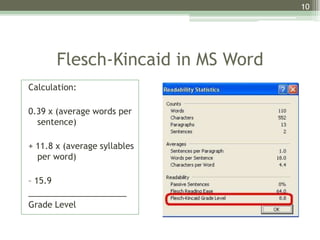
This document provides an overview of leveling systems used in libraries and schools. It discusses traditional quantitative leveling systems like SMOG and Flesch-Kincaid, second generation quantitative systems like Lexiles, and qualitative systems like Fountas & Pinnell. The document explains how each system measures text difficulty and provides examples of tools that use them. It notes the benefits of leveling for matching readers to texts but also cautions they are not precise and may limit choices. The document aims to help librarians and educators understand different leveling approaches.