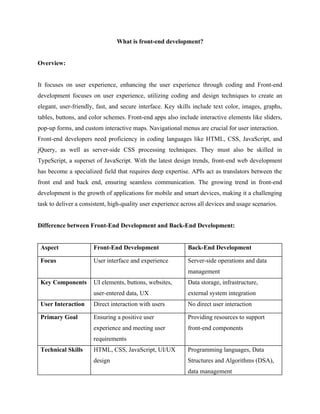
Front-end development focuses on the user experience by utilizing coding and design techniques to create user-friendly interfaces, requiring skills in languages like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Key components include UI elements and interactive features, while the distinction from back-end development lies in its direct user interaction and emphasis on user interface. Frameworks like React and Angular play a critical role in development, alongside emerging trends such as micro-frontends for enhanced scalability.