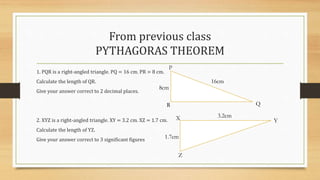
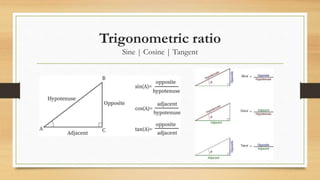
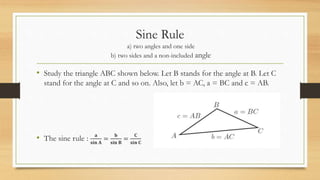
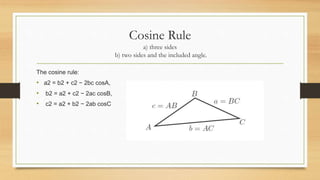
1) The document discusses trigonometry and solving right triangles using Pythagorean theorem, trigonometric ratios (sine, cosine, tangent), sine rule, and cosine rule.
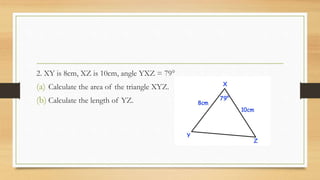
2) Examples are provided to use these concepts to calculate missing side lengths and angles of right triangles given various inputs.
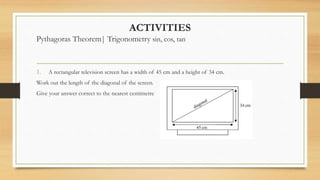
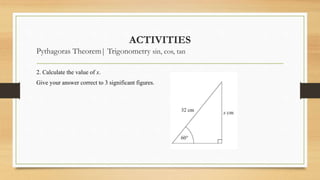
3) Activities at the end instruct students to solve additional right triangle problems applying these trigonometry concepts.