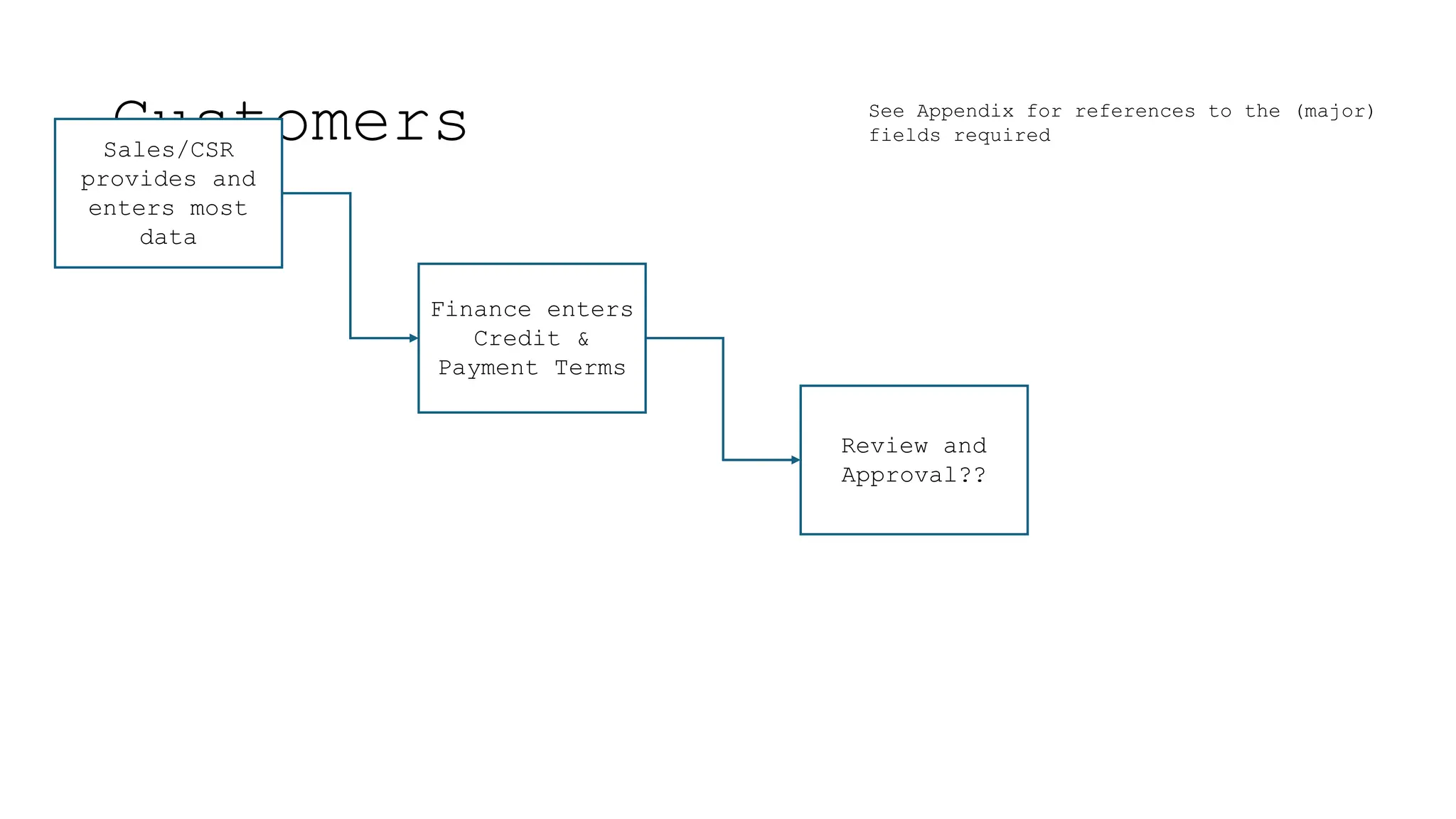
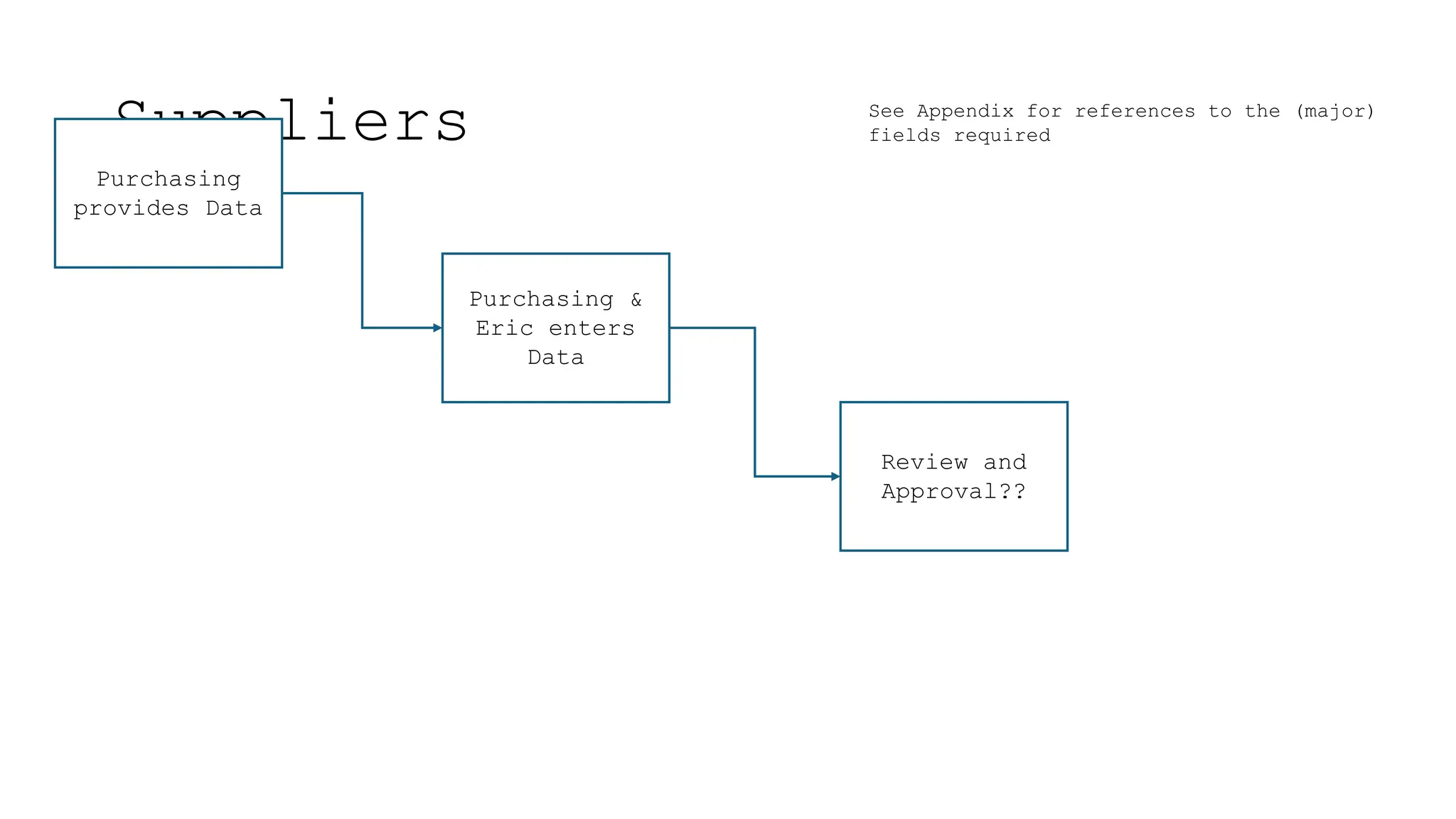
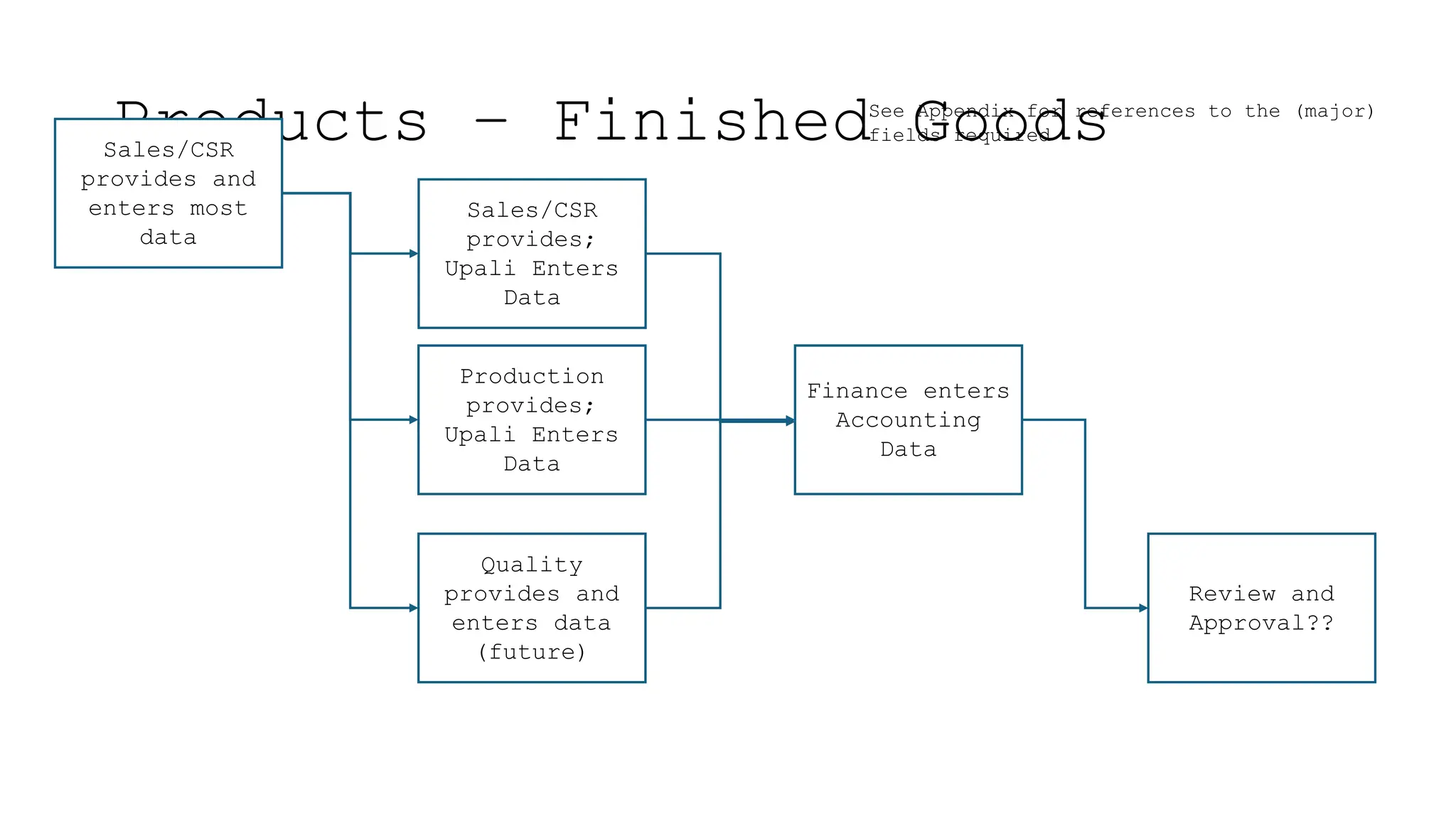
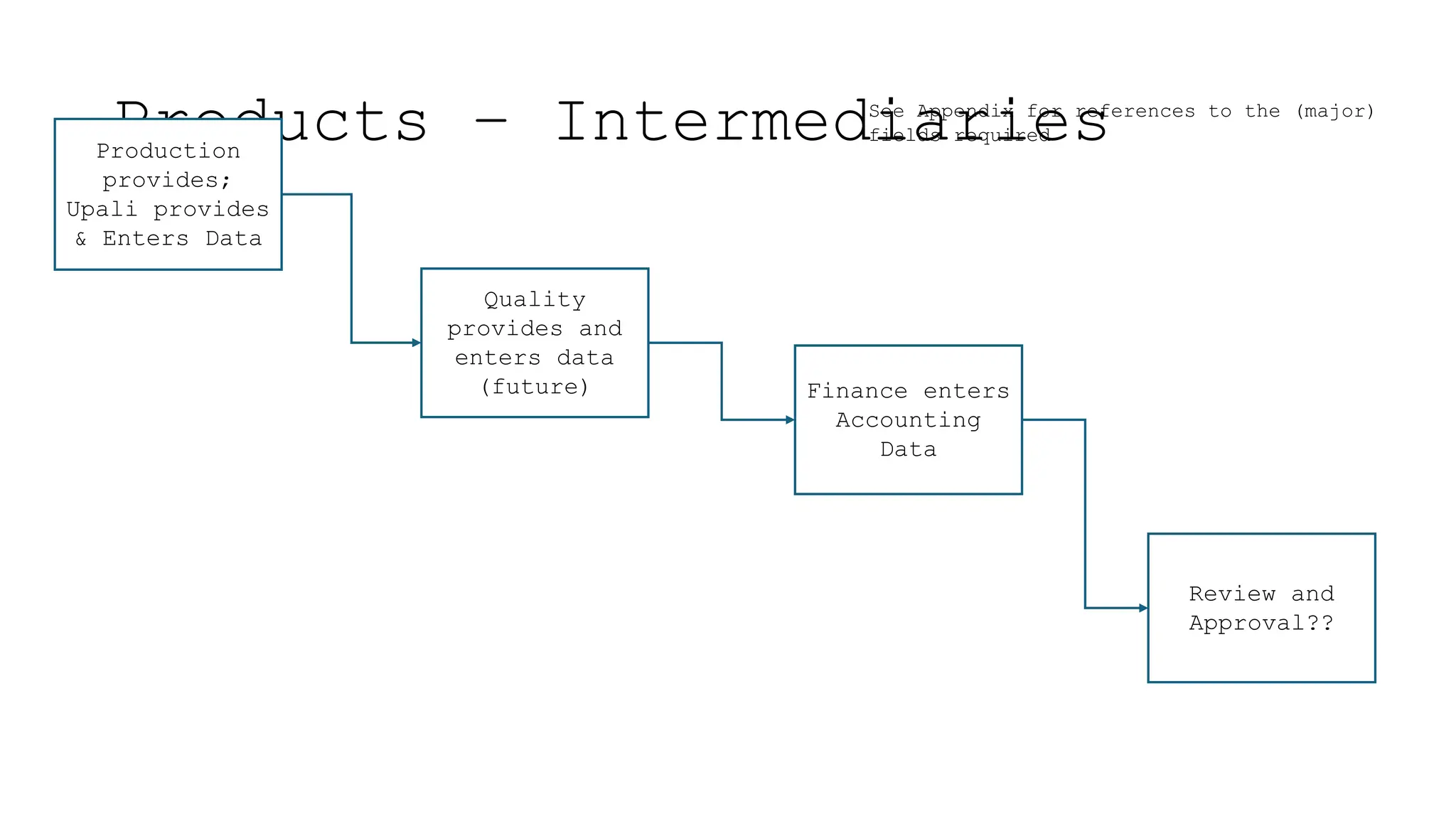
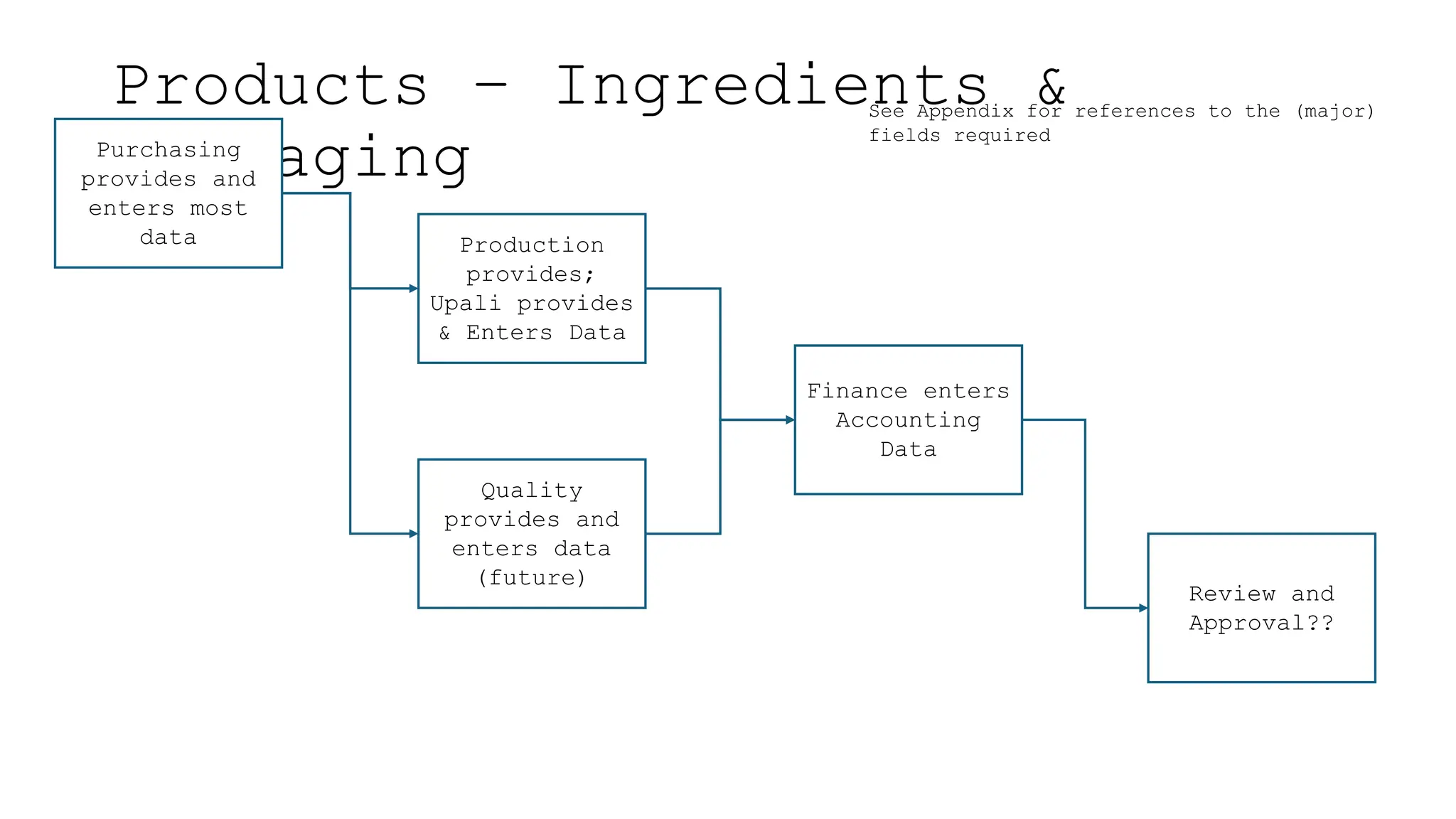
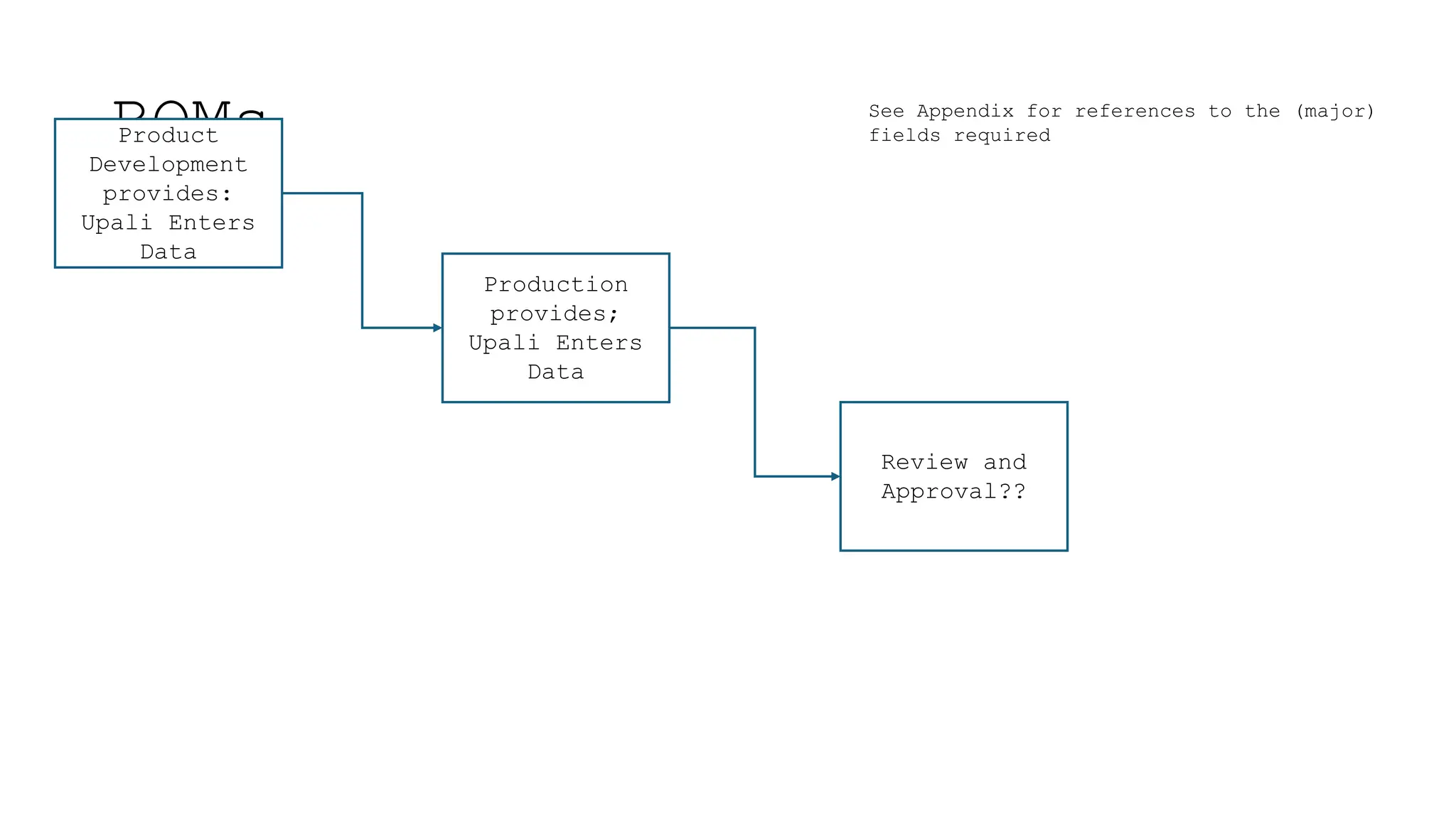
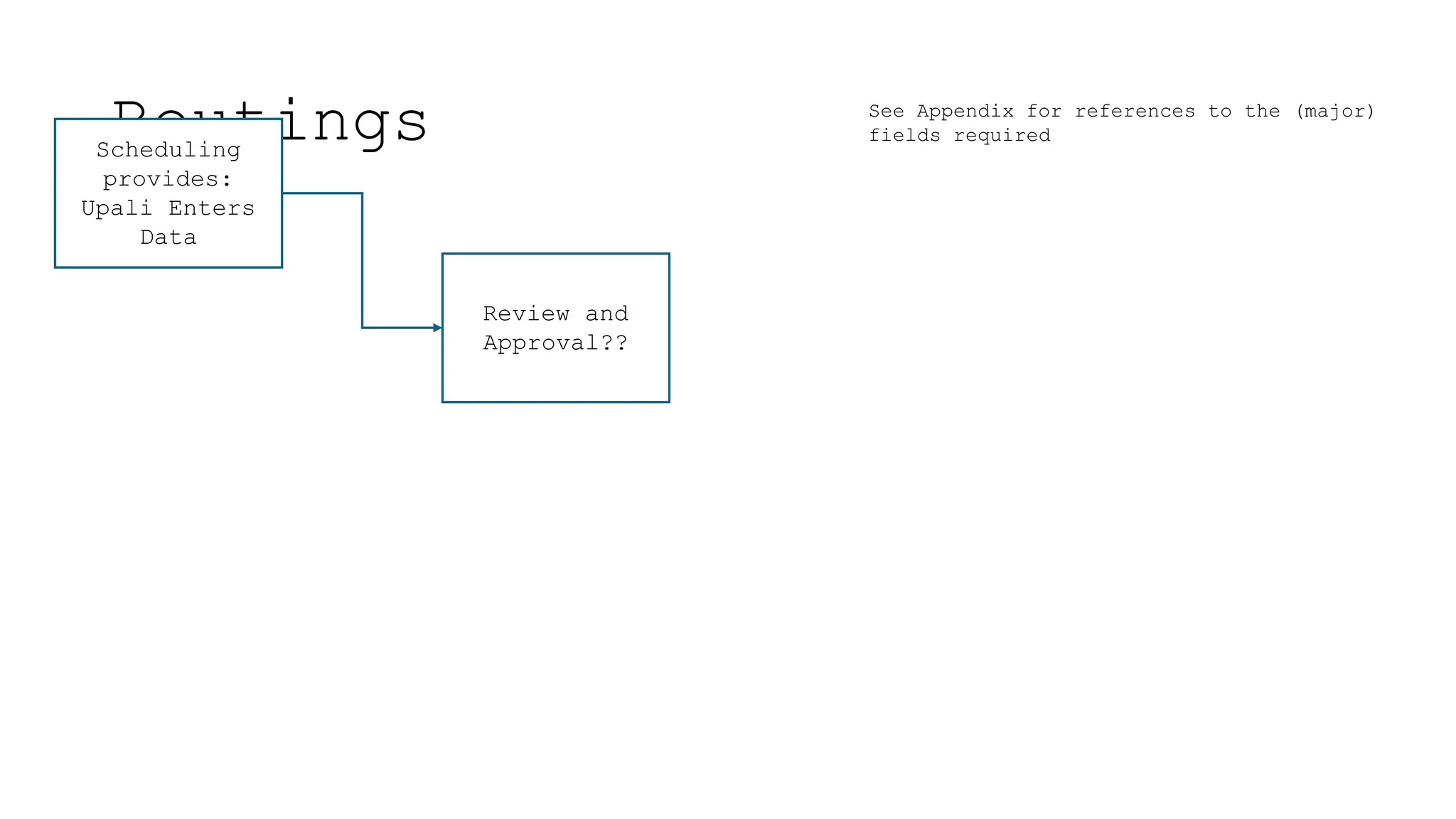
The document outlines the importance and classification of master data in ERP systems, distinguishing it from transactional data. It highlights the need for a controlled master data process to ensure data integrity, including guidelines for correcting errors and inconsistencies in master data entries. Furthermore, it details the responsibilities of various departments in providing, entering, and approving master data.