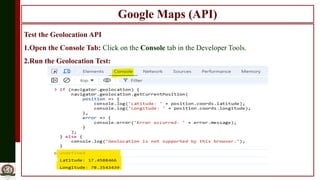
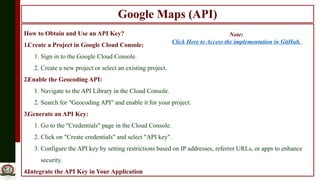
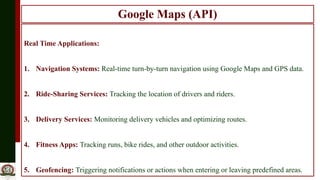
The document outlines the integration of Google Maps API with GPS location tracking to create location-based services, providing real-time data and mapping capabilities. It details the functionality of the geolocation API in modern browsers, including user permission prompts and location determination methods, as well as the necessity of an API key for enhanced features. Additionally, it describes steps to obtain and integrate the API key, along with examples of real-time applications such as navigation and delivery services.