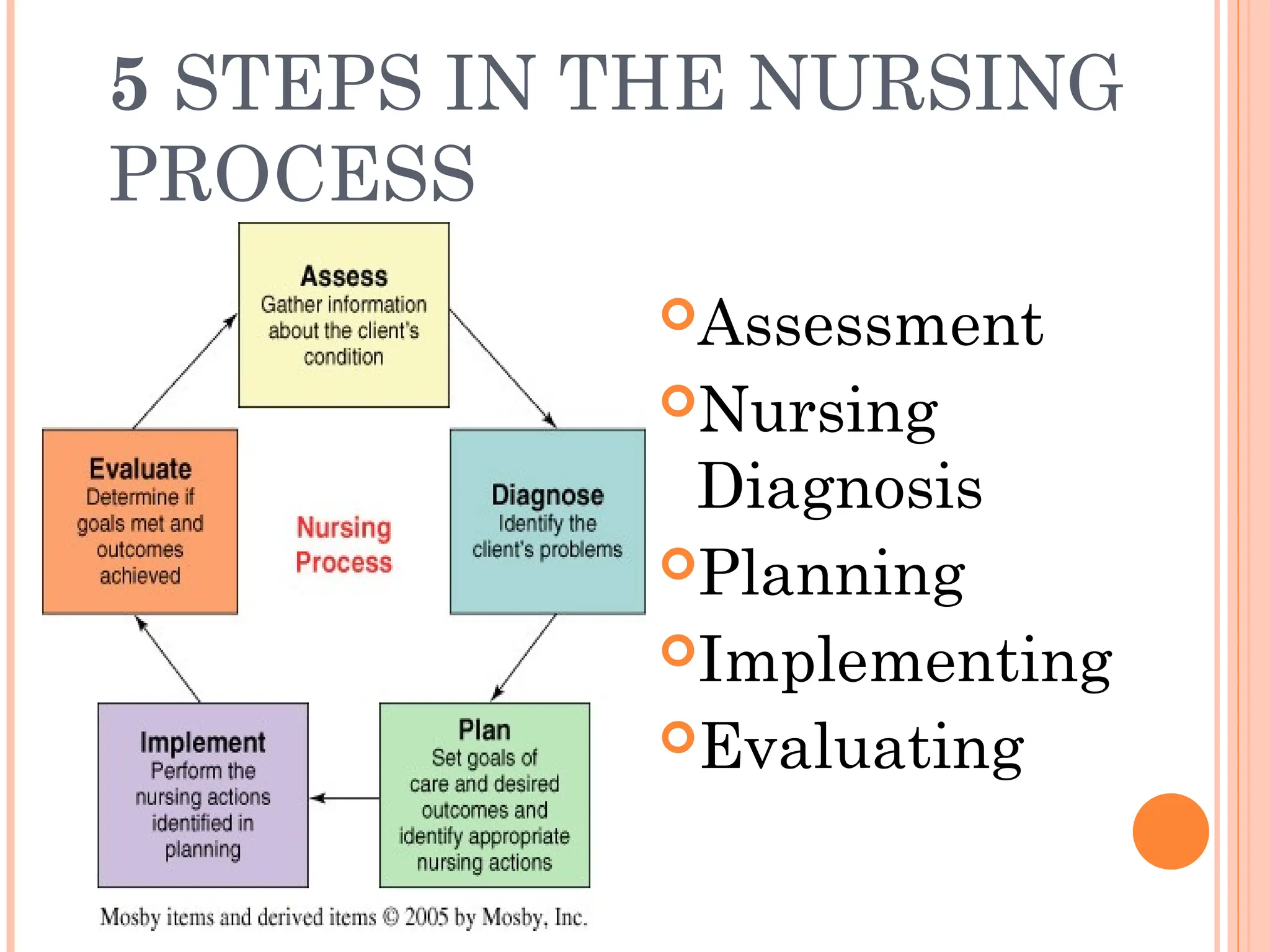
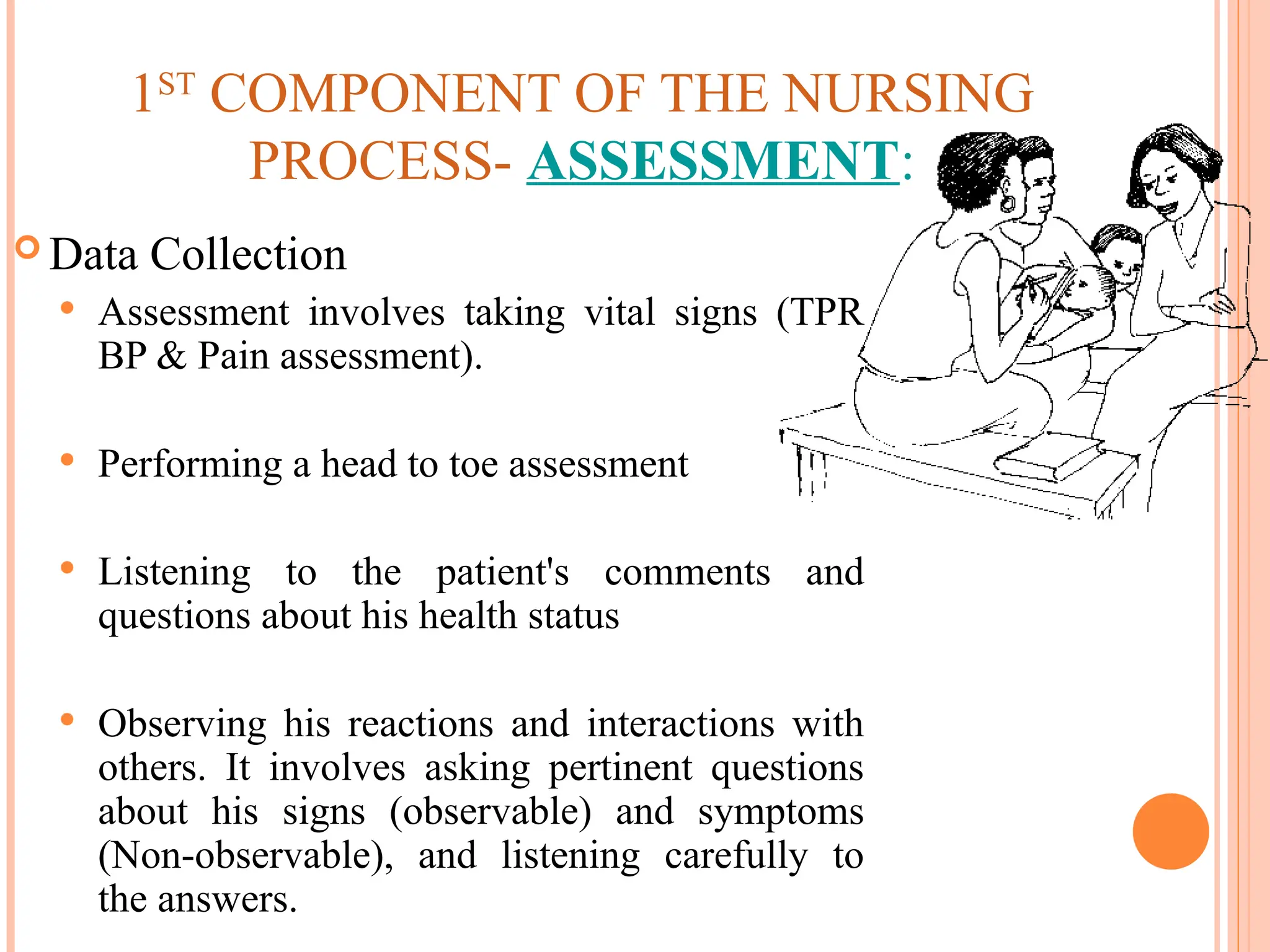
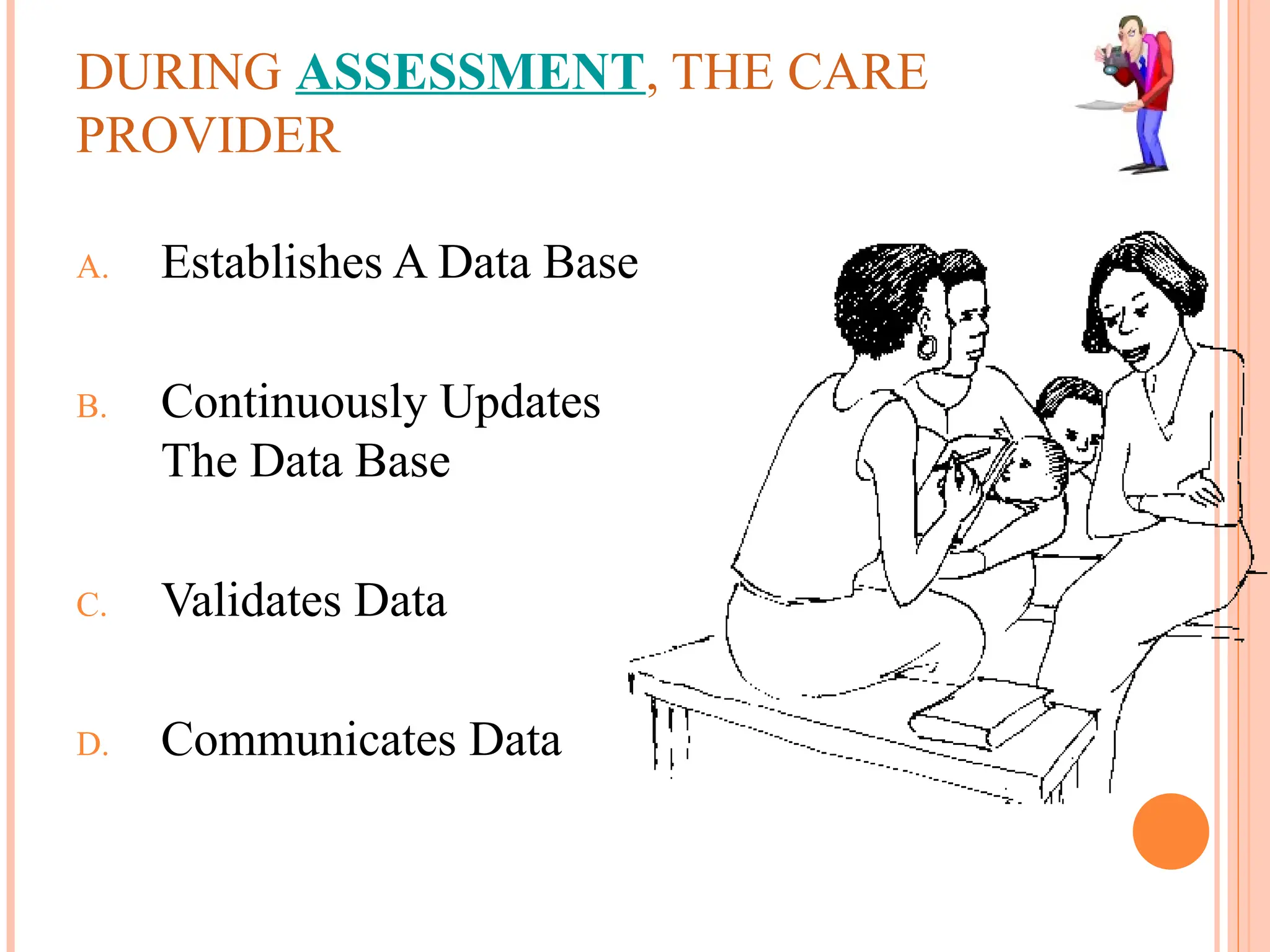
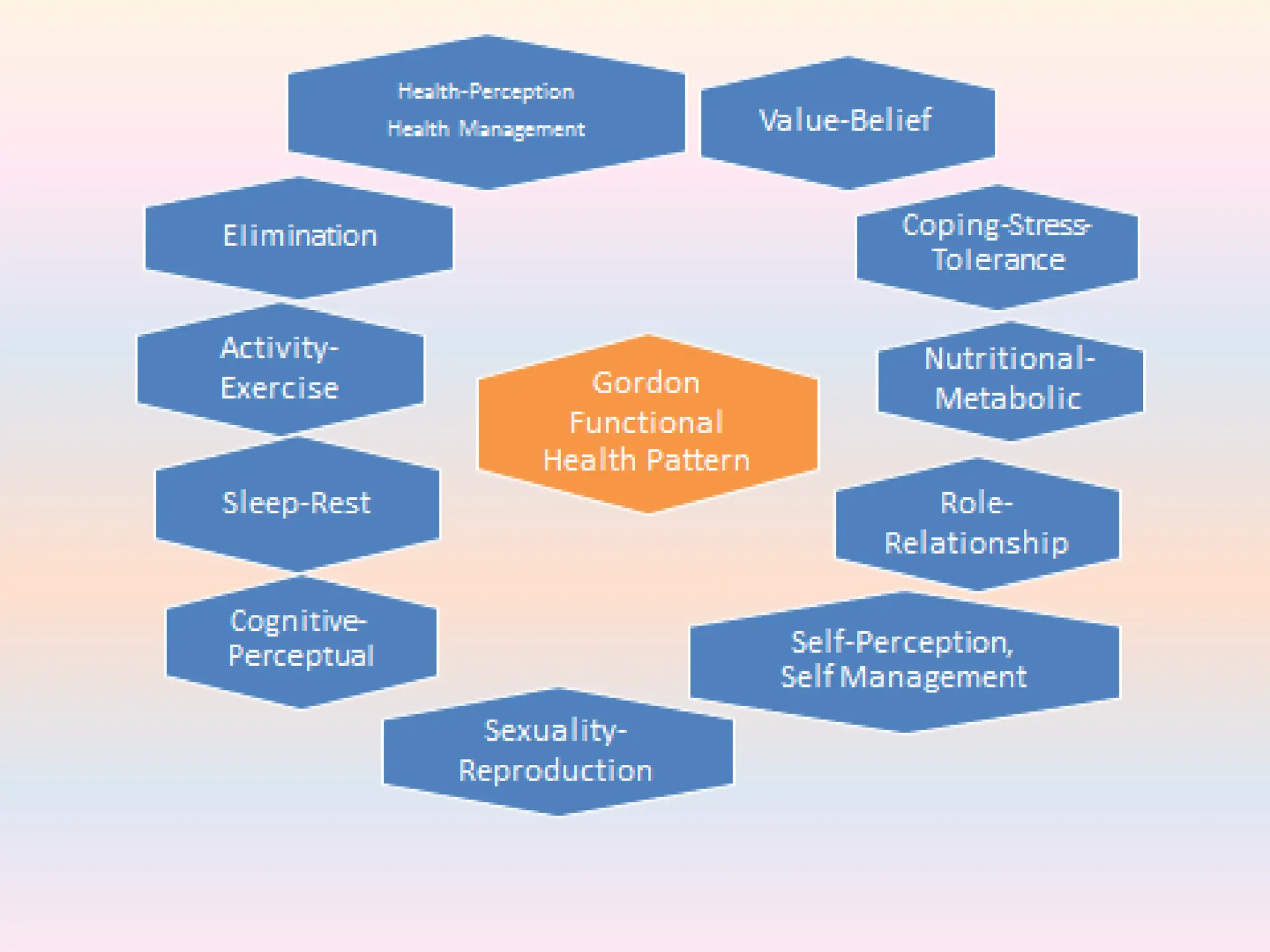
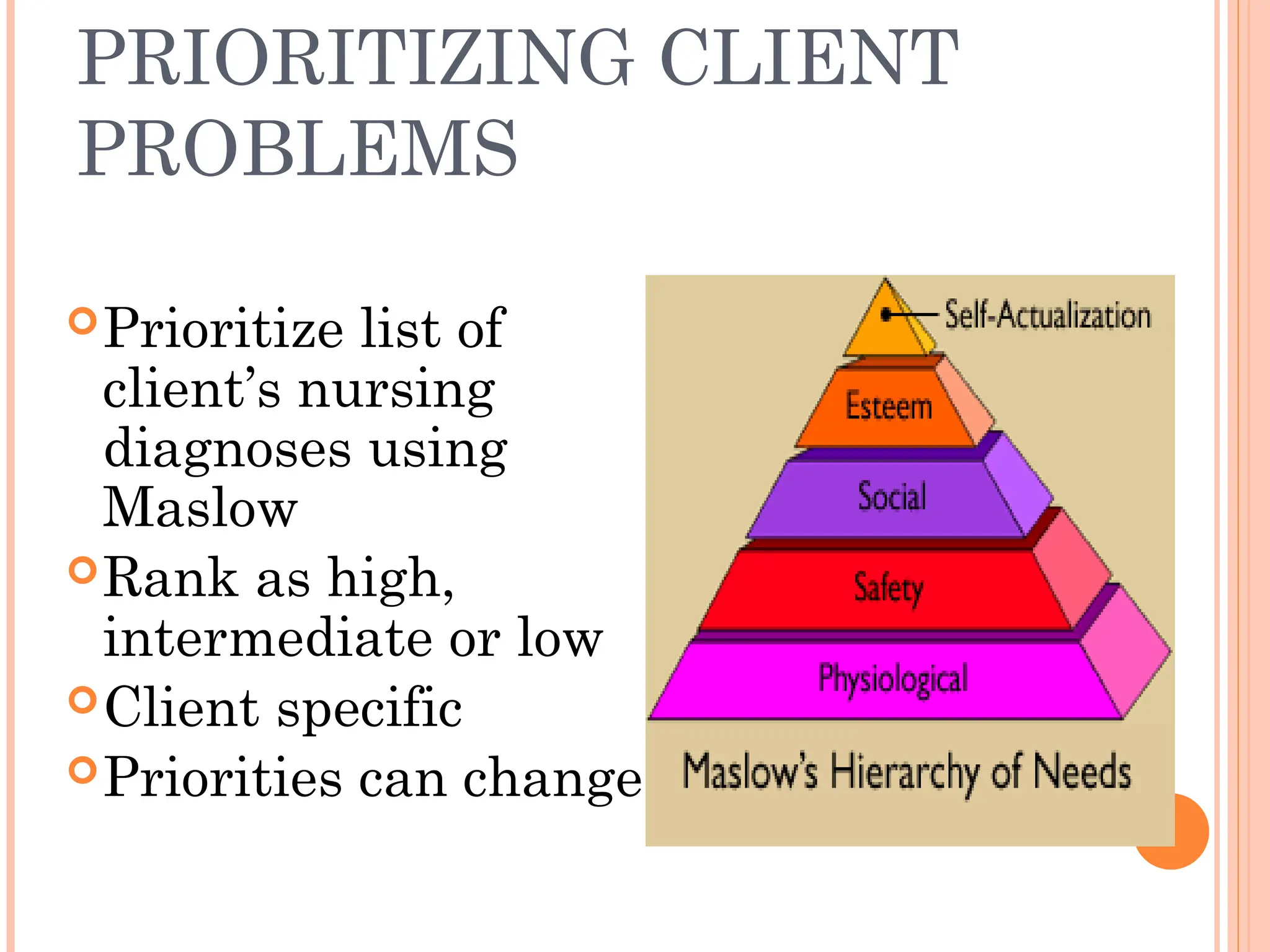
The document outlines the nursing process, which is a systematic method for providing individualized nursing care, including the steps of assessment, nursing diagnosis, planning, implementing, and evaluating. It emphasizes the importance of patient involvement, effective communication, and critical thinking in delivering holistic care that addresses both physical and psychosocial needs. The nursing process aims to improve patient outcomes through collaborative efforts and personalized care plans.