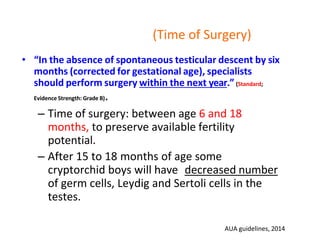
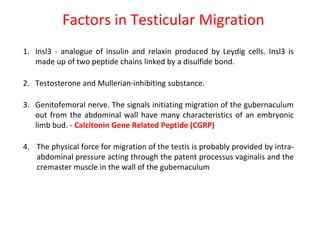
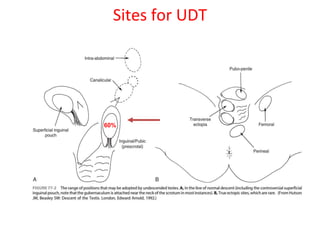
1. An undescended testis is a testis that fails to descend into the scrotum, and can occur at any point along its normal descent path. The most common locations are within the inguinal canal or just outside the external inguinal ring.
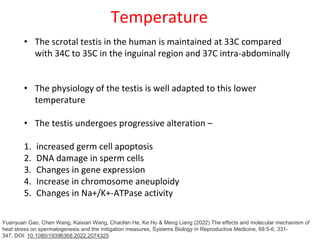
2. Complications of undescended testes include impaired fertility, increased risk of testicular cancer, and temperature-related damage to sperm production. Left uncorrected, nearly 40% of undescended testes lose their germ cells by age 2.
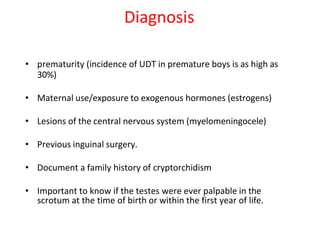
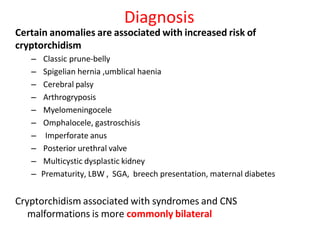
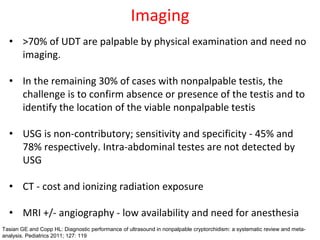
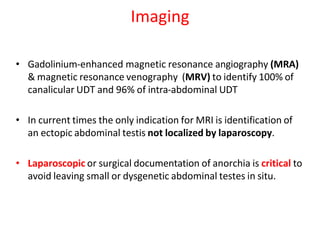
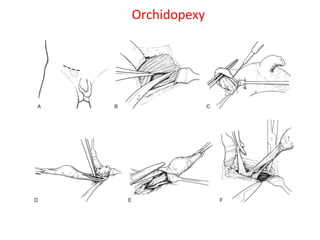
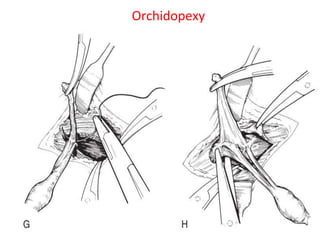
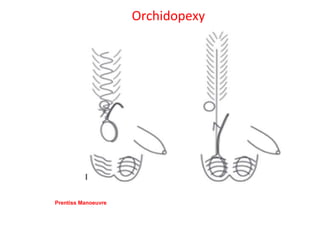
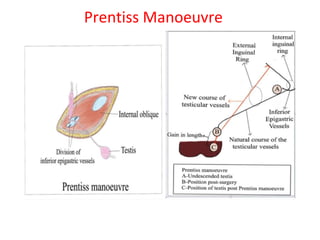
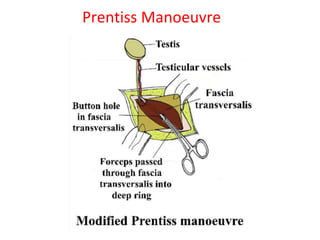
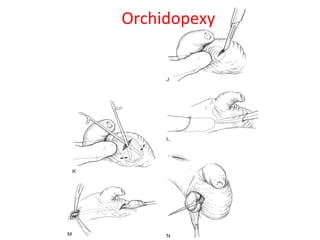
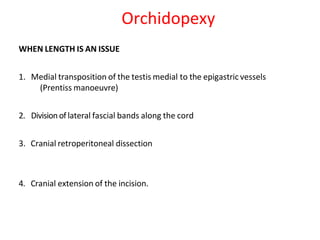
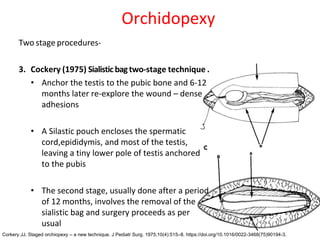
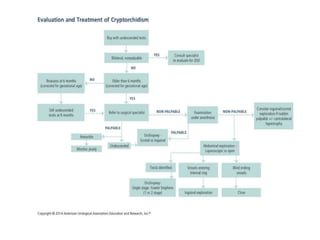
3. Diagnosis involves physical examination to locate the testis. Treatment is surgical orchiopexy between 6 months to 1 year of age to bring the testis into the sc


























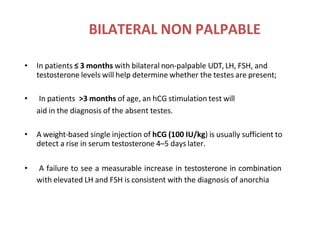

![“In boys with bilateral, nonpalpable testes who do
not have congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH),
providers should measure Müllerian Inhibiting
Substance (MIS or Anti- Müllerian Hormone [AMH])
and consider additional hormone testing to evaluate
for anorchia.” (Option; Evidence Strength: Grade C).
– Patient who has bil nonpalpable UDT with 46 XY
karyotype, may have hormonal workup or wait until
age 6 months to undergo laparoscopic exploration.
– Hormonal workup: Tes, LH, FSH, hCG stimulation test,
and MIS.
AUA guidelines, 2014](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/udt-240302134013-59d7107a/85/Undescended-Testis-Basics-and-Advanced-pptx-60-320.jpg)