The document provides an overview of the United Nations and opportunities for civil society involvement. It discusses:
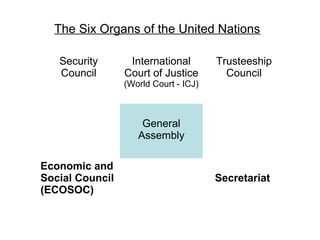
1) The UN as the most universal policy-making body that deals with peacekeeping and everyday issues across borders.
2) The UN being made up of governments, but that there are ways for people and civil society to influence the process from the bottom-up such as by participating in UN conferences and side events.
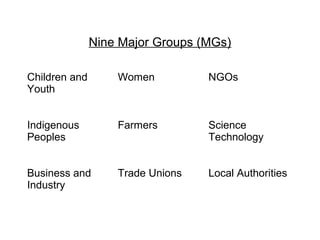
3) Key parts of the UN system like the General Assembly and opportunities for civil society to engage including by making statements to the nine Major Groups that advise the UN.